No products in the cart.
Glukonorm, 2.5mg+400 mg 40 pcs
€10.12 €8.86
Description
Gluconorm is a fixed combination of two oral hypoglycemic agents of different pharmacological groups: metformin and glibenclamide.
Metformin belongs to the biguanide group and reduces serum glucose levels by increasing the sensitivity of peripheral tissues to the action of insulin and increasing glucose uptake.
It reduces absorption of carbohydrates in the gastrointestinal tract and inhibits gluconeogenesis in the liver. The drug also has a favorable effect on the lipid profile of the blood, reducing the level of total cholesterol. LDL and triglycerides. It does not cause hypoglycemic reactions.
Glibenclamide belongs to the group of sulfonylurea derivatives of the II generation. It stimulates insulin secretion by reducing the threshold of glucose irritation of pancreatic β-cells, increases insulin sensitivity and the degree of its binding with target cells, increases insulin release, increases the effect of insulin on glucose absorption by muscles and liver, inhibits lipolysis in adipose tissue. Acts in the second stage of insulin secretion.
Pharmacokinetics
Glibenclamide
In oral administration, absorption from the GI tract is 48-84%. Time to reach Cmax is 1-2 hours. Vd – 9-10 liters. The binding to plasma proteins is 95%.
It is almost completely metabolized in the liver with the formation of two inactive metabolites, one of which is excreted by the kidneys and the other by the intestine. T1/2- from 3 to 10-16 h.
Metformin
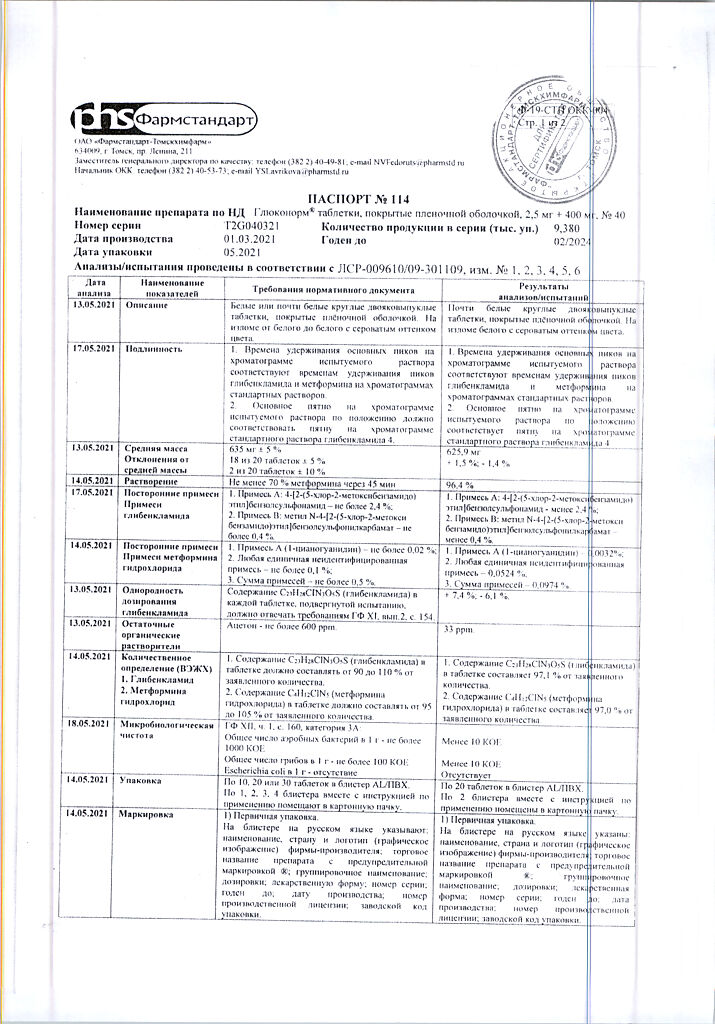
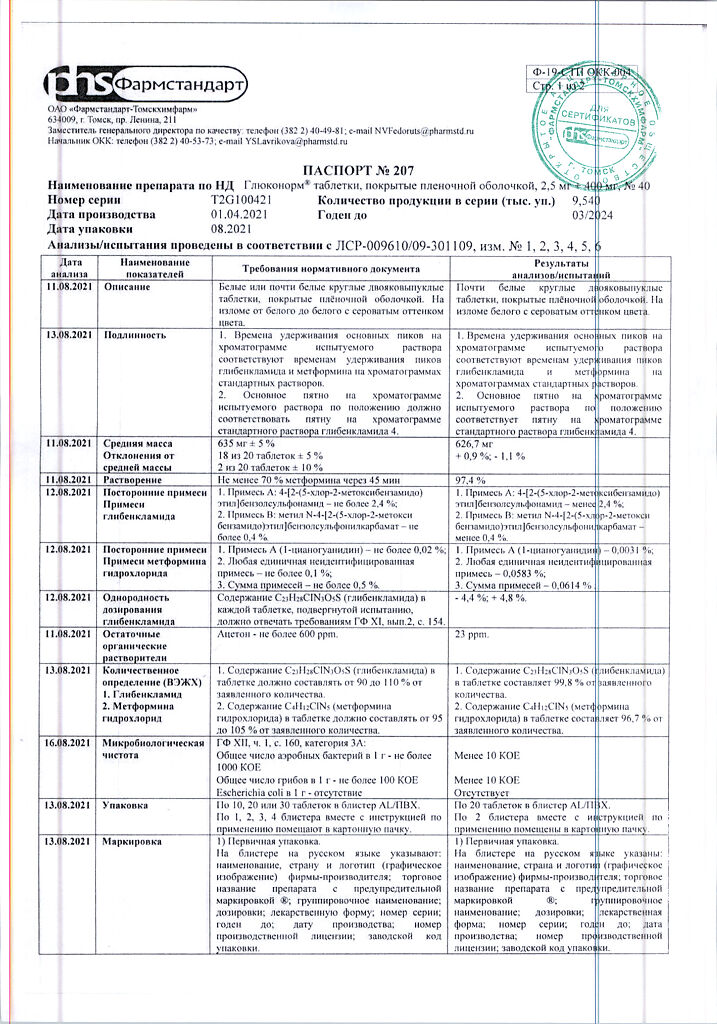
After oral administration is completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, 20-30% of the dose is found in the feces. Absolute bioavailability is 50 to 60%. When concomitant food intake, absorption of metformin is reduced and delayed. It is rapidly distributed in the tissues, practically does not bind with plasma proteins.
It is very poorly metabolized and excreted by the kidneys. T1/2 is approximately 9-12 hours.
Indications
Indications
Type 2 diabetes mellitus in adults:
