No products in the cart.
Description
Famvir is an antiviral drug. After oral administration, penciclovir is rapidly converted to penciclovir, which has activity against human herpes viruses, including Varicella zoster (herpes zoster virus) and Herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 (labial and genital herpes virus), as well as Epstein-Barr virus and cytomegalovirus.
Penciclovir enters virus-infected cells where it is rapidly converted into monophosphate by viral thymidine kinase, which in turn is converted into triphosphate with the help of cellular enzymes. Penciclovir triphosphate stays in virus-infected cells for more than 12 hours, suppressing viral DNA replication.
The concentration of penciclovir triphosphate in uninfected cells does not exceed the minimum detectable, so in therapeutic concentrations penciclovir has no effect on uninfected cells.
Penciclovir is active against newly detected acyclovir-resistant strains of Herpes simplex virus with altered DNA polymerase.
The incidence of resistance to famiclovir (penciclovir) does not exceed 0.3%, in patients with compromised immunity – 0.19%.
Resistance was detected at the beginning of treatment and did not develop during treatment or after completion of therapy. Famcyclovir has been shown to significantly reduce the severity and duration of post-herpetic neuralgia in patients with herpes zoster.
In immunocompromised patients due to HIV infection, famcyclovir at a dose of 500 mg twice daily has been shown to reduce the number of days of herpes simplex virus excretion (both with and without clinical manifestations).
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Famcyclovir is quickly and almost completely absorbed after oral administration and rapidly converts to active penciclovir. Bioavailability of pencyclovir after oral administration of Famvir is 77%. Cmax of pencyclovir after oral administration with doses of 125 mg, 250 mg or 500 mg of Famciclovir is reached in 45 minutes on average and is 0.8 µg/ml, 1.6 µg/ml and 3.3 µg/ml, respectively.
Distribution
The pharmacokinetic “concentration-time” curves coincide with a single dose of famcyclovir and when dividing the daily dose into 2 or 3 doses.
The binding to plasma proteins of penciclovir and its 6-deoxy precursor is less than 20%.
No cumulation was noted with repeated doses of the drug.
T1/2 of pencyclovir from plasma in the final phase after single and repeated doses is about 2 hours.
Famcyclovir is excreted mainly in the form of penciclovir and its 6-deoxy precursor, which are excreted unchanged in the urine; famcyclovir is not detected in the urine.
Indications
Indications
Infections caused by the Varicella zoster virus (herpes zoster), including ophthalmic herpes and postherpetic neuralgia.
Infections caused by the Herpes simplex virus (types 1 and 2): primary infection, exacerbation of chronic infection, suppression of recurrent infection (to prevent exacerbations).
Infections caused by Varicella zoster and Herpes simplex viruses (types 1 and 2) in patients with reduced immunity.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Famvir is an antiviral drug. After oral administration, famciclovir is rapidly converted to penciclovir, which has activity against human herpes viruses, including Varicella zoster virus (herpes zoster virus) and Herpes simplex types 1 and 2 (labial and genital herpes simplex virus), as well as Epstein-Barr virus and cytomegalovirus.
Penciclovir enters virus-infected cells, where, under the action of viral thymidine kinase, it is quickly converted into monophosphate, which, in turn, with the participation of cellular enzymes, turns into triphosphate. Penciclovir triphosphate remains in virus-infected cells for more than 12 hours, suppressing the replication of viral DNA in them.
The concentration of penciclovir triphosphate in uninfected cells does not exceed the minimum detectable level, therefore, at therapeutic concentrations, penciclovir has no effect on uninfected cells.
Penciclovir is active against recently discovered acyclovir-resistant strains of the Herpes simplex virus with altered DNA polymerase.
The incidence of resistance to famciclovir (penciclovir) does not exceed 0.3%, in patients with impaired immunity – 0.19%.
Resistance was detected at the beginning of treatment and did not develop during treatment or after completion of therapy. Famciclovir has been shown to significantly reduce the severity and duration of postherpetic neuralgia in patients with herpes zoster.
It has been shown that in patients with impaired immunity due to HIV infection, famciclovir at a dose of 500 mg 2 times a day. reduces the number of days of herpes simplex virus shedding (both with and without clinical manifestations).
