No products in the cart.
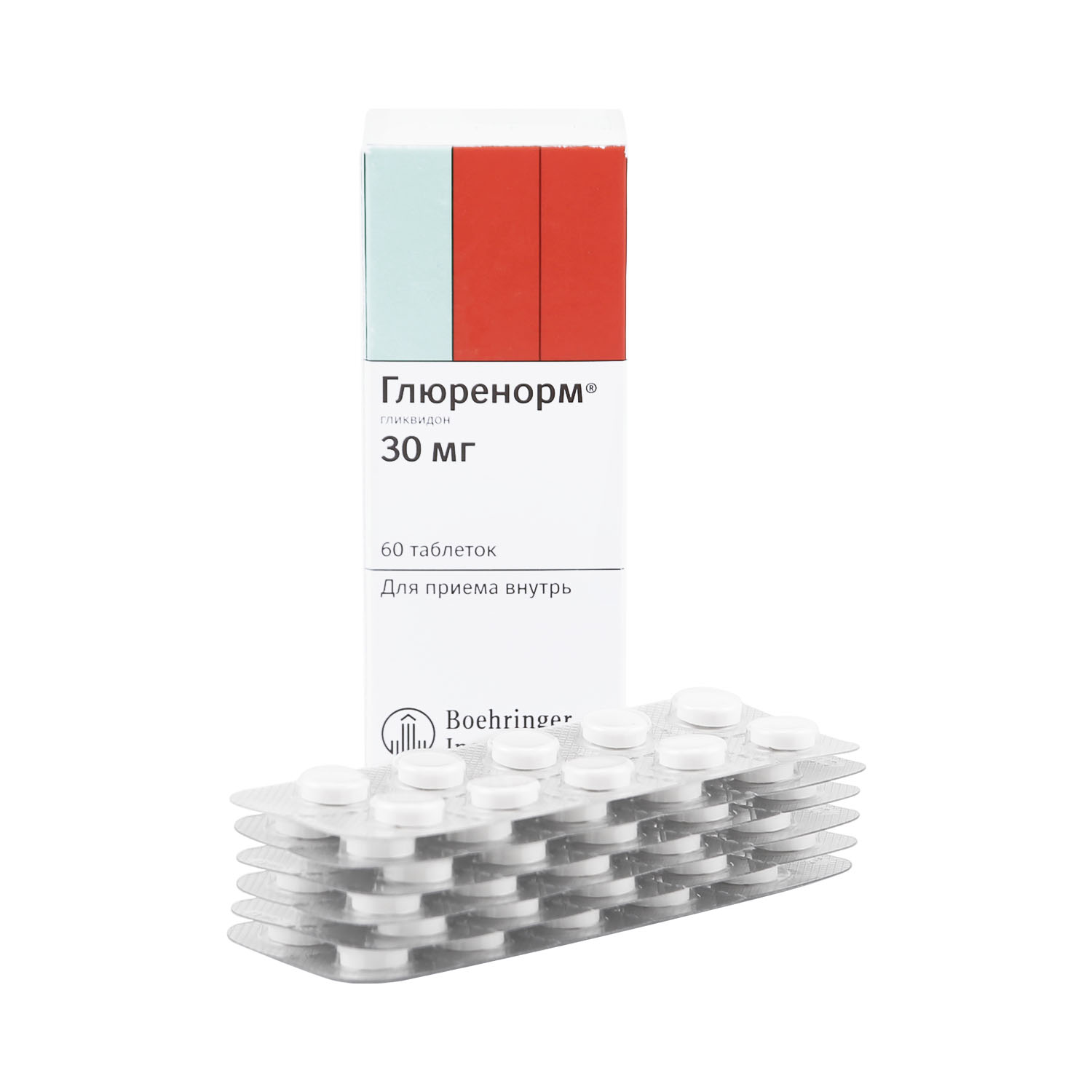
Glurenorm, tablets 30 mg 60 pcs
€17.59 €14.65
Description
Glurenorm is a hypoglycemic drug for oral use, a sulfonylurea derivative of the II generation.
It has pancreatic and extrapancreatic effects.
Stimulates insulin secretion by potentiating the glucose-mediated pathway of insulin formation.
In animal experiments, Glurenorm has been shown to reduce insulin resistance in the liver and adipose tissue by increasing insulin receptors and stimulating the insulin-mediated post-receptor mechanism.
