No products in the cart.
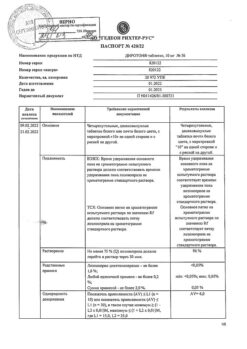
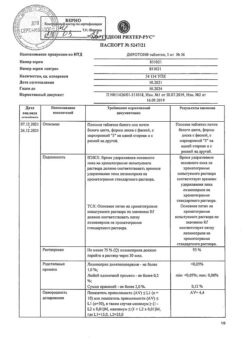
Diroton, tablets 20 mg 56 pcs
€16.51 €13.76
Description
Diroton tablets are an ACE inhibitor.
It reduces the formation of angiotensin II from angiotensin I. Reducing angiotensin II leads to a direct reduction in the release of aldosterone . Reduces bradykinin degradation and increases prostaglandin synthesis.
Recreases RPS, BP, preload, pulmonary capillary pressure, causes an increase in the minute blood volume and increases myocardial tolerance to exercise in patients with chronic heart failure. Dilates arteries to a greater extent than veins. Some effects are explained by the effect on tissue renin-angiotensin systems . Long-term use reduces myocardial hypertrophy and resistive arterial wall hypertrophy. It improves the blood supply to the ischemic myocardium.
The ACE inhibitors prolong life expectancy in patients with chronic heart failure and slow the progression of left ventricular dysfunction in patients who have had myocardial infarction without clinical manifestations of heart failure.
The onset of action of the drug is in 1 hour, reaches a maximum in 6-7 hours and lasts for 24 hours. The duration of the effect also depends on the dose taken. In case of arterial hypertension, the effect is noted in the first days after the start of treatment, the stable effect develops after 1-2 months. When the drug is abruptly withdrawn, no pronounced increase in BP was observed.
Diroton reduces albuminuria. In patients with hyperglycemia it normalizes the function of the damaged glomerular endothelium. It does not affect the blood glucose concentration in patients with diabetes mellitus and does not lead to increased incidence of hypoglycemia.
Indications
Indications
– Arterial hypertension (as monotherapy or in combination with other antihypertensive drugs).
– Chronic heart failure (as part of combination therapy for the treatment of patients taking digitalis and/or diuretics).
– Acute myocardial infarction (in the first 24 hours with stable hemodynamic parameters to maintain these parameters and prevent left ventricular dysfunction and heart failure).
– Diabetic nephropathy (to reduce albuminuria in patients with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus with normal blood pressure and in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus with arterial hypertension).
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Diroton tablets are an ACE inhibitor.
Reduces the formation of angiotensin II from angiotensin I. A decrease in the content of angiotensin II leads to a direct decrease in the release of aldosterone. Reduces the degradation of bradykinin and increases the synthesis of prostaglandins.
Reduces peripheral vascular resistance, blood pressure, preload, pressure in the pulmonary capillaries, causes an increase in minute blood volume and an increase in myocardial tolerance to stress in patients with chronic heart failure. Dilates arteries more than veins. Some effects have been attributed to effects on tissue renin-angiotensin systems. With long-term use, hypertrophy of the myocardium and the walls of resistive arteries decreases. Improves blood supply to ischemic myocardium.
ACE inhibitors prolong life expectancy in patients with chronic heart failure and slow the progression of left ventricular dysfunction in patients who have suffered a myocardial infarction without clinical manifestations of heart failure.
The onset of action of the drug is after 1 hour, reaches a maximum after 6-7 hours and lasts for 24 hours. The duration of the effect also depends on the size of the dose taken. In case of arterial hypertension, the effect is observed in the first days after the start of treatment, a stable effect develops after 1-2 months. When the drug was abruptly discontinued, no pronounced increase in blood pressure was observed.
Diroton reduces albuminuria. In patients with hyperglycemia, it helps to normalize the function of damaged glomerular endothelium. Does not affect the concentration of glucose in the blood in patients with diabetes and does not lead to an increase in cases of hypoglycemia.
