No products in the cart.
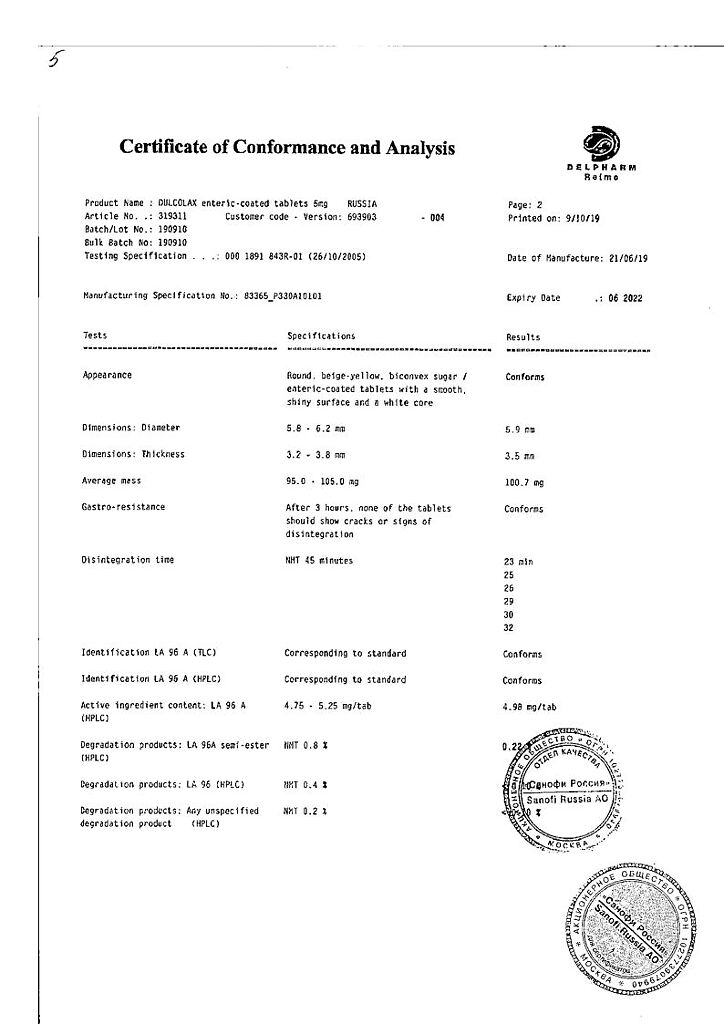
Dulcolax, 5 mg 30 pcs.
€6.72 €5.00
Description
Pharmacodynamics
Laxative drug, derivative of diphenylmethane. As a local laxative with antiresorptive effect, after hydrolysis in the colon, bisacodyl increases secretion of water and electrolytes in the colon and accelerates and increases its peristalsis. This leads to stimulation of the act of defecation, reduction of evacuation time and softening of stools.
The time of development of the laxative effect of the drug is 6-12 hours.
Bisacodyl being a laxative acting at the level of the large intestine, stimulates the natural process of evacuation in the lower parts of the gastrointestinal tract. Therefore, bisacodyl has no effect on digestion or absorption of caloric foods or essential nutrients in the small intestine.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption and distribution
Absorption is slight. The enteric-coated tablets are resistant to the action of gastrointestinal juice. Bisacodyl is released in the colon to form the active metabolite, bis-(p-hydroxyphenyl)-pyridyl-2-methane, which has an irritant effect on the colon mucosa.
The Cmax of active metabolite in plasma after drug administration is reached after 4-10 hours, the laxative effect develops after 6-12 hours. There is no correlation between the laxative effect of Bisacodyl and the concentration of active metabolite in plasma.
Metabolism and excretion
The drug is almost completely metabolized in the intestinal wall and liver to inactive glucuronide. Metabolism occurs under the influence of mucosal enzymes of the large intestine.
The T1/2 is about 16.5 hours. Excretion of active metabolite occurs mainly in the feces (up to 51.8%), about 10.5% is excreted in the urine.
Indications
Indications
As a laxative in the following cases:
constipation caused by hypotension of the colon (including chronic);
preoperative preparation, postoperative treatment;
preparation for instrumental and x-ray examinations;
medical conditions requiring relief of bowel movements.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacodynamics
Laxative drug, diphenylmethane derivative. As a local laxative with an antiresorptive effect, bisacodyl, after hydrolysis in the colon, increases the secretion of water and electrolytes in the colon, accelerates and increases its peristalsis. This leads to stimulation of the act of defecation, reduction of evacuation time and softening of the stool.
The development time of the laxative effect of the drug is 6-12 hours.
Bisacodyl, being a laxative acting at the level of the colon, stimulates the natural process of evacuation in the lower gastrointestinal tract. Therefore, bisacodyl does not affect the digestion or absorption of high-calorie foods or essential nutrients in the small intestine.
Pharmacokinetics
Suction and distribution
Absorption is negligible. Enteric-coated tablets are resistant to gastrointestinal juice. Bisacodyl is released in the colon to form an active metabolite, bis-(p-hydroxyphenyl)-pyridyl-2-methane, which is an irritant to the colonic mucosa.
The Cmax of the active metabolite in plasma after taking the drug is achieved after 4-10 hours, the laxative effect develops after 6-12 hours. There is no relationship between the laxative effect of bisacodyl and the concentration of the active metabolite in plasma.
Metabolism and excretion
The drug is almost completely metabolized in the intestinal wall and liver to an inactive glucuronide. Metabolism occurs under the action of enzymes in the mucous membrane of the large intestine.
T1/2 is about 16.5 hours. Excretion of the active metabolite occurs mainly in feces (up to 51.8%), about 10.5% is excreted in urine.
