No products in the cart.
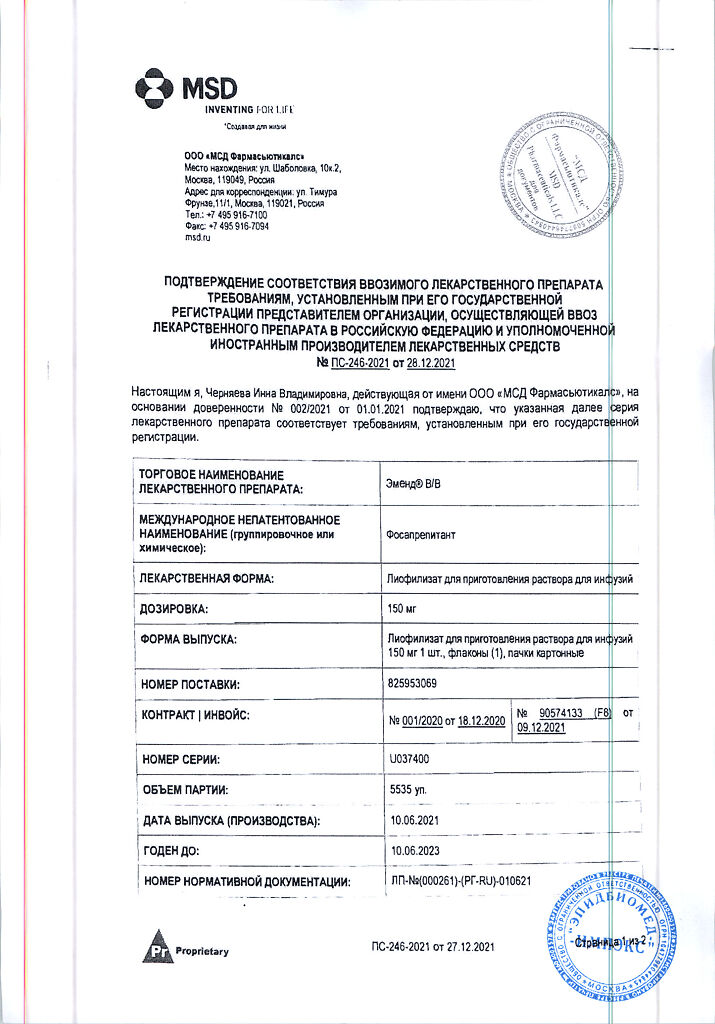
Emend B/V, lyophilizate 150 mg
€1.00
Out of stock
(E-mail when Stock is available)
Description
An antiemetic drug. The active metabolite of fosaprepitant is aprepitant, a selective high-affinity neurokinin 1 (NK1) receptor antagonist of Substance P. Isotopic studies have shown that the selectivity of aprepitant binding to NK1 receptors is at least 3000 times higher than to other enzymes, transport proteins, ion channels and receptors, including dopamine and serotonin receptors, which are targets of existing drugs to prevent nausea and vomiting in chemotherapy.
In preclinical studies, NK1 receptor antagonists have been shown to prevent vomiting caused by chemotherapy drugs such as cisplatin through a central mechanism of action. According to positron emission tomography (PET) studies, aprepitant penetrates the brain and binds to brain NK1 receptors. The central action of aprepitant has a long duration, and it inhibits both the acute and delayed phases of cisplatin-induced vomiting and increases the antiemetic activity of 5-HT3-receptor antagonists (e.g., ondansetron) and GCS (dexamethasone).
In a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of QTc interval, a single administration of fosaprepitant at a dose of 200 mg had no effect on the QTc interval value.
When a single 150 mg dose of fosaprepitant was administered intravenously in healthy volunteers, brain NK1-receptor binding was 100% after 24 h, at least 97% after 48 h, and 75% after 120 h. The proportion of NK1-receptor binding correlated with the plasma concentration of aprepitant.
Indications
Indications
For the prevention of acute and delayed nausea and vomiting caused by highly or moderately emetogenic anticancer drugs (in combination with other anti-emetic drugs).
