No products in the cart.
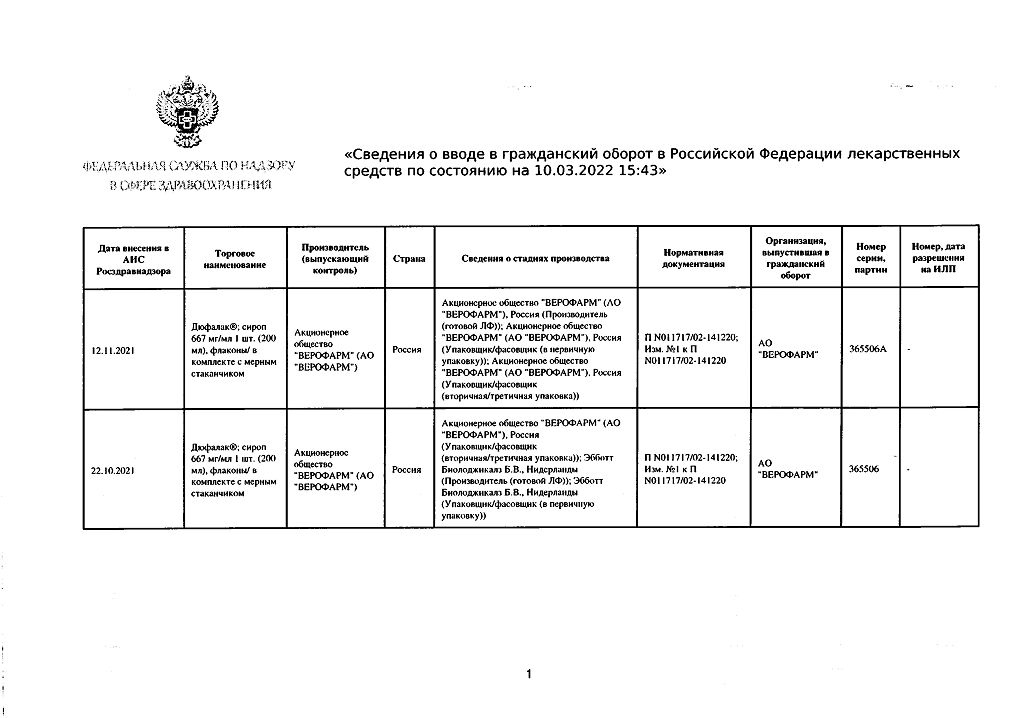
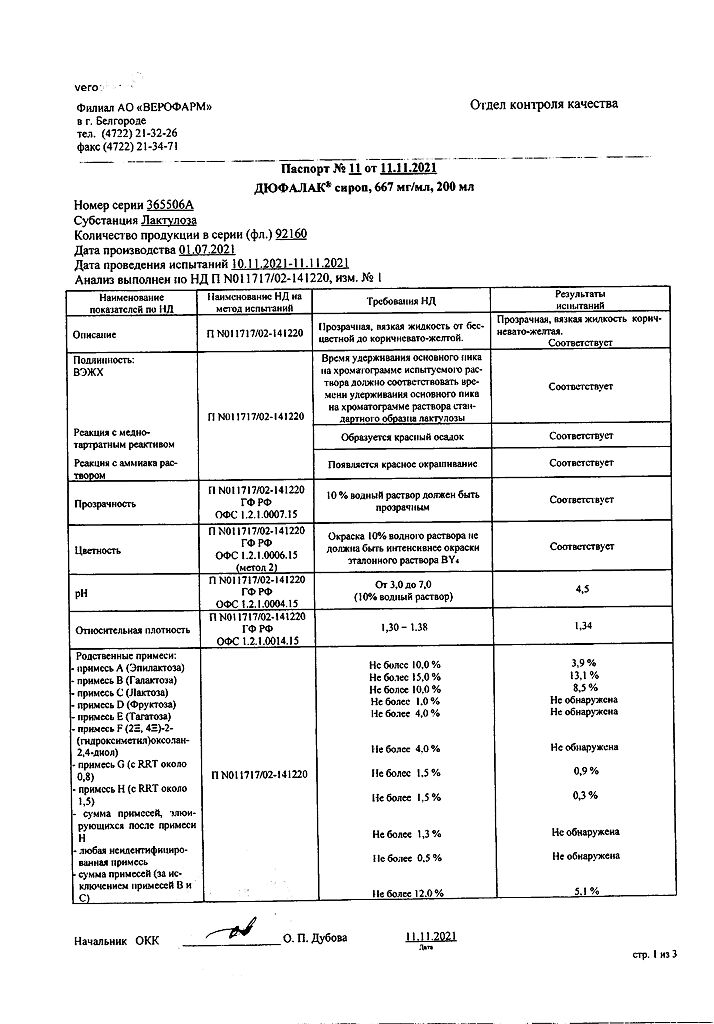
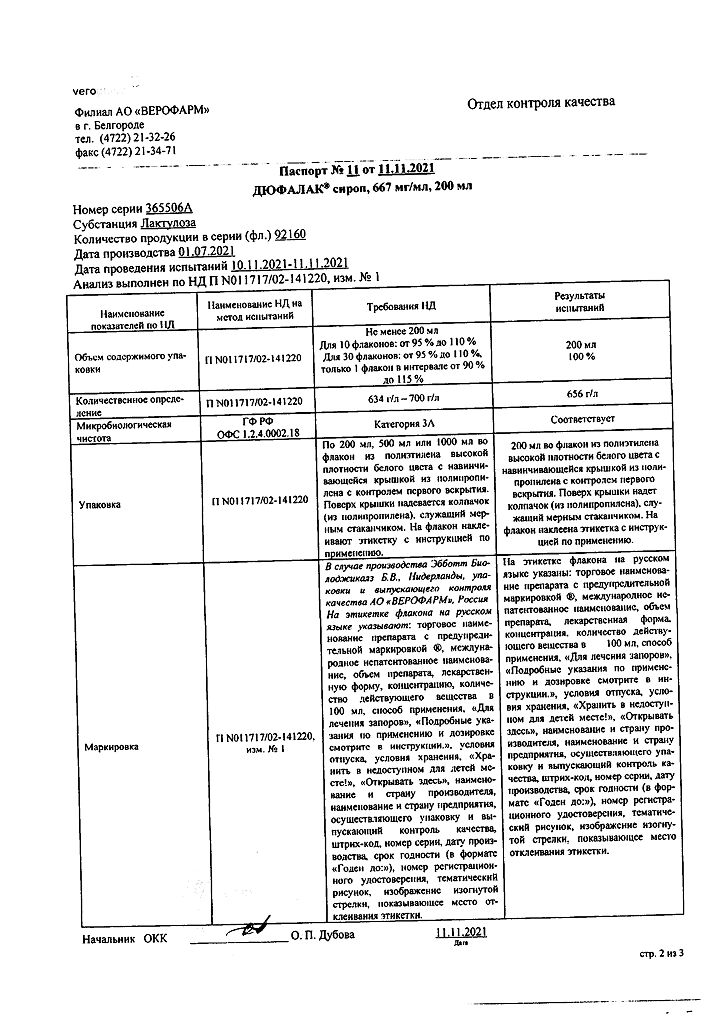
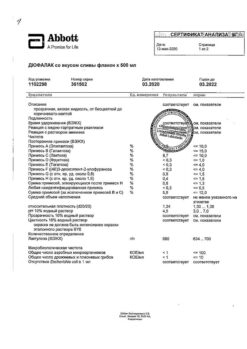
Dufalac, 667 mg/ml syrup 200 ml
€9.83 €8.00
Out of stock
(E-mail when Stock is available)
Description
Pharmacodynamics
Laxative drug. It has hyperosmotic laxative effect, stimulates intestinal peristalsis, improves absorption of phosphates and calcium salts, promotes excretion of ammonium ions.
Lactulose is broken down by the intestinal flora of the large intestine into low-molecular organic acids, which lead to a decrease in pH and an increase in osmotic pressure and as a consequence an increase in the volume of intestinal content. These effects stimulate intestinal peristalsis and influence the consistency of the stool. As a result, the physiological rhythm of emptying the large intestine is restored.
. In hepatic encephalopathy, the effect is attributed to suppression of proteolytic bacteria by increasing the number of acidophilic bacteria (such as lactobacilli), conversion of ammonia into an ionic form by acidifying the contents of the colon, emptying the intestine by reducing the pH in the colon and osmotic effect, and reducing nitrogenous toxic substances by stimulating bacteria that utilize ammonia for bacterial protein synthesis.
Lactulose as a prebiotic substance enhances the growth of beneficial bacteria such as bifidobacteria and lactobacilli, while suppressing the growth of potentially pathogenic bacteria such as Clostridium spp. and Escherichia coli, resulting in a more favorable balance of intestinal flora.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption is low. After oral administration it reaches the large intestine unchanged, where it is broken down by the intestinal flora.
It is completely metabolized when administered in doses up to 45-70 ml. When administered in higher doses it is partially excreted unchanged.
Indications
Indications
Constipation: regulation of the physiological rhythm of colon emptying.
Softening of stool for medical purposes (hemorrhoids, conditions after surgery on the colon and anus).
Hepatic encephalopathy: treatment and prevention of hepatic coma or precoma (in adults).
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacodynamics
Laxative drug. It has a hyperosmotic laxative effect, stimulates intestinal motility, improves the absorption of phosphates and calcium salts, and promotes the excretion of ammonium ions.
