No products in the cart.
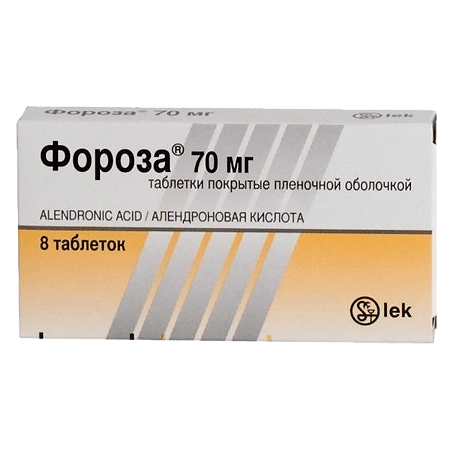
Foroza, 70 mg 8 pcs.
€24.85 €21.53
Out of stock
(E-mail when Stock is available)
Description
Bone resorption inhibitor.
Aminobisphosphonate is an analogue of pyrophosphate.
The mechanism of action is associated with inhibition of osteoclast activity.
Indications
Indications
treatment of osteoporosis in men to prevent fractures;
treatment of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women, incl. to reduce the risk of vertebral compression fractures and hip fractures;
treatment of osteoporosis caused by long-term use of corticosteroids.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Bone resorption inhibitor.
Aminobisphosphonate is an analogue of pyrophosphate.
The mechanism of action is associated with the suppression of osteoclast activity.
Special instructions
Special instructions
You should take Foroz tablets only with plain water, because other drinks (including mineral water, tea, coffee, fruit juices) impair the absorption of the drug. Taking alendronate before bed or in a horizontal position increases the risk of developing esophagitis.
If symptoms of esophageal irritation occur, such as dysphagia, chest pain, or new/worsening of existing heartburn, patients should consult a physician to evaluate the possibility of continuing therapy. The risk of severe esophageal side effects is greater in patients who take alendronic acid not in accordance with these instructions and/or who continue to take it after symptoms suggestive of esophageal irritation have occurred. It is important to explain in detail to the patient the rules for taking the drug and make sure that he understands them. Patients should be aware of the increased risk of adverse events from the esophagus if they deviate from the instructions.
Before starting therapy with Forosa, correction of hypocalcemia and other metabolic disorders (such as vitamin D deficiency) is necessary. Due to the increase in bone mineral density during alendronate therapy, a slight clinically asymptomatic decrease in serum calcium and phosphate levels is possible, especially in patients receiving corticosteroids, in whom calcium absorption may be reduced. Therefore, ensuring that sufficient amounts of calcium and vitamin D enter the body is especially important in patients receiving corticosteroids.
Patients should be warned that if they accidentally miss a dose of the drug once a week, they should take 1 tablet. in the morning of the next day (it is unacceptable to take 2 tablets in one day). Subsequently, you should continue to take 1 tablet. on the day of the week that was chosen at the beginning of therapy.
There is also evidence of osteonecrosis of the jaw in patients with osteoporosis receiving oral bisphosphonates. Before prescribing bisphosphonate therapy, patients with associated risk factors (eg, cancer, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, corticosteroids, poor oral hygiene, anemia, coagulopathy, infection, gum disease) should undergo a dental examination with appropriate preventive dental treatment. During treatment, these patients should avoid invasive dental procedures if possible. For patients who develop osteonecrosis of the jaw during bisphosphonate treatment, dental surgery may worsen the condition.
There are no data regarding the possible reduction in the risk of osteonecrosis of the jaw after discontinuation of bisphosphonates in patients requiring dental intervention.
Low-energy fractures (also known as stress fractures) of the proximal femoral shaft may occur in patients taking alendronic acid long-term. Fractures can occur after minimal or no trauma, and some patients may experience hip pain, often with outward signs of stress fractures weeks/months before a complete femur fracture occurs.
Low-energy proximal femoral shaft fractures were often bilateral, so patients with a long-standing femoral shaft fracture taking bisphosphonates should have the contralateral hip evaluated. It is advisable to discontinue bisphosphonates in patients with stress fractures after assessing their condition based on an individual assessment of the risk/benefit ratio.