Special instructions
Special instructions
The drug, like all laxatives, should not be used regularly or for a long period of time without identifying the cause of constipation. Long-term use of high doses of the drug can lead to fluid loss, electrolyte imbalance, and hypokalemia.
Loss of fluid through the intestines can lead to dehydration, which may be accompanied by symptoms such as thirst and oliguria. Dehydration can harm the body (for example, in case of kidney failure, in elderly patients), therefore, if the above symptoms occur, the drug should be stopped and can only be restarted under medical supervision.
Patients may experience a small amount of blood in their stool. This manifestation is usually mild and goes away on its own.
Dizziness and/or fainting have been observed in patients taking Dulcolax®. The analysis showed that these cases were associated with syncope with defecation (or syncope caused by straining to defecate) or with a vasovagal response to abdominal pain, which could be due to constipation and not necessarily related to the drug.
1 tablet (5 mg) corresponds to 0.006 XE.
Children should take the drug after consulting a doctor.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and other mechanisms that require increased concentration of attention
No special clinical studies have been conducted on the effect of the drug on the ability to drive a car or use machinery. However, patients should be advised that they may experience dizziness and/or fainting due to a vasovagal reaction (i.e. during bowel spasm). If patients experience intestinal spasms, they should avoid potentially hazardous activities, incl. driving vehicles or operating machinery.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Bisacodyl
Composition
Composition
Active ingredients:
bisacodyl 5 mg.
Excipients:
corn starch – 8.3 mg,
glycerol 85% – 0.2 mg,
soluble corn starch – 1.5 mg,
lactose – 34.9 mg,
magnesium stearate – 0.1 mg.
Composition of the enteric coating:
sucrose – 23.3819 mg, talc – 16.1608 mg, acacia gum – 1.9354 mg, titanium dioxide – 0.3995 mg, copolymer of methacrylic acid and methyl methacrylate (1:2) (Eudragit S100) – 2.2147 mg, copolymer of methacrylic acid and methyl methacrylate (1:1) (Eudragit L100) – 0.9866 mg, castor seed oil (castor oil) – 0.9762 mg, magnesium stearate – 3.8225 mg, macrogol (polyethylene glycol) 6000 – 0.0462 mg, iron dye yellow oxide (E172) – 0.0657 mg, white beeswax – 0.0015 mg, carnauba wax – 0.003 mg, shellac – 0.006 mg.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
During long-term experience with the use of the drug, no adverse events were identified during pregnancy. However, due to the lack of research, the use of Dulcolax® during pregnancy is recommended only in cases where the potential benefit to the mother outweighs the possible risk to the fetus.
Bisacodyl is not excreted in breast milk.
During pregnancy and breastfeeding, the drug can be used only after consultation with a specialist.
Clinical studies of the drug’s effect on fertility have not been conducted.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to bisacodyl or excipients;
intestinal obstruction;
obstructive bowel diseases;
acute diseases of the abdominal organs, including appendicitis;
acute inflammatory bowel diseases;
severe abdominal pain associated with nausea and vomiting, which may be a symptom of a more serious condition;
severe dehydration;
children under 4 years of age;
One tablet (5 mg) contains 33.2 mg of lactose. The maximum recommended daily dose of tablets for adults and children over 10 years of age for the treatment of constipation and for radiographic examination contains 66.4 mg and 132.8 mg of lactose, respectively. Patients with rare hereditary galactose intolerance, such as galactosemia, should not take the drug;
one tablet (5 mg) contains 23.4 mg of sucrose. The maximum recommended daily dose of tablets for adults and children over 10 years of age for the treatment of constipation and for radiographic examination contains 46.8 mg and 93.6 mg of sucrose, respectively. Patients with rare hereditary fructose intolerance should not take the drug.
With caution: the drug should be prescribed to patients with hepatic and/or renal insufficiency.
Side Effects
Side Effects
The most commonly reported adverse reactions during use of the drug are abdominal cramps and diarrhea.
From the digestive system: cramping pain or discomfort in the abdomen, diarrhea (dehydration, muscle weakness, cramps, decreased blood pressure), nausea, vomiting, a small amount of blood in the stool, anorectal discomfort, colitis.
From the nervous system: dizziness, fainting. These side effects that occur after using the drug are associated with a vasovagal reaction (i.e. due to intestinal spasm, straining during bowel movements).
From the immune system: hypersensitivity, angioedema, anaphylactic reactions.
Interaction
Interaction
Simultaneous use of Dulcolax in high doses and diuretics or corticosteroids increases the risk of electrolyte imbalance (hypokalemia).
Electrolyte imbalance (hypokalemia) enhances the effect of cardiac glycosides.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: in case of acute overdose, diarrhea, dehydration, decreased blood pressure, water-electrolyte imbalance, hypokalemia, convulsions are possible.
Symptoms: in case of chronic overdose – chronic diarrhea, abdominal pain, hypokalemia, hyperaldosteronism, urolithiasis. Due to chronic laxative abuse, renal tubular damage, metabolic alkalosis, and muscle weakness associated with hypokalemia may develop.
Treatment: should be symptomatic. There is no specific antidote. To reduce the absorption of the drug after oral administration, you can induce vomiting or perform gastric lavage. Fluid replacement and correction of electrolyte balance may be required, as well as antispasmodics.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
In a dry place, at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C
Shelf life
Shelf life
5 years
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Delpharm Reims, France
Additional information
| Shelf life | 5 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | In a dry place, at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C |
| Manufacturer | Delpharm Reims, France |
| Medication form | enteric-soluble film-coated tablets |
| Brand | Delpharm Reims |
Related products
Buy Dulcolax, 5 mg 30 pcs. with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.