Hypoglycemic effect develops 60-90 minutes after oral administration, maximum action occurs after 2-3 h and lasts about 8-10 h.
Pharmacokinetics
Intake
. After a single oral dose of glyquidone (15 mg or 30 mg), the drug is rapidly and almost completely (80-95%) absorbed from the GI tract, reaching plasma concentrations of 0.65 µg/ml (range 0.12-2.14 µg/ml). Average time to reach Cmax of the drug in plasma is 2 h 15 min (range: 1.25-4.75 h). The AUC0-∞ value is 5.1 µg×h/ml (range: 1.5-10.1 µg×h/ml).
There are no differences in pharmacokinetic parameters between diabetic patients and healthy subjects.
Distribution
Glyquidone has high affinity to plasma proteins (>99%). There are no data on the possible passage of glyquidone or its metabolites through the GEB or the placenta. There are no data on the possibility of glyquidone penetration into breast milk.
Metabolism
Glyquidone is completely metabolized by the liver, mainly by hydroxylation and demethylation. Glyquidone metabolites have no or little pharmacological activity compared to the parent substance.
The bulk of the metabolites are excreted through the intestine. Only a small portion of the metabolites is excreted by the kidneys. In studies it has been shown that after oral administration about 86% of the isotope-labeled drug (14C) is excreted through the intestine. Regardless of the dose and route of administration, the kidneys excrete about 5% (as metabolites) of the administered amount. The level of excretion of Glurenorm by the kidneys remains minimal even with regular administration.
The T1/2 is 1.2 h (range – 0.4-3.0 h), the final T1/2 is approximately 8 h (range – 5.7-9.4 h).
Pharmacokinetics in special clinical cases
In elderly and middle-aged patients the pharmacokinetic parameters are similar.
The bulk of the drug is excreted through the intestine. There is evidence that the metabolism of the drug is not altered in patients with hepatic impairment. Excretion of glyquidone by the kidneys is insignificant, in patients with impaired renal function the drug does not accumulate.
Indications
Indications
Diabetes mellitus type II in adults.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Glyurenorm is a hypoglycemic drug for oral use, a sulfonylurea derivative of the second generation.
It has pancreatic and extrapancreatic effects.
Stimulates insulin secretion by potentiating the glucose-mediated pathway of insulin formation.
In animal experiments, Glurenorm has been shown to reduce insulin resistance in the liver and adipose tissue by increasing insulin receptors, as well as stimulating the post-receptor mechanism mediated by insulin.
The hypoglycemic effect develops 60-90 minutes after oral administration, the maximum effect occurs after 2-3 hours and lasts about 8-10 hours.
Pharmacokinetics
Suction
After oral administration of a single dose of gliquidone (15 mg or 30 mg), the drug is quickly and almost completely (80-95%) absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, reaching a plasma concentration of 0.65 mcg/ml (range 0.12-2.14 mcg/ml). The average time to reach Cmax of the drug in plasma is 2 hours 15 minutes (range: 1.25-4.75 hours). The AUC0-∞ value is 5.1 μg×h/ml (range: 1.5-10.1 μg×h/ml).
There are no differences in pharmacokinetic parameters in patients with diabetes mellitus and healthy individuals.
Distribution
Gliquidone has a high affinity for plasma proteins (>99%). There is no data on the possible passage of gliquidone or its metabolites through the BBB or placenta. There is no data on the possibility of gliquidone passing into breast milk.
Metabolism
Gliquidone is completely metabolized by the liver, mainly by hydroxylation and demethylation. Metabolites of gliquidone have no or weak pharmacological activity compared to the parent substance.
Removal
The main part of the metabolites is excreted through the intestines. Only a small part of the metabolites is excreted by the kidneys. Studies have shown that after oral administration, about 86% of the isotope-labeled drug (14C) is excreted through the intestines. Regardless of the dose and route of administration, about 5% of the administered amount of the drug is excreted by the kidneys (in the form of metabolites). The level of excretion of Glurenorm by the kidneys remains minimal even with regular administration.
T1/2 is 1.2 hours (range – 0.4-3.0 hours), final T1/2 is approximately 8 hours (range – 5.7-9.4 hours).