Special instructions
Special instructions
Most often, a pronounced decrease in blood pressure occurs with a decrease in fluid volume caused by diuretic therapy, reducing the salt content in food, dialysis, diarrhea or vomiting.
Before starting treatment with Diroton, if possible, the sodium concentration should be normalized and/or the lost fluid volume should be replaced, and the effect of the initial dose of Diroton on the patient’s blood pressure should be carefully monitored.
During extensive surgical interventions, as well as when using other drugs that cause a decrease in blood pressure, lisinopril, by blocking the formation of angiotensin II, can cause a pronounced, unpredictable decrease in blood pressure.
Since the potential risk of agranulocytosis cannot be excluded, periodic monitoring of the blood picture is required.
– Use in chronic heart failure In chronic heart failure with or without simultaneous renal failure, a pronounced decrease in blood pressure is possible. More often, a pronounced decrease in blood pressure is detected in patients with severe chronic heart failure, as a result of the use of diuretics in high doses, hyponatremia or impaired renal function. In such patients, treatment with Diroton should be started under the strict supervision of a physician (with caution in selecting the dose of the drug and diuretics). When using Diroton, some patients with chronic heart failure, but with normal or low blood pressure, may experience a decrease in blood pressure, which is usually not a reason to stop treatment. A transient hypotensive reaction is not a contraindication for taking the next dose of the drug.
– Use for coronary heart disease and cerebrovascular insufficiency Prescribing Diroton to patients with coronary artery disease and cerebrovascular insufficiency can cause a sharp decrease in blood pressure, which can lead to myocardial infarction or stroke. In such patients, treatment with Diroton should be started under the strict supervision of a physician (with caution in selecting the dose of the drug and diuretics).
– Use for renal artery stenosis In case of renal artery stenosis (especially with bilateral stenosis or in the presence of stenosis of the artery of a single kidney), as well as with circulatory failure due to lack of sodium and/or fluid, the use of Diroton can lead to impaired renal function, acute renal failure, which is usually irreversible after discontinuation of the drug.
– Use in acute myocardial infarction The use of standard therapy (thrombolytics, acetylsalicylic acid, beta-blockers) is indicated. It is possible to use Diroton in conjunction with intravenous administration or with the use of therapeutic transdermal nitroglycerin systems.
– Use in elderly patients In elderly patients, the use of standard doses leads to higher concentrations of the drug in the blood, so special care is required when determining the dose, despite the fact that no differences in the antihypertensive effect of Diroton were identified in elderly and young patients.
– Use of the drug in dialysis conditions When using the drug in dialysis conditions with a polyacryl-nitrile membrane, anaphylactic shock may occur, therefore, either a different type of dialysis membrane or the prescription of other antihypertensive drugs is recommended.
– Effect on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery There is no data on the effect of lisinopril on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery, however, it must be taken into account that dizziness may occur, so caution should be exercised.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Lisinopril
Composition
Composition
One tablet contains:
Active ingredients
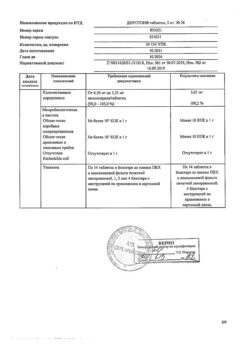
– Lisinopril 20 mg.
Excipients
Magnesium stearate,
talc,
mannitol,
corn starch,
calcium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
The use of Diroton during pregnancy is contraindicated. Lisinopril penetrates the placental barrier. If pregnancy is established, the drug should be stopped as soon as possible.
Taking ACE inhibitors in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy has an adverse effect on the fetus (a marked decrease in blood pressure, renal failure, hyperkalemia, cranial hypoplasia, and intrauterine death are possible).
There is no data on the negative effects of the drug on the fetus when used in the first trimester. For newborns and infants who have been exposed in utero to ACE inhibitors, it is recommended to establish careful monitoring for the timely detection of a pronounced decrease in blood pressure, oliguria, and hyperkalemia.
There is no data on the penetration of lisinopril into breast milk. If it is necessary to prescribe the drug during lactation, breastfeeding should be stopped.
