No products in the cart.
Dopamine, 40 mg/ml concentrate 5 ml 10 pcs
€1.00
Out of stock
(E-mail when Stock is available)
Description Cardiotonic drug of non-glycoside structure Pharmacodynamics: Pharmacokinetics:
ATX: C.01.C.A.04 Dopamine
Dopamine is a catecholamine identical to the human body’s natural neurotransmitter, dopamine, and is also a precursor of noradrenaline.
It excites beta-adrenoceptors (in low and medium doses) and alpha-adrenoceptors (in high doses). Improvement of systemic hemodynamics leads to a diuretic effect. It has a specific stimulatory effect on postsynaptic dopamine receptors in vascular smooth muscle and the kidneys.
In low doses (0.5-3 µg/kg/min), it acts predominantly on dopamine receptors, causing dilation of renal, mesenteric, coronary and cerebral vessels. Renal vasodilation results in increased renal blood flow, increased glomerular filtration rate, increased diuresis, and excretion of sodium ions. The action on the renal and mesenteric vessels differs from that of other catecholamines.
In low to medium doses (2-10 µg/kg/min), it stimulates postsynaptic beta1-adrenoreceptors, which causes a positive inotropic effect and an increase in the minute volume of blood circulation. Systolic blood pressure and pulse pressure may increase; diastolic blood pressure is unchanged or slightly increased. Total peripheral vascular resistance (TPR) usually does not change. Coronary blood flow and myocardial oxygen consumption tend to increase.
In high doses (10 µg/kg/min or more), alpha1-adrenoreceptor stimulation predominates, causing increased RPS, heart rate, and renal vasoconstriction (the latter may reduce previously increased renal blood flow and diuresis). Both systolic and diastolic blood pressure increase as a consequence of the increase in the minute volume of blood circulation and RPS.
The onset of therapeutic effect is within 5 min against the background of intravenous administration and lasts for 10 min.
Strictly controlled studies of dopamine in children under 18 years of age have not been conducted.
Intravenous only.
About 25% of the dose is taken up by neurosecretory vesicles, where hydroxylation occurs and norepinephrine is formed. It is widely distributed in the body and partially passes through the blood-brain barrier. The apparent volume of distribution is 0.89 l/kg. Binding with blood plasma proteins is 50%.
It is quickly metabolized in liver, kidneys and plasma by monoamine oxidase (MAO) and catechol-O-methyltransferase to inactive metabolites – homovanilic acid and 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetate.
Half-life of dopamine: adults, from blood plasma – 2 min, from tissues – 9 min. Dopamine clearance is 4.4 l/kg/h. Excreted by the kidneys: 80% of the dose – as metabolites within 24 hours, minor amounts (less than 10%) – unchanged.
.
Indications
Indications
– Shock of various origins: cardiogenic, postoperative, infectious-toxic, anaphylactic, hypovolemic (only after restoration of circulating blood volume);
– acute cardiovascular failure, “low minute volume” syndrome in cardiac surgery patients;
– acute arterial hypotension.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Cardiotonic drug of non-glycoside structure
ATX: C.01.C.A.04 Dopamine
Pharmacodynamics:
Dopamine is a catecholamine, identical to the natural neurotransmitter of the human body, dopamine, and is also a precursor of norepinephrine.
Stimulates beta-adrenergic receptors (in low and medium doses) and alpha-adrenergic receptors (in high doses). Improving systemic hemodynamics leads to a diuretic effect. It has a specific stimulating effect on postsynaptic dopamine receptors in vascular smooth muscle and kidneys.
In low doses (0.5-3 mcg/kg/min) it acts predominantly on dopamine receptors, causing dilation of the renal, mesenteric, coronary and cerebral vessels. Dilatation of renal vessels leads to increased renal blood flow, increased glomerular filtration rate, increased diuresis and excretion of sodium ions. The effect on the renal and mesenteric vessels differs from the effect of other catecholamines.