if diet therapy, exercise and previous therapy with metformin or glibenclamide are ineffective;
to replace previous therapy with two drugs (metformin and glibenclamide) in patients with stable and well-controlled blood glucose levels.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Gluconorm is a fixed combination of two oral hypoglycemic agents of different pharmacological groups: metformin and glibenclamide.
Metformin belongs to the group of biguanides and reduces serum glucose levels by increasing the sensitivity of peripheral tissues to the action of insulin and enhancing glucose uptake.
Reduces the absorption of carbohydrates in the gastrointestinal tract and inhibits gluconeogenesis in the liver. The drug also has a beneficial effect on the blood lipid profile, reducing total cholesterol levels. LDL and triglycerides. Does not cause hypoglycemic reactions.
Glibenclamide belongs to the group of sulfonylurea derivatives of the second generation. Stimulates insulin secretion by lowering the threshold for irritation of pancreatic β-cells by glucose, increases sensitivity to insulin and the degree of its binding to target cells, increases insulin release, enhances the effect of insulin on glucose uptake by muscles and liver, and inhibits lipolysis in adipose tissue. Acts in the second stage of insulin secretion.
Pharmacokinetics
Glibenclamide
When taken orally, absorption from the gastrointestinal tract is 48-84%. Time to reach Cmax – 1-2 hours. Vd – 9-10 l. Communication with plasma proteins is 95%.
Almost completely metabolized in the liver with the formation of two inactive metabolites, one of which is excreted by the kidneys and the other by the intestines. T1/2 – from 3 to 10-16 hours.
Metformin
After oral administration, it is absorbed quite completely from the gastrointestinal tract; 20-30% of the dose is found in feces. Absolute bioavailability ranges from 50 to 60%. With simultaneous food intake, the absorption of metformin is reduced and delayed. It is quickly distributed into tissues and practically does not bind to plasma proteins.
