No products in the cart.
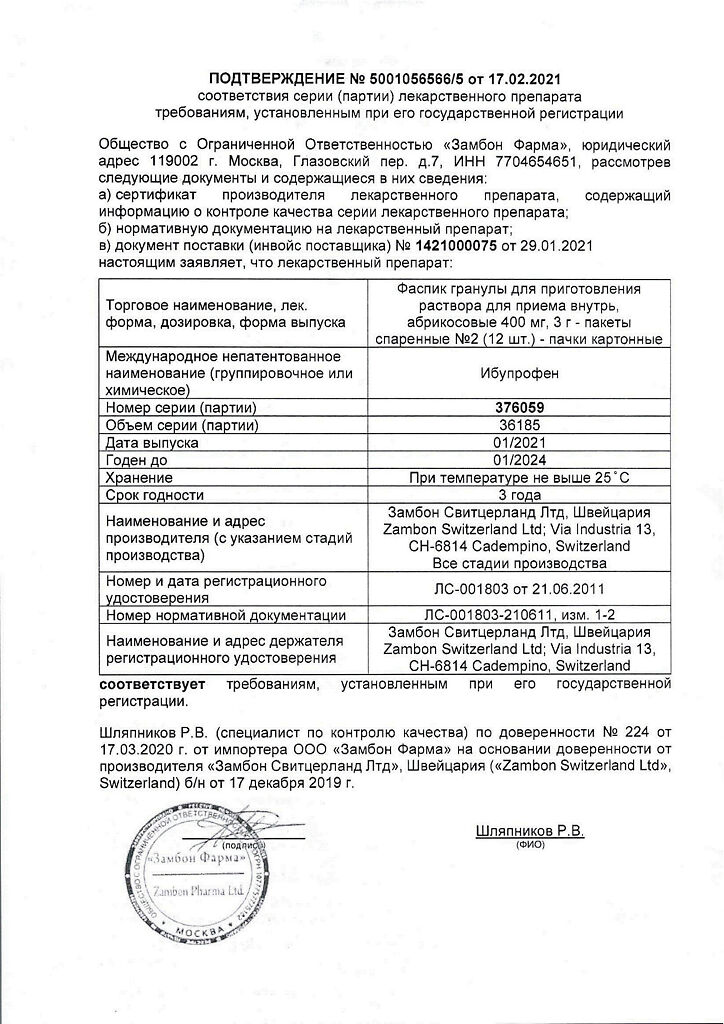
Faspik, 400 mg sachet 12 pcs
€4.09 €3.64
Description Pain syndrome of different etiology (including sore throat, headache, migraine, toothache, neuralgia, post-operative pain, post-traumatic pain, primary algodysmenorrhea). Inflammatory and degenerative diseases of the joints and spine (including rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis).
Joint pain (arthralgia), Migraine, Colds, Arthrosis and arthritis, Painful menstruation (algodysmenorrhea), Pain after injuries and operations, Flu, Pain, Neuralgia, Increased body temperature, Rheumatoid arthritis, Periarthritis, Neck pain, Myalgia (muscle pain), Back pain, Headache, Toothache, Osteoarthritis, Sore throat.Li>Fever syndrome of various genesis.
Indications
Indications
Feverish syndrome of various origins.
Pain syndrome of various etiologies (including sore throat, headache, migraine, toothache, neuralgia, postoperative pain, post-traumatic pain, primary algodismenorrhea).
Inflammatory and degenerative diseases of the joints and spine (including rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis).
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID).
Special instructions
Special instructions
In patients with infection, the drug should be prescribed with caution and subject to adequate antimicrobial therapy, since ibuprofen can mask objective and subjective signs of infection.
Patients with allergic reactions and bronchial asthma (including a history) have an increased risk of bronchospasm during therapy with ibuprofen.
With long-term use of NSAIDs, there is a risk of developing analgesic nephropathy.
If symptoms of gastrointestinal bleeding occur, Faspik is discontinued.
Patients who notice blurred vision during therapy should stop taking the drug and consult an ophthalmologist.