In low and medium doses (2-10 mcg/kg/min) it stimulates postsynaptic beta1-adrenergic receptors, which causes a positive inotropic effect and an increase in minute volume of blood circulation. Systolic blood pressure and pulse pressure may increase; at the same time, diastolic blood pressure does not change or increases slightly. Total peripheral vascular resistance (TPVR) usually does not change. Coronary blood flow and myocardial oxygen consumption tend to increase.
At high doses (10 mcg/kg/min or more), alpha1-adrenergic receptor stimulation predominates, causing an increase in peripheral vascular resistance, heart rate, and renal vasoconstriction (the latter may reduce previously increased renal blood flow and diuresis). Due to an increase in minute volume of blood circulation and peripheral vascular resistance, both systolic and diastolic blood pressure increases.
The onset of the therapeutic effect is within 5 minutes during intravenous administration and continues for 10 minutes.
There have been no strictly controlled studies of dopamine in children under 18 years of age.
Pharmacokinetics:
It is administered intravenously only.
About 25% of the dose is captured by neurosecretory vesicles, where hydroxylation occurs and norepinephrine is formed. Widely distributed in the body, partially passes through the blood-brain barrier. The apparent volume of distribution is 0.89 l/kg. Communication with blood plasma proteins – 50%.
Rapidly metabolized in the liver, kidneys and plasma by monoamine oxidase (MAO) and catechol-O-methyltransferase to inactive metabolites – homovanillic acid and 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetate.
Half-life of dopamine: adults, from blood plasma – 2 minutes, from tissues – 9 minutes. Dopamine clearance is 4.4 l/kg/h. Excreted by the kidneys: 80% of the dose – in the form of metabolites within 24 hours, in small quantities (less than 10%) – unchanged.
Special instructions
Special instructions
Dopamine is intended for intravenous infusion only and can only be used in diluted form!
Dopamine improves atrioventricular conduction, so patients with atrial fibrillation should be given cardiac glycosides before using the drug; hypoxia, hypercapnia and acidosis reduce the effectiveness of dopamine, increasing the likelihood of side effects.
Before administration to patients in shock, hypovolemia should be corrected by administering plasma and other blood substitute fluids.
The infusion should be carried out under the control of diuresis and minute blood volume; blood pressure, ECG, heart rate. A decrease in urine output without a concomitant decrease in blood pressure indicates the need to reduce the dose of dopamine.
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors, increasing the pressor effect of sympathomimetics, can cause headache, arrhythmia, vomiting and other manifestations of hypertensive crisis, therefore, in patients who have received monoamine oxidase inhibitors over the past 2-3 weeks, the initial doses of dopamine should be no more than 10% of the usual dose.
To reduce the risk of extravasation, the drug should be administered into large veins whenever possible. To prevent tissue necrosis in case of extravasal ingestion of the drug, infiltrate with 10-15 ml of 0.9% sodium chloride solution with 5-10 mg of phentolamine.
The use of the drug against the background of obliterating diseases of peripheral vessels and/or a history of disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome can cause a sharp and pronounced vasoconstriction, leading to skin necrosis and gangrene (careful monitoring should be carried out, and if signs of peripheral ischemia are detected, the drug should be stopped immediately).