The decision to proceed with treatment must be made individually for each patient after careful risk/benefit assessment, especially for patients with Barrett’s esophagus.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and engage in other activities that require increased concentration and speed of psychomotor reactions. Alendronic acid does not affect the ability to drive vehicles and engage in other activities that require increased concentration and speed of psychomotor reactions.
Special precautions when disposing of unused drug. There is no need for special precautions when disposing of unused drug.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Alendronic acid
Composition
Composition
1 film-coated tablet contains:
active ingredient:
alendronate sodium trihydrate 91.350 mg, which corresponds to the content of alendronic acid 70 mg;
excipients:
microcrystalline cellulose,
silicon dioxide colloidal anhydrous,
croscarmellose sodium,
magnesium stearate;
shell composition:
Luster Clear LC 103 (microcrystalline cellulose, carrageenan, macrogol 8000).
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
There is no data on the use of alendronic acid in pregnant women. Animal studies have revealed impaired formation of fetal bone tissue when using high doses of alendronic acid, and dysfunction of labor associated with hypokalemia. The drug should not be used during pregnancy.
It is not known whether alendronic acid passes into human breast milk, therefore, if it is necessary to use alendronic acid during lactation, the issue of stopping breastfeeding should be considered.
Contraindications
Contraindications
hypersensitivity to alendronate or other components of the drug Forosa;
strictures or achalasia of the esophagus and other conditions leading to slower movement of food through the esophagus;
the patient’s inability to stand or sit for 30 minutes;
hypocalcemia;
severe renal failure (creatinine Cl less than 35 ml/min);
severe disturbances of mineral metabolism;
pregnancy;
lactation period;
children’s age (efficacy and safety of use have not been established).
With caution: patients with gastrointestinal diseases such as dysphagia, gastritis, duodenitis, peptic ulcer in the acute stage, active gastrointestinal bleeding or a history of surgery on the upper gastrointestinal tract, hypovitaminosis D.
Side Effects
Side Effects
From the gastrointestinal tract: often – abdominal pain, dyspeptic disorders (constipation or diarrhea, flatulence), dysphagia, heartburn; uncommon – nausea, vomiting, esophagitis, gastritis; rarely – esophageal strictures, ulceration of the mucous membrane of the mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach and duodenum, bleeding from the upper gastrointestinal tract, melena; very rarely – perforation of the esophagus.
From the nervous system: frequency unknown – dizziness, taste disturbance, headaches, irritability.
From the organ of vision: rarely – scleritis, uveitis (inflammation of the choroid) and inflammation of the episcleral connective tissue.
From the skin and subcutaneous tissues: very rarely – hypersensitivity reactions (including skin hyperemia, urticaria, angioedema, severe skin reactions, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis); frequency unknown – alopecia, photosensitivity.
From the musculoskeletal and connective tissue side: often – muscle pain, bone pain; rarely – severe pain in muscles, bones and joints; frequency unknown – osteonecrosis of the jaw, low-energy fractures of the proximal femoral diaphysis, swelling of the joints.
Laboratory indicators: very rarely – asymptomatic transient hypocalcemia and hypophosphatemia.
Interaction
Interaction
Concomitant use of calcium supplements (including dietary supplements) and antacids impairs the absorption of alendronate. In this regard, it is recommended to take other medications no earlier than 30 minutes after taking Forosa.
NSAIDs (including acetylsalicylic acid) may increase the gastrointestinal side effects of alendronic acid.
Although specific drug interaction studies have not been conducted, the use of alendronate in clinical studies with a large number of commonly used drugs was not accompanied by the development of clinically significant interactions.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: abdominal pain, dyspeptic disorders, dysphagia, heartburn, esophagitis, gastritis; Hypocalcemia and hypophosphatemia may develop.
Treatment: symptomatic. The use of milk and antacids to bind alendronate is indicated. Due to the risk of damage to the esophagus, vomiting should not be induced and the patient should be in an upright position.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
In a dry place, protected from light, at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C
Shelf life
Shelf life
3 years
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Lek d.d., Slovenia
Additional information
| Shelf life | 3 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | In a dry, light-protected place at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C |
| Manufacturer | Lek d.d., Slovenia |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Lek d.d. |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Foroza, 70 mg 8 pcs. with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.