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Composition
Composition
Active ingredient: 257.6 mg of fosaprepitant dimeglumine, which is equivalent to 157.5 mg of fosaprepitant in 1 vial.
Auxiliary substances: disodium edetate – 19.7 mg, polysorbate 80 – 78.8 mg, anhydrous lactose – 393.8 mg, sodium hydroxide or hydrochloric acid – to pH 9.2 mg.
How to take, the dosage
How to take, the dosage
Emend® B/V (fosaprepitant) is used on day 1 of chemotherapy as an IV infusion lasting 20 to 30 minutes approximately 30 minutes before chemotherapy. Emend® B/V should be used in combination with corticosteroids and 5-NT3 antagonists.
Preparation of Emend® B/V 150 mg infusion solution:
1. The contents of the vial should be dissolved in 5 ml of 0.9% sodium chloride solution (to avoid foaming the solution should be directed along the wall of the vial). The vial should be rotated gently (do not shake!).
2. The resulting solution should be added to the infusion bag or bottle containing 145 ml of 0.9% sodium chloride solution to give a final volume of 150 ml. The contents of the bag or bottle should be mixed gently. The infusion solution should be inspected for sediment or discoloration before administration. The prepared solution should be stored at a temperature of up to 25°C and used within 24 hours.
All parenteral preparations should be carefully inspected prior to use for mechanical inclusions and discoloration whenever the properties of the solution and the container material permit.
Incompatibilities. Phosaprepitant is incompatible with solutions containing divalent cations (e.g., Ca, Mg), including Hartmann’s solution and Ringer’s solution with lactate. The drug Emend® B/B must not be diluted or mixed with solutions with which physical and chemical compatibility has not been proven.
Interaction
Interaction
Drug interactions after administration of fosaprepitant are most likely to occur with drugs that interact with aprepitant. Further information is derived from studies performed with oral aprepitant and studies of combined use of fosaprepitant with dexamethasone, midazolam or diltiazem.
Prepitant is a substrate, mild to moderate inhibitor and inducer of CYP3A4. Aprepitant is also an inducer of CYP2C9. When administered once daily, Emend® B/B 150 mg is a weak CYP3A4 inhibitor and does not induce CYP3A4 induction. It is expected that Emend® B/B 150 mg when administered intravenously will cause less or similar induction of CYP2C9 compared to aprepitant for oral administration.
Influence of fosaprepitant/aprepitant on the pharmacokinetics of other drugs
. Due to the fact that aprepitant is a weak to moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor and fosaprepitant is a weak CYP3A4 inhibitor, concomitant use of drugs whose metabolism occurs with CYP3A4 may increase their plasma concentrations.
Phosaprepitant should not be used concomitantly with pimozide, terfenadine, astemizole or cisapride. Inhibition of CYP3A4 by aprepitant may lead to increased plasma concentrations of these drugs and to potentially serious or life-threatening reactions.
Prepitant has been found to induce the metabolism of S(-) warfarin and tolbutamide, which are metabolized by CYP2C9. Concomitant use of fosaprepitant with these or other drugs that are also metabolized by CYP2C9 (e.g., phenytoin) may lead to lower plasma concentrations of these drugs.
A interaction of fosaprepitant with drugs that are substrates of the P-glycoprotein transporter is unlikely due to the fact that no interaction of aprepitant with digoxin when taken orally has been noted in clinical studies.
Serotonin 5-NT3 receptor antagonists
. In clinical drug interaction studies, it was found that aprepitant at a dose of 125 mg on day 1 and 80 mg on days 2 and 3 did not cause clinically significant changes in the pharmacokinetics of serotonin 5-NT3 receptor antagonists – ondansetron, granisetron and hydrodolasetron (the active metabolite of dolasetron).