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles. Wed and fur.:
Dopamine is a drug for use in hospital settings with a very short half-life. After discharge from the hospital, there is no possibility of the drug influencing the reaction rate when driving or operating other mechanisms.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Dopamine
Composition
Composition
Active ingredient:
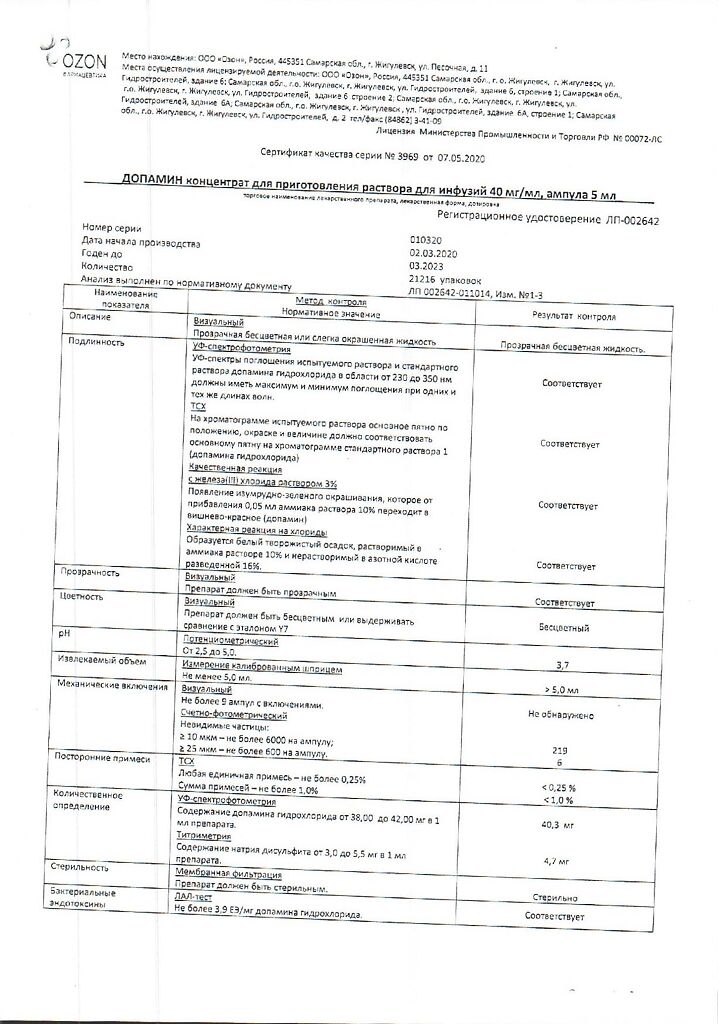
dopamine hydrochloride 40 mg;
Excipients:
disodium edetate 0.25 mg,
yatria metabisulfite 10 mg,
water for injections up to 1 ml.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
During pregnancy, Dopamine should be used only if the expected benefit to the mother outweighs the potential risk to the fetus (the experiment revealed an adverse effect on the fetus). There is insufficient clinical data on the use of the drug in pregnant women. Preclinical studies have demonstrated reproductive toxicity of dopamine.
It is unknown whether dopamine passes into breast milk. If it is necessary to use the drug Dopamine during lactation, breastfeeding should be stopped.
Contraindications
Contraindications
– Hypersensitivity to the components of the drug, incl. to sulfites;
– hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy;
– pheochromocytoma;
– thyrotoxicosis;
– tachyarrhythmia;
– fibrillation of the ventricles of the heart.
– angle-closure glaucoma;
– simultaneous use of cyclopropane and hydrocarbon derivatives for inhalation anesthesia, ergot alkaloids.
– age under 18 years (efficacy and safety have not been established).
With caution:
Hypovolemia, myocardial infarction, cardiac rhythm disturbances (ventricular arrhythmias, atrial fibrillation), severe stenosis of the aortic mouth, metabolic acidosis, hypercapnia, hypoxia, arterial hypotension in the pulmonary circulation, obliterating vascular diseases (including atherosclerosis, thromboembolism, thromboangiitis obliterans, thromboangiitis obliterans endarteritis, diabetic endarteritis, Raynaud’s disease, frostbite), diabetes mellitus, pregnancy, breastfeeding period.
Side Effects
Side Effects
From the cardiovascular system: tachycardia or bradycardia, palpitations, chest pain, angina pectoris, increased or decreased blood pressure, conduction disturbances, expansion of the QRS complex; vasospasm, increased end-diastolic pressure in the left ventricle; when used in high doses – ventricular or supraventricular arrhythmia.