Lactulose is broken down by the intestinal flora of the colon into low molecular weight organic acids, which leads to a decrease in pH and an increase in osmotic pressure and, as a result, an increase in the volume of intestinal contents. These effects stimulate intestinal motility and affect stool consistency. As a result, the physiological rhythm of colon emptying is restored.
In hepatic encephalopathy, the effect is attributed to suppression of proteolytic bacteria by increasing the number of acidophilic bacteria (eg, lactobacilli), conversion of ammonia to ionic form by acidification of colon contents, bowel emptying due to decreased colonic pH and osmotic effects, and reduction of nitrogen-containing toxic substances by stimulation of bacteria that utilize ammonia for bacterial protein synthesis.
Lactulose as a prebiotic substance enhances the growth of beneficial bacteria such as bifidobacteria and lactobacilli, while inhibiting the growth of potentially pathogenic bacteria such as Clostridium spp. and Escherichia coli, which provides a more favorable balance of intestinal flora.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption is low. After ingestion, it reaches the large intestine unchanged, where it is broken down by intestinal flora.
Completely metabolized when used in doses of up to 45-70 ml. When used in higher doses, it is partially excreted unchanged.
Special instructions
Special instructions
If abdominal pain of unknown origin occurs before starting therapy or there is no therapeutic effect for several days, the patient should consult a doctor.
Please note that Duphalac® may contain small amounts of bound sugars (for example, lactose, galactose, epilactose and fructose).
The content of residual sugars present in Duphalac® is about 0.075 XE per 5 ml of syrup.
When used at the dose recommended for the treatment of constipation, the sugar content should not pose a problem for patients with diabetes. When treating hepatic encephalopathy, higher doses of the drug are usually prescribed, which should be taken into account in patients with diabetes mellitus.
Long-term use in doses exceeding those recommended in the instructions, or improper use, can lead to diarrhea and water-electrolyte imbalance.
When treating children, laxatives should be used in exceptional cases and under medical supervision. It must be taken into account that during treatment, disorders of the emptying reflex may occur.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and other mechanisms that require increased concentration
The use of the drug Duphalac® does not affect or has an insignificant effect on the ability to drive a car or operate machines and mechanisms.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Lactulose
Composition
Composition
Active ingredients:
lactulose 66.7 g.
Excipients:
purified water
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
No effect on the fetus or nursing infant is expected because Systemic exposure to lactulose in a pregnant or lactating woman is negligible.
Duphalac® can be prescribed during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
No effect on reproductive function is expected, because Systemic exposure to lactulose is negligible.
Contraindications
Contraindications
galactosemia;
obstruction, perforation or risk of perforation of the gastrointestinal tract;
hypersensitivity to any component of the drug;
galactose or fructose intolerance, lactase deficiency or glucose-galactose malabsorption.
With caution
undiagnosed rectal bleeding;
colostomy, ileostomy.
Side Effects
Side Effects
In the first days of taking lactulose, flatulence may occur. As a rule, it disappears after a few days.
If high doses are used for a long time in the treatment of hepatic encephalopathy, the patient may develop water and electrolyte imbalance due to diarrhea.
During placebo-controlled clinical studies in patients receiving lactulose, the following adverse effects were observed with the following frequencies: [very common (≥1/10); often (from ≥1/100 to <1/10); uncommon (from ≥1/1000 to <1/100); rare (≥1/10,000 to <1/1000); very rare (< 1/10,000)], or they were reported spontaneously during post-marketing use of the drug [unknown frequency (precise frequency cannot be determined from available data)].
Immune system
Frequency unknown: hypersensitivity.
Gastrointestinal tract
Very common: diarrhea.
Common: flatulence, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting.
Skin and subcutaneous fat
Frequency unknown: rash, pruritus, urticaria, erythema.
Laboratory and instrumental data
Uncommon: water and electrolyte imbalance due to diarrhea.
When used in children, a similar safety profile is expected compared to that in adults.
Interaction
Interaction
Interaction studies with other drugs have not been conducted.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: when taking the drug in a very high dose, abdominal pain and diarrhea are possible.
Treatment: stop taking the drug or reduce the dose.
In case of large fluid loss due to diarrhea or vomiting, correction of water and electrolyte imbalance may be required.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
Store at a temperature not exceeding 25°C.
Keep out of the reach of children!
Shelf life
Shelf life
3 years.
Do not use after the expiration date indicated on the package.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Abbott Biologicals B.V., The Netherlands
Additional information
| Shelf life | 3 years. Do not use after the expiration date stated on the package. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | Store at a temperature not exceeding 25 ° C. Keep out of reach of children! |
| Manufacturer | Abbott Biologicals B.V., The Netherlands |
| Medication form | syrup |
| Brand | Abbott Biologicals B.V. |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Dufalac, 667 mg/ml syrup 200 ml with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.