The risk of side effects is reduced when taking Faspik in the minimum effective dose for the shortest possible course.
During treatment, it is necessary to periodically monitor the peripheral blood picture and the functional state of the kidneys and liver. Faspik should be discontinued 48 hours before in patients who are indicated for a test to determine 17-ketosteroids.
When signs of gastropathy appear, careful monitoring of the patient’s condition is required, including a stool test for occult blood, a blood test to determine hematocrit and hemoglobin, as well as esophagogastroduodenoscopy. To prevent the development of gastropathy associated with taking NSAIDs, it is recommended to combine the drug with prostaglandin E agents (for example, misoprostol).
Ibuprofen can negatively affect female fertility and is therefore not recommended for women planning pregnancy.
During treatment you should refrain from drinking alcoholic beverages.
1 tablet of Faspik contains 16.7 mg of sucrose. The sucrose content in granules with a dosage of 400 mg is 0.18 XE in 1 packet and 0.54 XE in the maximum daily dose.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate complex mechanisms. During therapy, patients are advised to refrain from performing any work that requires speed of reactions and increased attention, including driving a car and operating complex mechanisms.
The use of Faspik by pregnant and breastfeeding women is contraindicated.
Use in childhood Faspik in doses of 200 and 400 mg is contraindicated in children under 12 years of age, in a dosage of 600 mg – in children and adolescents under 18 years of age.
For renal dysfunction. Progressive kidney disease and severe renal failure with creatinine clearance (CC) less than 30 ml/min are contraindications to the use of Faspic. In chronic renal failure (creatinine clearance 30−60 ml/min), the drug should be used with caution.
For liver dysfunction. Severe liver failure and active liver disease are considered contraindications to the use of Faspik. In case of liver failure, the drug should be used with caution.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Ibuprofen
Composition
Composition
Active ingredient
ibuprofen 400 mg;
Excipients:
L-arginine,
sodium bicarbonate,
sodium saccharinate,
aspartame,
apricot flavoring,
sucrose.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
The use of Faspik by pregnant and breastfeeding women is contraindicated.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to any of the ingredients included in the drug.
History of hypersensitivity to acetylsalicylic acid or other NSAIDs.
Erosive and ulcerative diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (including peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum in the acute stage, Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis).
Aspirin-induced asthma.
Hemophilia and other bleeding disorders (including hypocoagulation), hemorrhagic diathesis.
Bleeding of any etiology.
Pregnancy.
Lactation period.
Children’s age up to 12 years.
Diseases of the optic nerve.
Caution is required in the following cases:
old age;
heart failure;
arterial hypertension;
liver cirrhosis with portal hypertension;
liver and/or renal failure, nephrotic syndrome, hyperbilirubinemia;
peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum (history), gastritis, enteritis, colitis;
blood diseases of unknown etiology (leukopenia and anemia).
Side Effects
Side Effects
shortness of breath, bronchospasm;
gastrointestinal tract (GIT): pain in the mouth, irritation or dryness of the oral mucosa, aphthous stomatitis, ulceration of the gum mucosa, pancreatitis, NSAID gastropathy (diarrhea, constipation, loss of appetite, heartburn, flatulence, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, ulceration of the gastrointestinal mucosa, in some cases complicated perforation and bleeding);
central and peripheral nervous system: hallucinations, nervousness, insomnia, confusion, irritability, dizziness, drowsiness, anxiety, psychomotor agitation, depression, headache, aseptic meningitis (more often in patients with autoimmune diseases);
cardiovascular system: increased blood pressure, tachycardia, heart failure;
hematopoietic organs: agranulocytosis, thrombocytopenic purpura, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, anemia (including hemolytic and aplastic);
urinary system: nephrotic syndrome (edema), cystitis, polyuria, allergic nephritis, acute renal failure;
hepatobiliary system: hepatitis; organ of vision: swelling of the conjunctiva and eyelids (allergic origin), blurred vision or double vision, toxic damage to the optic nerve, irritation and dry eyes, scotoma;
organ of hearing: ringing, tinnitus, hearing loss;
allergic reactions: skin itching, skin rash (usually urticarial and erythematous), allergic rhinitis, eosinophilia, fever, bronchospasm or shortness of breath, anaphylactoid reactions, Quincke’s edema, anaphylactic shock, toxic epidermal necrolysis (Lyell’s syndrome), erythema multiforme exudative (including Stevens’ syndrome – Johnson);
laboratory parameters: increased bleeding time, serum creatinine concentration and hepatic transaminase activity, decreased creatinine clearance, blood glucose concentration, hemoglobin or hematocrit.