Corticosteroids
Dexamethasone: When fosaprepitant at a dose of 150 mg and dexamethasone for oral administration at a dose of 8 mg on days 1, 2, and 3, administration of fosaprepitant on day 1 caused an approximately 2-fold increase in the AUC of dexamethasone on days 1 and 2. The standard dose of dexamethasone (when administered orally) in combination with fosaprepitant 150 mg (IV on day 1) should be reduced by approximately 50% to achieve the same dexamethasone exposure as when administered without fosaprepitant 150 mg IV on day 1.
Methylprednisolone: concomitant administration of oral aprepitant at a dose of 125 mg on day 1 and at a dose of 80 mg/day on days 2 and 3 resulted in a 1.3-fold on day 1 and 2.5-fold on day 3, with intravenous administration of methylprednisolone at a dose of 125 mg on day 1 and with oral administration at a dose of 40 mg on days 2 and 3.
Chemotherapeutic drugs
In clinical trials, chemotherapeutic drugs whose metabolism mainly or partially occurs with the participation of CYP3A4 were administered after oral administration of aprepitant: etoposide, vinorelbine, docetaxel, ifosfamide, cyclophosphamide, irinotecan, and paclitaxel. Doses of these drugs have not been adjusted for potential drug interactions. Caution should be exercised and the patient’s condition should be carefully monitored when using chemotherapeutic drugs whose metabolism mainly or partially occurs with the participation of CYP3A4. In post-registration studies there have been cases of neurotoxicity as a possible side effect of ifosfamide used concomitantly with aprepitant.
Docetaxel: In a separate pharmacokinetics study of oral aprepitant (to prevent chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting) no effect on the pharmacokinetics of docetaxel was noted.
Vinorelbine: In a separate pharmacokinetics study of oral aprepitant (to prevent chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting), no effect on the pharmacokinetics of vinorelbine was noted.
Warfarin
Prepitant was administered to healthy volunteers receiving long-term warfarin therapy at a single oral dose of 125 mg on day 1 and at a dose of 80 mg/day on days 2 and 3. In spite of no effect on AUC of R(+) or S(-) warfarin at day 3 of oral aprepitant administration, there was 34% decrease in minimum concentration of S(-) warfarin (CYP2C9 substrate) accompanied with 14% decrease in prothrombin time (MHO) 5 days after the end of oral aprepitant administration. In patients receiving long-term warfarin therapy, prothrombin time (MHO) should be carefully monitored for 2 weeks with each cycle of chemotherapy and especially 7-10 days after initiation of fosaprepitant.
Tolbutamide
Aprepitant administered orally at a dose of 125 mg on day 1 and 80 mg on days 2 and 3 caused a 23% reduction in the AUC of tolbutamide (a CYP2C9 substrate) on day 4, 28% on day 8 and 15% on day 15, with a single 500 mg dose of tolbutamide administered before starting the three-day oral regimen of aprepitant on both days 4, 8 and 15.
Oral contraceptives
. Concomitant use of aprepitant in 100 mg capsules once daily for 14 days and an oral contraceptive containing 35 µg of ethinylestradiol and 1 mg of norethindrone showed a 43% reduction in AUC of ethinylestradiol and an 8% reduction in AUC of norethindrone. In another study, the use of an oral contraceptive containing ethinylestradiol and norethindrone administered from days 1 through 21 was combined with the use of oral aprepitant at 125 mg on days 8 and 80 mg/day on days 9 and 10, ondansetron at an IV dose of 32 mg on day 8 and oral dexamethasone at 12 mg on day 8 and 8 mg/day on days 9, 10, 11.
In the study, the AUC of ethinylestradiol decreased by 19% on day 10, and there was a 64% decrease in the minimum ethinylestradiol concentration from days 9 to 21. Although oral aprepitant had no effect on the AUC of norethindrone on day 10, there was a 60% decrease in the minimum norethindrone concentration from days 9 to 21. The effectiveness of hormonal contraceptives during use and for 28 days after the end of fosaprepitant administration may be reduced. During treatment with fosaprepitant and for 1 month after the end of fosaprepitant use alternative or additional methods of contraception should be used.