Contraindications
Contraindications
– History of angioedema (including when using ACE inhibitors).
– Hereditary Quincke’s edema.
– Age up to 18 years (efficacy and safety have not been established).
– Hypersensitivity to lisinopril or other ACE inhibitors.
Side Effects
Side Effects
The most common side effects: dizziness, headache (5-6%), weakness, diarrhea, dry cough (3%), nausea, vomiting, orthostatic hypotension, skin rash, chest pain (1-3%).
The frequency of other adverse reactions is less than 1%.
From the cardiovascular system: marked decrease in blood pressure, chest pain; rarely – orthostatic hypotension, tachycardia, bradycardia, the appearance of symptoms of heart failure, impaired AV conduction, myocardial infarction.
From the digestive system: nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, dry mouth, diarrhea, dyspepsia, anorexia, taste disturbance, pancreatitis, hepatitis (hepatocellular and cholestatic), jaundice (hepatocellular or cholestatic), hyperbilirubinemia, increased activity of liver transaminases.
From the skin: urticaria, increased sweating, photosensitivity, itching, hair loss.
From the side of the central nervous system: mood lability, impaired concentration, paresthesia, increased fatigue, drowsiness, convulsive twitching of the muscles of the limbs and lips; rarely – asthenic syndrome, confusion.
From the respiratory system: dyspnea, dry cough, bronchospasm, apnea.
From the hematopoietic system: leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, neutropenia, agranulocytosis, anemia (decreased hemoglobin concentration, hematocrit, erythrocytopenia); with long-term treatment, a slight decrease in hemoglobin and hematocrit is possible, in some cases – agranulocytosis.
Allergic reactions: angioedema of the face, extremities, lips, tongue, epiglottis and/or larynx, intestinal angioedema, vasculitis, positive reactions to antinuclear antibodies, increased ESR, eosinophilia; in very rare cases – interstitial angioedema (swelling of the interstitial tissue of the lungs without the release of transudate into the lumen of the alveoli).
From the genitourinary system: uremia, oliguria, anuria, impaired renal function, acute renal failure, decreased potency.
Laboratory indicators: hyperkalemia and/or hypokalemia, hyponatremia, hypomagnesemia, hypochloremia, hypercalcemia, hyperuricemia, increased concentrations of urea and creatinine in blood plasma, hypercholesterolemia, hypertriglyceridemia, decreased glucose tolerance.
Other: arthralgia, arthritis, myalgia, fever, exacerbation of gout.
Interaction
Interaction
With caution, Diroton should be prescribed simultaneously with potassium-sparing diuretics (spironolactone, triamterene, amiloride), potassium, and salt substitutes containing potassium, because the risk of developing hyperkalemia increases, especially with impaired renal function. Therefore, these combinations should be prescribed only on the basis of the individual decision of the attending physician with regular monitoring of serum potassium levels and renal function.
When used simultaneously with diuretics and other antihypertensive drugs, an additive antihypertensive effect develops (risk of a pronounced decrease in blood pressure).
When used simultaneously with NSAIDs (including indomethacin), estrogens, and adrenergic stimulants, the antihypertensive effect of lisinopril is reduced.
When used concomitantly with lithium, lithium excretion may be reduced, so serum lithium concentrations should be regularly monitored.
When used simultaneously with antacids and cholestyramine, the absorption of lisinopril from the gastrointestinal tract is reduced.
When used simultaneously, Diroton may enhance the effect of ethanol (alcohol).
When used simultaneously with diuretics, lisinopril reduces potassium excretion.
Overdose
Overdose
– Symptoms: pronounced decrease in blood pressure.
– Treatment: If necessary, carry out symptomatic therapy (iv administration of fluids, control and normalization of blood pressure, water and electrolyte balance). Lisinopril can be removed from the body through dialysis.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
At 15–30 °C
Shelf life
Shelf life
3 years
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Gedeon Richter-RUS, Russia
Additional information
| Shelf life | 3 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | At 15-30 °C |
| Manufacturer | Gedeon Richter Rus, Russia |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Gedeon Richter Rus |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Diroton, tablets 20 mg 56 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.