No products in the cart.
Formetin, tablets 500 mg 30 pcs
€1.00
Out of stock
(E-mail when Stock is available)
Description
Hypoglycemic agent for oral use of the group of biguanides
CodeATH: A10BA02
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics.
Metformin inhibits gluconeogenesis in the liver, reduces glucose absorption from the intestine, increases peripheral glucose utilization, and increases tissue sensitivity to insulin.
At the same time it has no effect on insulin secretion by the beta cells of the pancreas, does not cause hypoglycemic reactions. Reduces the level of triglycerides and low-density lipoproteins in the blood. Stabilizes or reduces body weight. Has a fibrinolytic effect due to inhibition of tissue-type plasminogen activator inhibitor.
Pharmacokinetics.
After oral administration metformin is slowly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Bioavailability after a standard dose is 50-60%. Maximum plasma concentration is reached 2.5 h after oral administration.
It practically does not bind with plasma proteins. It accumulates in salivary glands, muscles, liver and kidneys. It is excreted unchanged by kidneys. The elimination half-life is 1.5-4.5 hours. Cumulation of the preparation is possible in patients with impaired renal function.
Indications
Indications
Type 2 diabetes mellitus when diet therapy is ineffective (especially in obese patients).
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Composition
Composition
1 tablet contains:
active ingredient – metformin hydrochloride 0.5 g or 0.85 g or 1 g
excipients:
povidone medium molecular weight (polyvinylpyrrole lidone),
croscarmellose sodium,
magnesium stearate for pharmaceuticals.
How to take, the dosage
How to take, the dosage
The dose of the drug is set by the doctor individually, depending on the level of glucose in the blood.
Take without chewing during or after a meal, drinking plenty of water. The initial dose is 0.5 g 1-2 times a day or 0.85 g once a day, the dose is gradually (once a week) increased to 2-3 g a day. The maximum daily dose is 3 g.
In elderly patients the daily dose should not exceed 1 g. Because of increased risk of lactoacidosis in patients with severe metabolic disorders the drug dose should be reduced.
Interaction
Interaction
Co-administration with sulfonylurea derivatives, acarbose, insulin, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, monoamine oxidase inhibitors, oxytetracycline, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, clofibrate derivatives, cyclophosphamide, (3-adrenoblockers may increase the hypoglycemic effect of metformin.
In concomitant use with glucocorticosteroids, oral contraceptives, epinephrine, sympathomimetics, glucagon, thyroid hormones, thiazide and “loop” diuretics, phenothiazine derivatives, nicotinic acid derivatives may reduce the hypoglycemic action of metformin.
Cimetidine slows metformin excretion, which increases the risk of lactoacidosis.
Metformin may weaken the effect of anticoagulants (coumarin derivatives). With the simultaneous use of alcohol, lactoacidosis may develop. Nifedipine increases absorption, maximum concentration, slows metformin excretion.
Cationic drugs (amiloride, digoxin, morphine, procainamide, quinidine, quinine, ranitidine, triamterene, vancomycin) that are secreted in the tubules compete for the tubule transport systems and may increase the maximum drug concentration by 60% with long-term therapy.
Special Instructions
Special Instructions
Key kidney function should be monitored during treatment. At least twice a year, as well as in case of myalgia, plasma lactate content should be determined.
The drug Formetin may be used in combination with sulfonylurea derivatives. In this case it is necessary to control the blood glucose level particularly carefully.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery:
When used in monotherapy, Formetin does not affect the ability to drive and operate machinery.
When combining Formetin with other hypoglycemic agents (sulfonylurea derivatives, insulin, etc.) hypoglycemic states may occur, in which the ability to drive vehicles and engage in other potentially dangerous activities that require increased attention and quick psychomotor reactions is impaired.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Side effects
Side effects
Digestive system disorders: nausea, vomiting, “metallic” taste in the mouth, lack of appetite, diarrhea, flatulence, abdominal pain.
Metabolism disorders: in rare cases lactoacidosis (requires discontinuation of treatment); with prolonged treatment – hypovitaminosis B12 (malabsorption).
Blood organs: in rare cases – megaloblastic anemia.
Endocrine system: hypoglycemia (in case of inadequate doses).
Allergic reactions: skin rash.
Overdose
Overdose
In case of metformin overdose, lactoacidosis with fatal outcome is possible. The cause of lactocidosis may also be cumulation of the drug due to renal dysfunction.
The early symptoms of lactocidosis are general weakness, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, decreased body temperature, abdominal pain, muscle pain, decreased blood pressure, reflex bradyarrhythmia; fast breathing, dizziness, loss of consciousness and coma may be noted later.
Treatment: If signs of lactocidosis occur, metformin treatment should be stopped immediately, the patient should be urgently hospitalized and the lactate concentration determined, the diagnosis confirmed.
The most effective measure for lactate and metformin elimination from the body is hemodialysis. Symptomatic treatment is also carried out.
Similarities
Similarities
Additional information
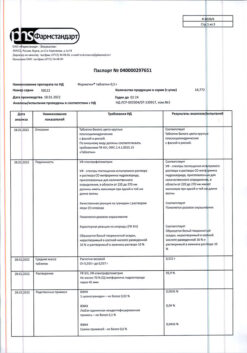
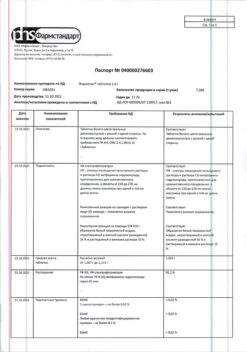
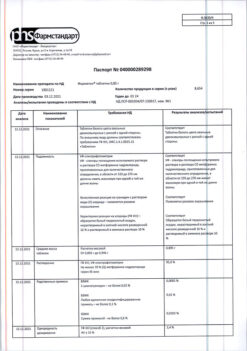
| Shelf life | 2 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | In a dry, light-protected place at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C |
| Manufacturer | Pharmstandard-Leksredstva, Russia |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Pharmstandard-Leksredstva |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Formetin, tablets 500 mg 30 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.