Midazolam
Concomitant administration of fosaprepitant w/v dose of 150 mg and single oral midazolam at a dose of 2 mg on day 1 resulted in approximately 1.8-fold increase in AUC0-âmidazolam. There was no effect on AUC with a similar dosing regimen on day 4. Fosaprepitant for IV administration at a dose of 150 mg is a weak CYP3A4 inhibitor because its use in a single single dose on day 1 resulted in neither inhibition nor induction of CYP3A4, unlike the results obtained on day 4.
Influence of other drugs on the pharmacokinetics of aprepitant
Prepitant is a substrate of CYP3A4, so the simultaneous use of fosaprepitant with drugs that inhibit CYP3A4 activity may lead to increased plasma concentrations of aprepitant.
Hence, caution should be exercised when prescribing fosaprepitant in combination with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole), but concomitant use of aprepitant with moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., diltiazem) does not cause clinically significant changes in plasma aprepitant concentration. Aprepitant is a CYP3A4 substrate, and therefore concomitant use of fosaprepitant with drugs that are strong CYP3A4 inducers (e.g., rifampicin) may lead to a decrease in its plasma concentrations and a decrease in efficacy.
Ketoconazole
. When aprepitant was administered orally once at a dose of 125 mg on day 5 of a 10-day regimen with ketoconazole (400 mg/day), which is a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor, the AUC of aprepitant increased approximately 5-fold and the final T1/2 of aprepitant increased approximately 3-fold. Caution should be exercised when prescribing fosaprepitant in combination with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors.
Rifampicin
. When aprepitant was administered orally once in dose of 375 mg on day 9 of 14-day regimen with rifampicin, which is a strong CYP3A4 inducer, AUC of aprepitant was decreased approximately 11-fold and final T1/2 of aprepitant was decreased approximately 3-fold. Concomitant use of fosaprepitant with drugs that are strong CYP3A4 inducers may lead to decreased plasma concentrations and decreased efficacy.
Additional data on interactions
Diltiazem
. In patients with mild to moderate arterial hypertension, infusion of fosaprepitant at a dose of 100 mg for 15 min in combination with diltiazem at a dose of 120 mg 3 times/day resulted in a 1-fold increase in AUC of aprepitant.5 times and increased AUC of diltiazem 1.4 times. Pharmacokinetic effects resulted in a small but clinically significant decrease in diastolic BP (decrease of 16.8 mm Hg with fosaprepitant and 10.5 mm Hg without fosaprepitant) and a small but clinically significant decrease in systolic BP (decrease of 24.4 mmHg with fosaprepitant and 18.8 mmHg without fosaprepitant), but did not cause clinically significant changes in HR, PR interval compared with changes in these parameters with diltiazem alone.
In the same study, aprepitant was administered once daily as tablets at a dose comparable to 230 mg of the drug in capsules and diltiazem at a dose of 120 mg 3 times daily for 5 days, resulting in a 2-fold increase in the AUC of aprepitant and a simultaneous 1.7-fold increase in the AUC of diltiazem. These pharmacokinetic effects did not result in clinically significant changes in ECG, HR or BP compared with changes in these parameters with diltiazem alone.
Paroxetine
. Concomitant use of aprepitant once daily in tablet form at a dose comparable to 85 mg or 170 mg of the drug in capsules and paroxetine at a dose of 20 mg once daily resulted in a reduction in AUC of approximately 25% and Cmax of approximately 20% for both aprepitant and paroxetine.
Special Instructions
Special Instructions
When using Emend® B/V in combination with other anti-emetic drugs, the instructions for use of these drugs should be followed.
According to the data obtained in clinical trials, the efficacy and safety of aprepitant in elderly patients (â¥65 years) were comparable to those in younger patients (< 65 years). No dose adjustment is required in elderly patients.
Pediatric use
The safety and effectiveness of the drug in children have not been studied.
Influence on ability to drive and operate machinery
There have been no studies about the effect of Emend® B/V on ability to drive and operate machinery. However, some side effects associated with use of Emend® B/V may affect the ability to drive vehicles and perform other activities requiring increased concentration and quick psychomotor reactions.