Pharmacokinetics in special clinical situations
In elderly and middle-aged patients, the pharmacokinetic parameters are similar.
The main part of the drug is excreted through the intestines. There is evidence that the metabolism of the drug does not change in patients with liver failure. Gliquidone excretion by the kidneys is insignificant; the drug does not accumulate in patients with impaired renal function.
Special instructions
Special instructions
Glurenorm should not replace a therapeutic diet, which helps control the patient’s body weight and reduce the risk of developing cardiovascular disorders.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Gliquidone
Composition
Composition
Active ingredient:
Gliquidone 30 mg.
Excipients:
lactose monohydrate – 134.6 mg,
dried corn starch – 70 mg,
soluble corn starch – 5 mg,
magnesium stearate – 0.4 mg.
Contraindications
Contraindications
type 1 diabetes mellitus;
diabetic acidosis, ketoacidosis, precoma and coma;
condition after resection of the pancreas;
acute intermittent porphyria;
severe liver failure;
some acute conditions (for example, infectious diseases or major surgery);
rare hereditary diseases such as galactosemia, lactase deficiency, lactose intolerance, glucose-galactose malabsorption;
pregnancy;
lactation period (breastfeeding period);
age under 18 years (due to insufficient data on the effectiveness and safety of the drug in this age group);
hypersensitivity to sulfonamides.
With caution
febrile syndrome;
diseases of the thyroid gland (with dysfunction);
deficiency of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase;
alcoholism.
Side Effects
Side Effects
From the hematopoietic system: thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, agranulocytosis.
Metabolism: hypoglycemia.
From the nervous system: headache, dizziness, drowsiness, paresthesia, feeling of fatigue.
From the organ of vision: disturbances of accommodation.
From the cardiovascular system: angina pectoris, extrasystole, cardiovascular failure, hypotension.
From the digestive system: loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, constipation, diarrhea, discomfort in the abdomen, dry mouth, cholestasis.
From the skin and subcutaneous tissue: rash, itching, urticaria, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, photosensitivity reaction.
Other: chest pain.
Interaction
Interaction
It is possible to enhance the hypoglycemic effect with the simultaneous administration of gliquidone and ACE inhibitors, allopurinol, analgesics and NSAIDs, antifungals, chloramphenicol, clarithromycin, clofibrate, coumarin derivatives, fluoroquinolones, heparin, MAO inhibitors, sulfinpyrazone, sulfonamides, tetracyclines and tricyclics antidepressants, cyclophosphamide and its derivatives, insulin and oral hypoglycemic agents.
Beta-blockers, sympatholytics (including clonidine), reserpine and guanethidine can enhance the hypoglycemic effect and at the same time mask the symptoms of hypoglycemia.
It is possible to reduce the hypoglycemic effect with the simultaneous administration of gliquidone and aminoglutethimide, sympathomimetics, corticosteroids, thyroid hormones, glucagon, thiazide and loop diuretics, oral contraceptives, diazoxide, phenothiazine and drugs containing nicotinic acid.
Barbiturates, rifampicin and phenytoin may also reduce the hypoglycemic effect of gliquidone.
An increase or decrease in the hypoglycemic effect of gliquidone has been described when taking histamine H2 receptor blockers (cimetidine, ranitidine) and ethanol.
Overdose
Overdose
Overdose of sulfonylurea derivatives can lead to hypoglycemia.
Symptoms: tachycardia, increased sweating, hunger, palpitations, tremor, headache, insomnia, irritability, speech and vision disturbances, restlessness and loss of consciousness.
Treatment: If symptoms of hypoglycemia appear, glucose (dextrose) or foods rich in carbohydrates should be taken orally. In case of severe hypoglycemia (loss of consciousness, coma), dextrose is administered intravenously. After regaining consciousness, take easily digestible carbohydrates (to avoid re-development of hypoglycemia).
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
The drug should be stored out of the reach of children at a temperature not exceeding 25°C.
Shelf life
Shelf life
5 years.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Boehringer Ingelheim Hellas A.E., Greece
Additional information
| Shelf life | 5 years. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | The drug should be kept out of reach of children at a temperature not exceeding 25°C. |
| Manufacturer | Boehringer Ingelheim Hellas A.E., Greece |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Boehringer Ingelheim Hellas A.E. |
Related products
Buy Glurenorm, tablets 30 mg 60 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.