No products in the cart.
Fluconazole-OBL, 150 mg capsules 2 pcs
€2.13 €1.77
Out of stock
(E-mail when Stock is available)
Description
Fluconazole, a member of the triazole antifungal class, is a potent selective inhibitor of the fungal 14-a-demethylase enzyme.
The drug prevents conversion of lanosterol into ergosterol, the main component of cell membranes of fungi.
The drug is effective against opportunistic mycoses, including those caused by Candida spp. (Candida albicans, Candida tropicalis), Cryptococcus neoformans, Microsporum spp.
Fluconazole activity has also been shown in models of endemic mycoses, including infections caused by Blastomyces dermatitidis, Coccidioides immitis and Histoplasma capsulatum.
Indications
Indications
Cryptococcosis, including cryptococcal meningitis and infections of other sites (for example, lungs, skin), incl. in patients with a normal immune response and in patients with AIDS, organ transplant recipients and patients with other forms of immunodeficiency; maintenance therapy to prevent relapses of cryptococcosis in patients with AIDS.
Generalized candidiasis, including candidemia, disseminated candidiasis and other forms of invasive candidiasis, such as infections of the peritoneum, endocardium, eyes, respiratory and urinary tract, incl. in patients with malignant tumors who are in the ICU and receiving cytotoxic or immunosuppressive drugs, as well as in patients with other factors predisposing to the development of candidiasis.
Candidiasis of the mucous membranes, including the mucous membranes of the oral cavity and pharynx, esophagus, non-invasive bronchopulmonary infections, candiduria, mucocutaneous and chronic atrophic candidiasis of the oral cavity (associated with wearing dentures), incl. in patients with normal and suppressed immune function; prevention of relapse of oropharyngeal candidiasis in patients with AIDS.
Genital candidiasis; acute or recurrent vaginal candidiasis; prevention to reduce the frequency of relapses of vaginal candidiasis (3 or more episodes per year); candidal balanitis.
Mycoses of the skin, including mycoses of the feet, body, groin area, pityriasis versicolor, onychomycosis and cutaneous candidal infections.
Deep endemic mycoses in patients with normal immunity, coccidioidomycosis, paracoccidioidomycosis, sporotrichosis and histoplasmosis.
Prevention of fungal infections in patients with malignant tumors who are predisposed to the development of such infections as a result of cytotoxic chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Fluconazole, a member of the triazole antifungal class, is a potent selective inhibitor of the fungal enzyme 14-a-demethylase.
The drug prevents the transition of lanosterol to ergosterol, the main component of fungal cell membranes.
The drug is effective against opportunistic mycoses, incl. caused by Candida spp. (Candida albicans, Candida tropicalis), Cryptococcus neoformans, Microsporum spp., Trichophyton spp.
Fluconazole has also been shown to be active in models of endemic mycoses, including infections caused by Blastomyces dermatitidis, Coccidioides immitis and Histoplasma capsulatum.
Special instructions
Special instructions
Use with caution in case of abnormal liver function tests during the use of fluconazole, when a rash appears during the use of fluconazole in patients with superficial fungal infection and invasive/systemic fungal infections, with simultaneous use of terfenadine and fluconazole at a dose of less than 400 mg/day, in potentially proarrhythmic conditions in patients with multiple risk factors (organic heart disease, electrolyte imbalance and concomitant therapy for such disorders).
The hepatotoxic effects of fluconazole were usually reversible; its signs disappeared after cessation of therapy. Patients whose liver function tests are impaired during treatment with fluconazole should be monitored for signs of more serious liver damage. If clinical signs or symptoms of liver damage that may be associated with fluconazole occur, it should be discontinued.
People with AIDS are more likely to develop severe skin reactions when taking many drugs. If a patient receiving treatment for a superficial fungal infection develops a rash that can be associated with the use of fluconazole, it should be discontinued. If rash occurs in patients with invasive/systemic fungal infections, they should be monitored closely and fluconazole should be discontinued if bullous lesions or erythema multiforme develop.
Concomitant use of fluconazole in doses less than 400 mg/day and terfenadine should be carried out under close supervision.
When using fluconazole, an increase in the QT interval and ventricular fibrillation/flutter were observed very rarely in patients with multiple risk factors, such as organic heart disease, electrolyte imbalances and concomitant therapy that contributes to the development of such disorders.
Therapy can be started pending results of cultures and other laboratory tests. However, anti-infective therapy needs to be adjusted accordingly when the results of these studies become known.
There have been reports of cases of superinfection caused by Candida strains other than Candida albicans, which are often not sensitive to fluconazole (for example, Candida krusei). In such cases, alternative antifungal therapy may be required.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Fluconazole
Composition
Composition
1 capsule contains:
Active substance:
fluconazole 150 mg.