Pharmacokinetics
Suction
After oral administration, famciclovir is rapidly and almost completely absorbed and is rapidly converted to active penciclovir. The bioavailability of penciclovir after oral administration of Famvir is 77%. Cmax of penciclovir after oral administration in doses of 125 mg, 250 mg or 500 mg of famciclovir is achieved on average after 45 minutes and is 0.8 µg/ml, 1.6 µg/ml and 3.3 µg/ml, respectively.
Distribution
The pharmacokinetic concentration-time curves are the same when taking famciclovir once and when the daily dose is divided into 2 or 3 doses.
Plasma protein binding of penciclovir and its 6-deoxy precursor is less than 20%.
No accumulation was observed with repeated doses of the drug.
Removal
T1/2 of penciclovir from plasma in the final phase after taking a single and repeated doses is about 2 hours.
Famciclovir is excreted primarily in the form of penciclovir and its 6-deoxy precursor, which are excreted unchanged in the urine; famciclovir is not detected in urine.
Special instructions
Special instructions
Treatment should begin immediately after diagnosis. Caution should be exercised when treating patients with impaired renal function, for whom dosage adjustment may be required. No special precautions are required in elderly patients. Genital herpes is a sexually transmitted disease.
During relapses, the risk of infection increases. In the presence of clinical manifestations of the disease, even if antiviral treatment is started, patients should avoid sexual intercourse. During maintenance treatment with antiviral drugs, the incidence of viral infection is significantly reduced, but the risk of transmission of infection theoretically exists. Therefore, patients should take appropriate protective measures during sexual intercourse.
Tablets of the drug 125 mg, 250 mg and 500 mg contain lactose (26.9 mg, 53.7 mg and 107.4 mg, respectively). Famvir should not be used in patients with rare hereditary disorders associated with galactose intolerance, severe lactase deficiency or glucose-galactose malabsorption.
Tolerable doses of Famvir and duration of treatment. Famvir was well tolerated in the treatment of infection caused by the Varicella zoster virus when used at a dose of 750 mg 3 times a day for 7 days; in patients with genital herpes when using the drug at a dose of up to 750 mg 3 times / day for 5 days and at a dose of up to 500 mg 3 times / day for 10 days. The drug was also shown to be well tolerated when administered at 250 mg three times daily for 12 months for the treatment of genital herpes. Famvir was well tolerated in patients with reduced immunity when treating infections caused by the Varicella zoster virus when taken 500 mg 3 times a day for 10 days, as well as infections caused by Herpes simplex viruses when taken up to 500 mg 2 times a day for 7 days or 500 mg 2 times a day for 8 weeks.
Use in pediatrics: the effectiveness and safety of Famvir in children has not been established. Therefore, the use of famciclovir in children is not recommended unless the expected benefit of treatment justifies the potential risk associated with the drug.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery:
Famvir is not expected to affect the ability of patients to drive a car or use other machinery, however, patients who experience dizziness, drowsiness, confusion or other central nervous system disorders while using Famvir should refrain from driving a car or operating machinery during the period of use of the drug.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Famciclovir
Composition
Composition
Active ingredient:
famciclovir 125 mg.
Excipients:
hydroxypropylcellulose,
lactose anhydrous,
sodium starch glycolate,
magnesium stearate.
Shell composition:
hypromellose,
titanium dioxide,
polyethylene glycol 4000 (macrogol),
polyethylene glycol 6000 (macrogol).
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
Since the safety of Famvir in pregnant and lactating women has not been studied, its use during pregnancy and lactation is not recommended unless the possible benefits of treatment outweigh the potential risks.
It is not known whether penciclovir is excreted into breast milk in humans. Famciclovir does not have a significant effect on sperm count, morphology or motility of human sperm.
Experimental studies did not reveal the embryotoxic and teratogenic effects of famciclovir and penciclovir. Studies in rats administered oral famciclovir have shown that penciclovir is excreted in breast milk.
A decrease in fertility was noted in an experimental model in male rats receiving famciclovir at a dose of 500 mg/kg body weight; in female rats, no pronounced decrease in fertility was noted.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity; hypersensitivity to penciclovir.
Side Effects
Side Effects
Clinical studies have shown good tolerability of Famvir, incl. in patients with reduced immunity. Cases of headache and nausea have been reported, but these events were mild to moderate and occurred with the same frequency in patients receiving placebo.
