No products in the cart.
Description
Pharmacodynamics
The anti-tumor anti-estrogenic non-steroidal drug, a triphenylethylene derivative.
Toremifene specifically binds to estrogen receptors, competing with estradiol, inhibits estrogen-induced DNA synthesis and cell replication. At high doses, toremifene can have an antitumor effect unrelated to estrogen-dependent action.
In breast cancer patients the antitumor effect of toremifene is mainly related to its anti-estrogen activity, although other mechanisms (regulation of oncogene expression, growth factor secretion, apoptosis induction, influence on cell cycle kinetics) cannot be excluded.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Toremifene is completely absorbed after oral administration. Cmax in blood plasma is reached after 3 h (2-5 h). Food intake has no effect on the completeness of absorption, but may increase the time to reach Cmax by 1.5-2 hours. These changes have no clinical significance.
Distribution
The binding to plasma proteins (mainly to albumin) is 99.5%. Css in plasma is established within 3-4 weeks (at a dose of 60 mg/day).
Metabolism and excretion
The rapid phase of distribution with a mean T1/2 of about 4 h (2-12 h) is followed by a slow phase of excretion with a mean T1/2 of about 5 days (2-10 days).
Toremifene is metabolized in the liver by hydroxylation and demethylation with the participation of CYP3A4 isoenzyme to form the active metabolite, N-demethyltoremifene. Average T1/2 of N-demethyltremifene is 11 days (4-20 days). In blood serum we found 3 more metabolites: deaminohydroxytoremifene, 4-hydroxytoremifene and N,N-didemethyltoremifene. Total clearance is 5 l/h.
Extracted through the intestine, mainly as metabolites; about 10% – by the kidneys.
Indications
Indications
Estrogen-dependent breast cancer in postmenopausal women.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacodynamics
Antitumor antiestrogenic non-steroidal drug, triphenylethylene derivative.
Toremifene specifically binds to estrogen receptors, competing with estradiol, and inhibits estrogen-induced DNA synthesis and cell replication. In high doses, toremifene may have an antitumor effect that is not associated with an estrogen-dependent effect.
In patients with breast cancer, the antitumor effect of toremifene is mainly associated with its antiestrogenic activity, although other mechanisms cannot be excluded (regulation of oncogene expression, growth factor secretion, induction of apoptosis, effect on cell cycle kinetics).
Pharmacokinetics
Suction
After oral administration, toremifene is completely absorbed. Cmax in blood plasma is achieved after 3 hours (2-5 hours). Eating does not affect the completeness of absorption, but may increase the time to reach Cmax by 1.5-2 hours. These changes are not clinically significant.
Distribution
Binding to plasma proteins (mainly albumin) – 99.5%. Css in blood plasma is established within 3-4 weeks (at a dose of 60 mg/day).
Metabolism and excretion
The fast distribution phase with an average T1/2 of about 4 hours (2-12 hours) is followed by a slow elimination phase with an average T1/2 of about 5 days (2-10 days).
Toremifene is metabolized in the liver by hydroxylation and demethylation with the participation of the CYP3A4 isoenzyme to form the active metabolite – N-demethyltoremifene. The average T1/2 of N-demethyltoremifene is 11 days (4-20 days). Three more metabolites were found in the blood serum: deaminohydroxytoremifene, 4-hydroxytoremifene and N,N-didemethyltoremifene. Total clearance – 5 l/h.
Excreted through the intestines, mainly in the form of metabolites; about 10% – by the kidneys.
Special instructions
Special instructions
Before starting treatment, the patient must undergo an examination by a gynecologist. Particular attention should be paid to the condition of the endometrial mucosa. Then gynecological examinations must be repeated at least once a year.
Patients suffering from diseases such as arterial hypertension, diabetes mellitus, having a high body mass index (>30) or receiving long-term HRT are at risk for endometrial cancer and therefore require careful monitoring.
Toremifene is not recommended for use in patients with a history of severe thromboembolic disease.
Patients with decompensated heart failure or severe angina require careful monitoring.