Excipients:
corn starch,
povidone (low molecular weight polyvinylpyrrolidone),
calcium stearate.
Hard gelatin capsules:
titanium dioxide,
patented blue dye,
gelatin,
preservatives – methylhydroxybenzoate,
propylhydroxybenzoate.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Concomitant use of terfenadine during repeated use of fluconazole at a dose of 400 mg/day or more;
simultaneous use of cisapride; hypersensitivity to fluconazole;
increased sensitivity to azole derivatives with a structure similar to fluconazole;
lactation period; children under 3 years of age (for this dosage form).
Side Effects
Side Effects
From the nervous system: headache, dizziness, convulsions, change in taste.
From the digestive system: abdominal pain, diarrhea, flatulence, nausea, dyspepsia, vomiting, hepatotoxicity (including rare cases with fatal outcome), increased levels of alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin, serum levels of aminotransferases (ALT and AST), impaired liver function, hepatitis, hepatocellular necrosis, jaundice.
From the cardiovascular system: increased QT interval on the ECG, ventricular fibrillation/flutter.
Dermatological reactions: rash, alopecia, exfoliative skin diseases, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis.
From the hematopoietic system: leukopenia, including neutropenia and agranulocytosis, thrombocytopenia.
From the side of metabolism: increased levels of cholesterol and triglycerides in plasma, hypokalemia.
Allergic reactions: anaphylactic reactions (including angioedema, facial swelling, urticaria, itching).
Interaction
Interaction
When used simultaneously with warfarin, fluconazole increases prothrombin time (by 12%), and therefore bleeding may develop (hematomas, bleeding from the nose and gastrointestinal tract, hematuria, melena). In patients receiving coumarin anticoagulants, prothrombin time must be constantly monitored.
After oral administration of midazolam, fluconazole significantly increases midazolam concentrations and psychomotor effects, and this effect is more pronounced after fluconazole is administered orally than when administered intravenously. If concomitant benzodiazepine therapy is necessary, patients taking fluconazole should be monitored for an appropriate benzodiazepine dose reduction.
With the simultaneous use of fluconazole and cisapride, adverse reactions from the heart are possible, incl. ventricular fibrillation/flutter (pirouette arrhythmia). The use of fluconazole at a dose of 200 mg 1 time / day and cisapride at a dose of 20 mg 4 times / day leads to a marked increase in plasma concentrations of cisapride and an increase in the QT interval on the ECG. Concomitant use of cisapride and fluconazole is contraindicated.
In patients after kidney transplantation, the use of fluconazole at a dose of 200 mg/day leads to a slow increase in cyclosporine concentrations. However, with repeated doses of fluconazole at a dose of 100 mg/day, no changes in cyclosporine concentrations were observed in bone marrow recipients. When using fluconazole and cyclosporine concomitantly, it is recommended to monitor the concentration of cyclosporine in the blood.
Repeated use of hydrochlorothiazide simultaneously with fluconazole leads to an increase in plasma concentrations of fluconazole by 40%. An effect of this magnitude does not require a change in the fluconazole dosage regimen in patients receiving concomitant diuretics, but this should be taken into account.
With simultaneous use of a combined oral contraceptive with fluconazole at a dose of 50 mg, no significant effect on hormone levels has been established, while with daily intake of 200 mg of fluconazole, the AUC of ethinyl estradiol and levonorgestrel increases by 40% and 24%, respectively, and when taking 300 mg of fluconazole once a week, the AUC of ethinyl estradiol and norethindrone increase by 24% and 13%, respectively. Thus, repeated use of fluconazole in the indicated doses is unlikely to affect the effectiveness of the combined oral contraceptive.
Concomitant use of fluconazole and phenytoin may be accompanied by a clinically significant increase in phenytoin concentrations. With this combination, phenytoin concentrations should be monitored and the dose adjusted accordingly to ensure therapeutic serum concentrations.
Concomitant use of fluconazole and rifabutin may lead to increased serum concentrations of the latter. Cases of uveitis have been described with the simultaneous use of fluconazole and rifabutin. Patients receiving rifabutin and fluconazole concomitantly should be monitored closely.
The simultaneous use of fluconazole and rifampicin leads to a decrease in AUC by 25% and the duration of T1/2 of fluconazole by 20%. In patients concomitantly taking rifampicin, the advisability of increasing the dose of fluconazole must be considered.
Fluconazole, when taken simultaneously, leads to an increase in T1/2 of oral sulfonylurea drugs (chlorpropamide, glibenclamide, glipizide and tolbutamide). In patients with diabetes mellitus, fluconazole and oral sulfonylureas can be prescribed together, but the possibility of hypoglycemia should be taken into account.
The simultaneous use of fluconazole and tacrolimus leads to an increase in plasma concentrations of the latter. Cases of nephrotoxicity have been described. Patients with this combination should be carefully monitored.