Contraindications
Contraindications
With caution. Since fosaprepitant is rapidly metabolized to aprepitant (is a weak to moderate inhibitor of CYP3A4 isoenzyme), it should be used with caution in patients concomitantly receiving drugs that are metabolized primarily with the participation of CYP3A4 isoenzyme; some chemotherapy drugs are metabolized with the participation of CYP3A4 isoenzyme. A weak inhibitory effect of phosaprepitant at a dose of 150 mg on CYP3A4 isoenzyme may lead to increased concentrations of these concomitantly administered drugs.
There have been isolated reports of immediate allergic reactions such as redness, erythema, and dyspnea that occurred during infusion of fosaprepitant and usually disappeared after discontinuation of the infusion and appropriate therapy. It is not recommended to resume the infusion of the drug in patients who have had similar allergic reactions.
The concomitant administration of oral fosaprepitant with warfarin may result in a clinically significant decrease in prothrombin time (INR). In patients receiving long-term warfarin therapy, MHO should be monitored closely for 2 weeks, especially 7 to 10 days after initiation of fosaprepitant for each cycle of chemotherapy.
The effectiveness of hormonal contraceptives may decrease during and for 28 days after administration of fosaprepitant. Alternative or complementary methods of contraception should be used during treatment with fosaprepitant and for 1 month after taking fosaprepitant.
Side effects
Side effects
Because phosaprepitant is metabolized to aprepitant, the same adverse reactions as for aprepitant are possible when using the drug.
Aprepitant for oral use
The most common adverse events associated with highly emetheogenic chemotherapy in patients receiving aprepitant on a three-day regimen and observed with a higher frequency than with standard therapy were: hiccups (4.6%), increased ALT activity (2.8%), dyspepsia (2.6%), constipation (2.4%), headache (2%), and decreased appetite (2%). The most common adverse event associated with moderate-emetogenic chemotherapy in patients receiving aprepitant, and noted with a higher frequency than with standard therapy, was fatigue (1.4%).
In a pooled analysis of studies of highly emetogenic and moderately emetogenic chemotherapy, the following drug-related adverse events were observed in patients treated with aprepitant on a three-day regimen, with a greater frequency than with standard therapy.
The frequency was defined as follows: frequently (>1/100, < 1/10), infrequently (â¥1/1000, < 1/100), rarely (â¥1/10,000, < 1/1000).
Infectious and parasitic diseases: Rarely, candidiasis, staphylococcal infection.
Hematopoietic system disorders: infrequent – anemia, febrile neutropenia.
Psychiatric disorders: infrequent – anxiety; rarely – euphoria, disorientation.
Nervous system disorders: infrequent – dizziness, somnolence; rare – cognitive disorders, lethargy, perversion of taste.
An organ of vision: rarely – conjunctivitis.
Hearing organ and labyrinth disorders: rarely – tinnitus.
Cardiovascular system disorders: infrequent – palpitations, hot flashes (hot flashes); rare – bradycardia, cardiovascular disorders.
In the respiratory system:often – hiccups; rarely – sore throat, sneezing, cough, postnasal congestion syndrome, irritation of the pharynx.
From the digestive system:often, dyspepsia; infrequently, belching, nausea, gastroesophageal reflux, vomiting, abdominal pain, dry mouth, flatulence; rarely, hard stools, perforative duodenal ulcer, neutropenic colitis, stomatitis, bloating.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue: infrequent – rash, acne; rarely – photosensitization, increased sweating, seborrhea, increased skin oiliness, itchy rash.
Muscular system disorders: seldom – muscle cramps, muscle weakness.
Since the urinary system: infrequent – dysuria; rarely – pollaciuria.
General disorders and disorders at the site of administration:often, fatigue, decreased appetite; infrequently, weakness, discomfort; rarely, polydipsia, edema, feeling of chest discomfort, gait disturbance.
Laboratory and instrumental data:often – increased ALT activity; infrequently – increased ACT activity, ALP; rarely – increased diuresis, presence of red blood cells in urine, hyponatremia, decreased body weight, glucosuria, decreased neutrophil count.