From the digestive tract: nausea, vomiting, bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract.
From the central and peripheral nervous system: headache; anxiety, motor restlessness, tremor of fingers.
Allergic reactions: severe hypersensitivity reactions and bronchospasm (due to the presence of sulfites in the drug), shock.
Local reactions: if dopamine gets under the skin, necrosis of the skin and subcutaneous tissue may occur, and gangrene may develop.
Other: shortness of breath, azotemia, piloerection, polyuria (when administered in low doses).
Interaction
Interaction
The sympathomimetic effect is enhanced by adrenergic stimulants, monoamine oxidase inhibitors (including furazolidone, procarbazine, selegiline), guanethidine (increased duration and enhanced cardiac stimulating and pressor effects).
Dopamine may potentiate the effect of diuretics.
The cardiotonic effect of dopamine is enhanced by inhaled drugs for general anesthesia, hydrocarbon derivatives such as cyclopropane, chloroform, enflurane, halothane, isoflurane, methoxyflurane (increased risk of severe atrial or ventricular arrhythmias), tricyclic antidepressants, including maprotiline (risk of developing cardiac arrhythmias, severe arterial hypertension or hyperpyrexia), cocaine, other sympathomimetics; weaken – butyrophenones and beta-blockers (propranolol).
Dopamine weakens the antihypertensive effect of guanadrel, guanethyline, mekanilamine, methyldopa, rauwolfia alkaloids (the latter prolong the effect of dopamine).
When used simultaneously with levodopa, there is an increased risk of developing arrhythmias; with thyroid hormones – it is possible to enhance the effect of both dopamine and thyroid hormones.
Ergometrine, ergotamine, methylergometrine, oxytocin increase the vasoconstrictor effect and the risk of ischemia and gangrene, as well as severe arterial hypertension, including intracranial hemorrhage.
Phenytoin may contribute to the development of arterial hypotension and bradycardia (depending on the dose and rate of administration); ergot alkaloids – narrowing of blood vessels and the development of gangrene.
With cardiac glycosides, an increased risk of arrhythmias and an additive inotropic effect are possible (ECG monitoring is required).
Reduces the antianginal effect of nitrates, which in turn can reduce the pressor effect of sympathomimetics and increase the risk of arterial hypotension (simultaneous use is allowed depending on the achievement of a therapeutic effect).
Pharmaceutical incompatibility
Incompatible with acyclovir, alteplase, amikacin, amphotericin B, ampicillin, cephalothin, dacarbazine citrate, theophylline ethylenedamide (aminophylline), theophylline calcium (aminophylline calcium), furosemide, gentamicin, sodium heparin, sodium nitroprusside, benzylpenicillin, tobramycin, alkaline solutions, oxidizing agents, iron salts, thiamine (promotes its destruction).
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: excessive increase in blood pressure, spasm of peripheral arteries, arrhythmia, tachycardia, ventricular extrasystole, angina pectoris, dyspnea, headache, psychomotor agitation.
Treatment: due to the rapid elimination of dopamine from the body, these phenomena are stopped by reducing the dose or stopping the administration; if ineffective, short-acting alpha-blockers (for excessive increases in blood pressure) and beta-blockers (for rhythm disturbances).
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
In a place protected from light, at a temperature not exceeding 25 ° C. Do not freeze.
Keep out of the reach of children.
Shelf life
Shelf life
3 years.
Do not use after expiration date.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Ozon, Russia
Additional information
| Shelf life | 3 years. Do not use after the expiration date. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | In protected from light, at a temperature not exceeding 25 ° C. Do not freeze. Store out of the reach of children. |
| Manufacturer | Ozon, Russia |
| Medication form | concentrate for preparation of infusion solution |
| Brand | Ozon |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Dopamine, 40 mg/ml concentrate 5 ml 10 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.