With the simultaneous use of azole antifungals and terfenadine, serious arrhythmias may occur as a result of an increase in the QT interval. When taking fluconazole at a dose of 200 mg/day, an increase in the QT interval has not been established, however, the use of fluconazole at doses of 400 mg/day and above causes a significant increase in the concentration of terfenadine in plasma. Concomitant use of fluconazole in doses of 400 mg/day or more with terfenadine is contraindicated. Treatment with fluconazole in doses less than 400 mg/day in combination with terfenadine should be carried out under close monitoring.
When used simultaneously with fluconazole at a dose of 200 mg for 14 days, the average rate of plasma clearance of theophylline is reduced by 18%. When prescribing fluconazole to patients taking high doses of theophylline or to patients at increased risk of developing theophylline toxicity, monitor for symptoms of theophylline overdose and, if necessary, adjust therapy accordingly.
When used simultaneously with fluconazole, an increase in zidovudine concentrations is observed, which is likely due to a decrease in the metabolism of the latter to its main metabolite. Before and after therapy with fluconazole at a dose of 200 mg/day for 15 days in patients with AIDS and ARC (AIDS-related complex), a significant increase in the AUC of zidovudine (20%) was found.
When used in HIV-infected patients with zidovudine at a dose of 200 mg every 8 hours for 7 days in combination with fluconazole at a dose of 400 mg/day with or without an interval of 21 days between the two regimens, a significant increase in the AUC of zidovudine (74%) was found when used simultaneously with fluconazole. Patients receiving this combination should be monitored for side effects of zidovudine.
The simultaneous use of fluconazole with astemizole or other drugs whose metabolism is carried out by isoenzymes of the cytochrome P450 system may be accompanied by an increase in serum concentrations of these drugs. Patients with such combinations should be carefully monitored.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea; in severe cases, convulsions, hallucinations, and paranoid behavior may occur.
Treatment: symptomatic, gastric lavage; because fluconazole is excreted by the kidneys; forced diuresis is recommended. Hemodialysis within 3 hours reduces plasma concentrations by 2 times.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Alium JSC, Russia
Additional information
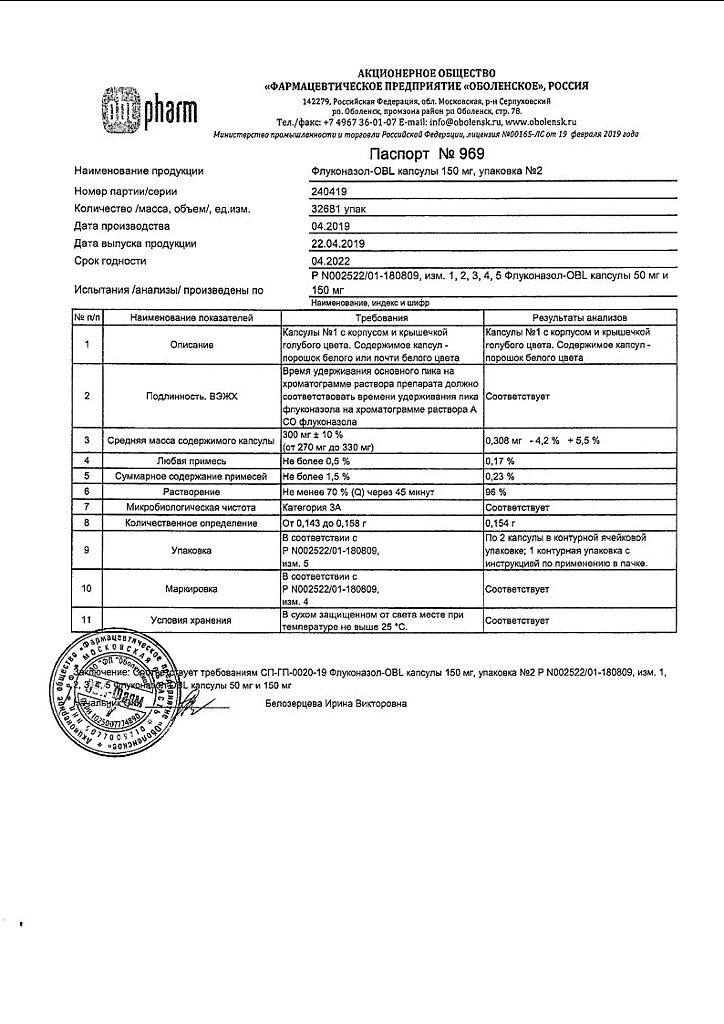
| Manufacturer | Alium JSC, Russia |
|---|---|
| Medication form | capsules |
| Brand | Alium JSC |
Related products
Buy Fluconazole-OBL, 150 mg capsules 2 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.