The profile of adverse events during 6 cycles of chemotherapy in studies of high-emetogenic and moderately emetogenic chemotherapy with aprepitant was comparable to that during the first cycle of chemotherapy.
In another study using aprepitant to prevent chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting, a serious adverse event, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, was reported.
Phosaprepitant for IV
. In a controlled clinical trial in patients receiving highly emetogenic chemotherapy, the safety profiles of Emend® B/B (phosaprepitant) administered on day 1 were comparable to those in studies of oral aprepitant administration on a three-day schedule.
The following are additional, clinically relevant adverse events associated with the 150 mg dose of fosaprepitant that were not observed in the oral aprepitant (3-day regimen) clinical studies described above.
General disorders and disorders together with administration: infrequent – erythema, itching, pain at the site of administration; rarely – thickening at the site of administration.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: infrequent – erythema.
Cardiovascular disorders: infrequently – increased BP, hot flashes (hot flashes), thrombophlebitis (mainly thrombophlebitis at the injection site).
Other studies
A single use of Emend® (aprepitant) at a dose of 40 mg to prevent postoperative nausea and vomiting in patients (not receiving chemotherapy) after general anesthesia has been studied. The following adverse reactions were observed in these studies, the number of which was greater than with the comparison drug (ondansetron): increased ALT activity, upper abdominal pain, atypical bowel noise, dysarthria, dyspnea, hypoesthesia, insomnia, miosis, nausea, sensory disturbances, bowel discomfort, decreased visual acuity, wheezing (wheezing).
There have been reports of 2 serious adverse events when studying the use of aprepitant at higher doses to prevent postoperative nausea and vomiting – 1 case of constipation and 1 case of partial bowel obstruction.
One report of angioedema and urticaria was reported as a serious adverse event in a study of aprepitant not for the prevention of postoperative or chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting.
Data from post-registration studies
In the post-registration period, side effects were reported as follows. Due to the fact that the reports came from volunteers from populations of uncertain size, it is not possible to reliably determine the expected frequency or causal relationship with use of the drug.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue:Itching, rash, urticaria, rarely Stevens-Johnson syndrome.
In immune system disorders:hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylactic reactions.
There have been reports of immediate-type allergic reactions, such as redness, erythema, and dyspnea, that occurred during infusion of fosaprepitant.
Overdose
Overdose
A single injection of up to 200 mg of fosaprepitant v/v or up to 600 mg of aprepitant orally was well tolerated in volunteers. In 3 of 33 volunteers treated with 200 mg of fosaprepitant, mild thrombosis at the injection site was observed.
In studies not involving studies of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting, there was good tolerability of aprepitant when administered at a dose of 375 mg once daily for 42 days. In 33 cancer patients, there was good tolerability of aprepitant when administered once at a dose of 375 mg on day 1 and 250 mg once daily from days 2 through 5.
The occurrence of somnolence and headache was reported in 1 patient who took 1,440 mg of aprepitant.
Treatment:There is no specific information about the management of symptoms of overdose with Emend® B/V; the drug should be discontinued and general supportive therapy and monitoring of the patient should be provided. Due to the antiemetic effect of aprepitant, drugs causing vomiting may be ineffective. Hemodialysis is ineffective in aprepitant overdose.
Pregnancy use
Pregnancy use
An adequate and strictly controlled clinical study on the use of the drug in pregnant and lactating women has not been conducted. Administration of the drug in pregnancy is possible only when the estimated benefit to the mother outweighs the potential risk to the fetus.
There are no data on excretion of the drug with the breast milk. Due to the fact that many of the drugs are excreted with the breast milk and due to the risk of adverse effects on the breastfed child, the decision to stop breastfeeding or to discontinue the drug should be made taking into account the necessity of the drug for the mother.
Additional information
| Weight | 0.023 kg |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Pateon Manufacturing Services LLC, USA |
| Medication form | lyophilizate |
| Brand | Pateon Manufacturing Services LLC |
Related products
Buy Emend B/V, lyophilizate 150 mg with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.