Below are the adverse reactions and their incidence based on spontaneous reports and cases reported in the literature for the entire period during which Famvir has been used in clinical practice. Adverse events reported in clinical trials in immunocompromised patients were consistent with those reported in immunocompromised patients.
To assess the frequency of adverse reactions, the following criteria were used: very often (> 1/10); often (from > 1/100, 1/1000, 1/10000, < 1/1000); very rare (< 1/10000), including isolated reports.
From the hematopoietic system: very rarely – thrombocytopenia.
From the side of the central nervous system: rarely – headache, confusion (mainly in elderly patients); very rarely – dizziness, drowsiness (mainly in elderly patients), hallucinations.
From the digestive system: rarely – nausea; very rarely – vomiting, jaundice.
Dermatological reactions: very rarely – rash, itching, severe skin reactions.
Allergic reactions: very rarely – urticaria, severe skin reactions (including erythema multiforme).
Interaction
Interaction
There were no clinically significant pharmacokinetic interactions between famciclovir and other drugs.
There was no effect of famciclovir on the cytochrome P450 system.
Drugs that block tubular secretion may increase penciclovir plasma concentrations.
In the course of clinical studies, there was no interaction between zidovudine and famciclovir when taken together.
Overdose
Overdose
The described cases of overdose (10.5 g) of the drug Famvir were not accompanied by clinical manifestations.
Treatment: symptomatic and supportive therapy. If recommendations for reducing the dose of famciclovir are not followed, taking into account renal function, cases of acute renal failure have been reported in patients with kidney disease.
Penciclovir is eliminated by hemodialysis. Penciclovir plasma concentrations are reduced by 75% after hemodialysis for 4.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
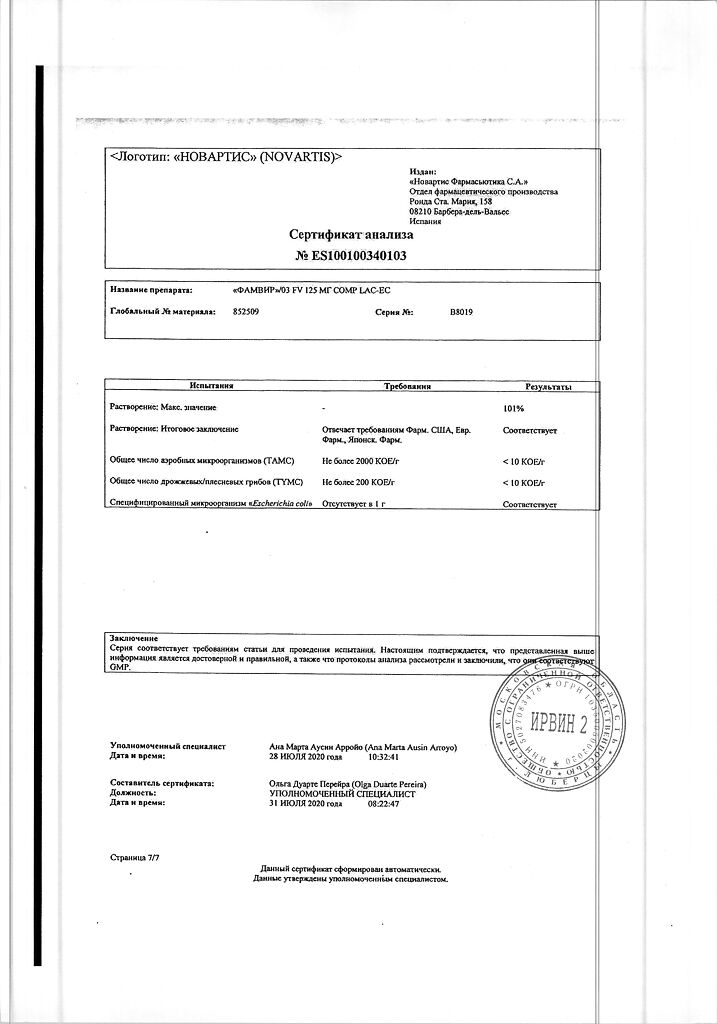
Siegfried Barbera S.L., Spain
Additional information
| Manufacturer | Siegfried Barbera S.L., Spain |
|---|---|
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Siegfried Barbera S.L. |
Related products
Buy Famvir, 125 mg 10 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.