It is metabolized to a very weak extent and is excreted by the kidneys. T1/2 is approximately 9-12 hours.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Glibenclamide, Metformin
Composition
Composition
Active ingredients:
glibenclamide 2.5 mg;
metformin hydrochloride 400 mg;
Excipients:
microcrystalline cellulose – 100 mg,
corn starch – 20 mg,
colloidal silicon dioxide – 20 mg,
gelatin – 10 mg,
glycerol – 10 mg,
magnesium stearate – 7 mg,
purified talc – 15 mg,
croscarmellose sodium – 30 mg,
sodium carboxymethyl starch – 18.3 mg,
cellacephate – 2 mg,
diethyl phthalate – 0.2 mg
Contraindications
Contraindications
type 1 diabetes mellitus;
diabetic ketoacidosis, diabetic precoma, diabetic coma;
hypoglycemia;
severe renal dysfunction;
acute conditions that can lead to changes in kidney function (dehydration, severe infection, shock);
acute or chronic diseases accompanied by tissue hypoxia (heart or respiratory failure, recent myocardial infarction, shock);
liver failure;
porphyria;
simultaneous use of miconazole;
infectious diseases, major surgical interventions, injuries, extensive burns and other conditions requiring insulin therapy;
chronic alcoholism, acute alcohol intoxication;
lactic acidosis (including history);
use for at least 48 hours before and 48 hours after radioisotope or x-ray studies with the introduction of an iodine-containing contrast agent;
following a hypocaloric diet (less than 1000 cal/day);
pregnancy;
breastfeeding period;
hypersensitivity to metformin, glibenclamide or other sulfonylurea derivatives, as well as to excipients.
It is not recommended to use the drug in people over 60 years of age who perform heavy physical work, which is associated with an increased risk of developing lactic acidosis.
With caution: febrile syndrome, adrenal insufficiency, hypofunction of the anterior pituitary gland, diseases of the thyroid gland with impaired function.
Side Effects
Side Effects
From the side of carbohydrate metabolism: hypoglycemia is possible.
From the gastrointestinal tract and liver: rarely – nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, loss of appetite, “metallic” taste in the mouth; in some cases – cholestatic jaundice, increased activity of liver enzymes, hepatitis.
From the hematopoietic system: rarely – leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, erythrocytopenia; very rarely – agranulocytosis, hemolytic or megaloblastic anemia, pancytopenia.
From the central nervous system: headache, dizziness, weakness, increased fatigue; rarely – paresis, sensory disturbances.
Allergic and immunopathological reactions: rarely – urticaria, erythema, itching, fever, arthralgia, proteinuria.
Dermatological reactions: rarely – photosensitivity.
Metabolism: lactic acidosis.
Other: acute reaction of alcohol intolerance after drinking it, expressed by complications in the circulatory and respiratory organs (disulfiram-like reaction: vomiting, feeling of heat in the face and upper body, tachycardia, dizziness, headache).
Interaction
Interaction
The hypoglycemic effect of the drug is enhanced by ACE inhibitors (captopril, enalapril), histamine H2 receptor blockers (cimetidine), antifungal agents (miconazole, fluconazole), NSAIDs (phenylbutazone, azapropazone, oxyphenbutazone), fibrates (clofibrate, bezafibrate), antituberculosis agents (ethionamide), salicylates, coumarin anticoagulants, anabolic steroids, beta-blockers, MAO inhibitors, long-acting sulfonamides, cyclophosphamide, chloramphenicol, fenfluramine, fluoxetine, guanethidine, pentoxifylline, tetracycline, theophylline, tubular secretion blockers, reserpine, bromocriptine, disopyramide, pyridoxine, other hypoglycemic drugs (acarbose, biguanides, insulin), allopurinol.
The effect is weakened by barbiturates, corticosteroids, adrenergic stimulants (epinephrine, clonidine), antiepileptic drugs (phenytoin), blockers of “slow” calcium channels, carbonic anhydrase inhibitors (acetazolamide), thiazide diuretics, chlorthalidone, furosemide, triamterene, asparaginase, baclofen, danazol, diazoxide, isoniazid, morphine, ritodrine, salbutamol, terbutaline, glucagon, rifampicin, iodine-containing thyroid hormones, lithium salts, in high doses – nicotinic acid, chlorpromazine, oral contraceptives and estrogens.
Medicines that acidify urine (ammonium chloride, calcium chloride, ascorbic acid in large doses) enhance the effect by reducing the degree of dissociation and increasing reabsorption of glibenclamide.
Ethanol increases the likelihood of developing lactic acidosis.
Metformin reduces Cmax and T1/2 of furosemide by 31% and 42.3%, respectively.
Furosemide increases the Cmax of metformin by 22%.
Nifedipine increases absorption, Cmax slows down the excretion of metformin.
Cationic drugs (amiloride, digoxin, morphine, procainamide, quinidine, quinine, ranitidine, triamterene and vancomycin) secreted in the tubules compete for tubular transport systems and, with long-term therapy, can increase the Cmax of metformin by 60%.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
In a dry place, protected from light, at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C.
Shelf life
Shelf life
3 years
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
M.J.Biopharm Pvt.Ltd, India
Additional information
| Shelf life | 3 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | In a dry, light-protected place at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C. |
| Manufacturer | M J Biopharm, India |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | M J Biopharm |
Related products
Buy Glukonorm, 2.5mg+400 mg 40 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.