Since hypercalcemia may develop in patients with bone metastases at the beginning of treatment with the drug, these patients require careful monitoring.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Toremifene
Composition
Composition
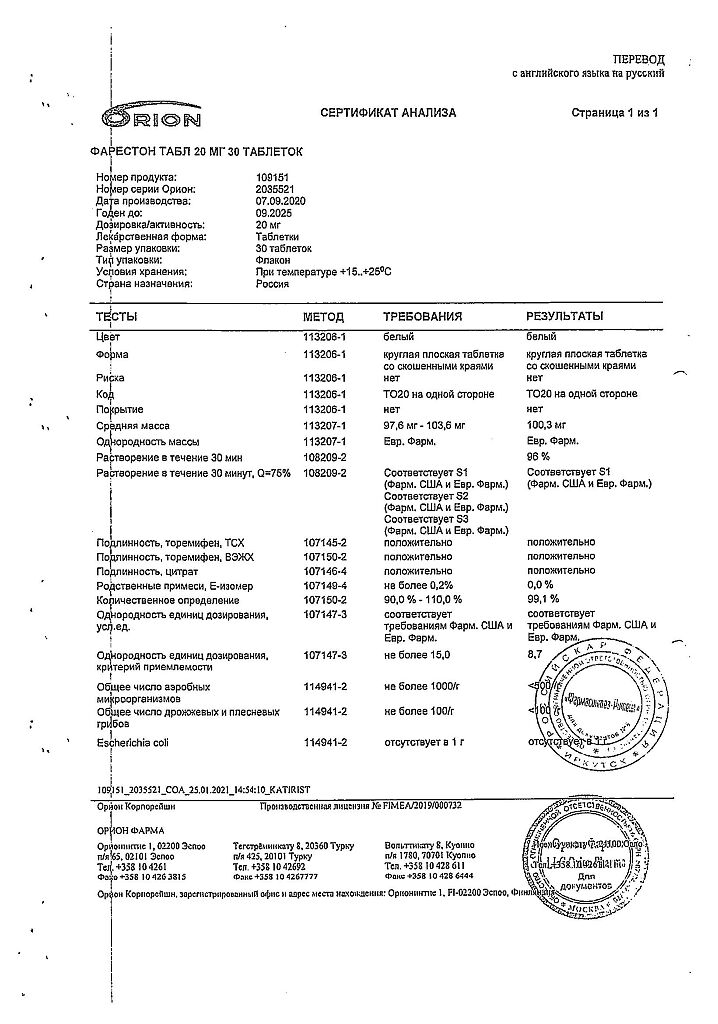
1 tablet contains:
Active ingredients:
toremifene (citrate form) 20 mg.
Excipients:
corn starch,
lactose,
povidone,
sodium starch glycolate (type A),
magnesium stearate,
microcrystalline cellulose,
colloidal silicon anhydrous.
There are 10 tablets in a blister pack.
In a cardboard package there are 3 blister packs.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
Fareston is contraindicated for use during pregnancy and lactation (breastfeeding).
Contraindications
Contraindications
Endometrial hyperplasia (including history);
severe liver failure (including history);
thromboembolism (including history);
pregnancy;
lactation (breastfeeding);
hypersensitivity to the drug.
With caution: the drug is prescribed for leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, hypercalcemia (including metastases to bone tissue).
Side Effects
Side Effects
Effects due to anti-estrogenic action: most often – paroxysmal sensations of heat (hot flashes), increased sweating, vaginal bleeding or discharge, increased fatigue, nausea, rash, itching in the genital area, fluid retention, dizziness, depression. These effects are usually mild.
From the endocrine system: rarely – weight gain.
From the digestive system: rarely – anorexia, vomiting, constipation.
From the central nervous system: rarely – headache, insomnia, increased transaminase levels; in some cases – severe liver dysfunction (jaundice).
From the organ of vision: rarely – visual impairment, including changes in the cornea, cataracts.
From the cardiovascular system: rarely – deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism.
Dermatological reactions: rarely – skin rash, alopecia.
Other: rarely – shortness of breath.
In patients with bone metastases, cases of hypercalcemia have been reported at the very beginning of treatment.
The risk of endometrial changes such as hyperplasia, polyposis and cancer increases. This may be caused by the main pharmacological property of the drug – estrogen stimulation.
Interaction
Interaction
Drugs that reduce renal excretion of calcium (including thiazide diuretics) may increase the risk of hypercalcemia.
Inducers of microsomal oxidation (for example, phenobarbital, phenytoin or carbamazepine) may accelerate the metabolism of toremifene, reducing its serum concentration. In such cases, the daily dose should be doubled.
The interaction between antiestrogens and warfarin can lead to a marked increase in bleeding time (simultaneous use of toremifene and drugs of this group should be avoided).
Theoretically, the metabolism of toremifene may be slowed down by drugs that inhibit the CYP3A4 isoenzyme, which is involved in the metabolism of toremifene. Such drugs include ketoconazole and other similar antifungal drugs, as well as erythromycin, oleandomycin.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: with a daily dose of Fareston 680 mg, dizziness, headaches, nausea and/or vomiting were observed. Theoretically, overdose may result in increased antiestrogenic effects (hot flashes) or increased estrogenic effects (vaginal bleeding).
Treatment: symptomatic therapy.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
In a dry place, at a temperature of 15–25 °C
Shelf life
Shelf life
5 years
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Orion Corporation, Finland
Additional information
| Shelf life | 5 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | In a dry place, at 15-25 °C |
| Manufacturer | Orion Corporation, Finland |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Orion Corporation |
Related products
Buy Fareston, tablets 20 mg 30 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.