With long-term use of Faspik in high doses, the risk of developing ulcerations of the gastrointestinal mucosa, bleeding (gingival, gastrointestinal, hemorrhoidal or uterine) and visual impairment (damage to the optic nerve, impaired color vision and the development of scotoma) increases.
Interaction
Interaction
acetylsalicylic acid (ASA): its antiplatelet effect is reduced (and therefore the incidence of acute coronary insufficiency in patients receiving ASA as an antiplatelet agent may increase);
other NSAIDs (including ASA): the likelihood of side effects from the gastrointestinal tract increases;
methotrexate: its concentration in plasma increases;
furosemide, thiazide diuretics: their effectiveness may be reduced due to sodium retention due to inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis in the kidneys;
indirect anticoagulants, antiplatelet agents, fibrinolytics: their effect is enhanced, the risk of hemorrhagic complications increases;
vasodilators (including angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and slow calcium channel blockers): their hypotensive effect is reduced;
tacrolimus: the likelihood of developing nephrotoxicity increases;
caffeine: the analgesic effect of ibuprofen increases;
zidovudine: the risk of developing hematomas and hemarthrosis increases in HIV-infected patients with concomitant hemophilia;
myelotoxic drugs: the manifestation of hematotoxicity of ibuprofen increases;
inhibitors of microsomal liver enzymes: the risk of hepatotoxicity is reduced;
inducers of microsomal liver enzymes (tricyclic antidepressants, barbiturates, phenylbutazone, phenytoin, rifampicin, ethanol): the risk of severe hepatotoxic reactions increases due to an increase in active and hydroxylated metabolites);
anticoagulants, thrombolytic agents (streptokinase, urokinase, alteplase): the likelihood of bleeding increases;
plicamycin, cefotetan, cefoperazone, cefamandole, valproic acid: the incidence of hypoprothrombinemia increases;
gold preparations, cyclosporine: the nephrotoxicity of ibuprofen increases due to its increased effect on the synthesis of prostaglandin in the kidneys;
cyclosporine: its plasma concentration increases and, as a result, the risk of developing hepatotoxic effects;
antacids, cholestyramine: absorption of ibuprofen decreases;
ethanol, estrogens, glucocorticosteroids, colchicine: possible development of ulcerogenic effects with bleeding;
insulin, oral hypoglycemic drugs: their effect is enhanced, which may require dose adjustment;
agents that block tubular secretion: the excretion decreases and the plasma concentration of ibuprofen increases;
phenytoin, lithium, digoxin: the possibility of an increase in their plasma concentrations cannot be excluded.
Overdose
Overdose
An overdose of ibuprofen may cause the following symptoms: drowsiness, lethargy, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, acute renal failure, metabolic acidosis, tinnitus, headache, depression, decreased blood pressure, tachycardia, bradycardia, atrial fibrillation, coma, respiratory arrest.
Clinical pharmacology
Clinical pharmacology
Pharmacodynamics
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
Store out of reach of children at temperatures up to 25 °C.
Shelf life
Shelf life
3 years.
Do not use after the expiration date stated on the package.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Zambon S.p.A., Italy
Additional information
| Shelf life | 3 years. Do not use after the expiration date printed on the package. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | Keep out of reach of children at temperatures up to 25 ° C. |
| Manufacturer | Zambon S.p.A., Italy |
| Medication form | granules for preparation of oral solution |
| Brand | Zambon S.p.A. |
Related products
Buy Faspik, 400 mg sachet 12 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.