No products in the cart.
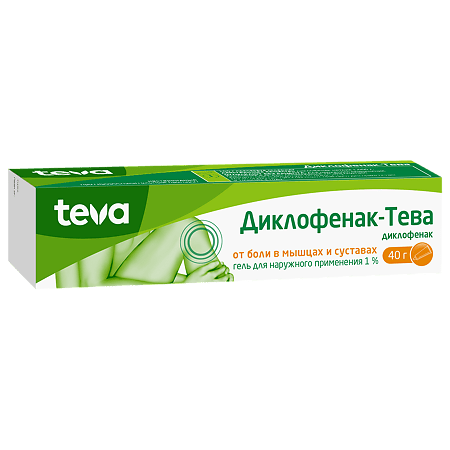
Diclofenac-Teva, gel 1% 40 g
€10.47 €9.16
Description
Pharmacotherapeutic group: nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAIDs)
ATX code: M02AA15
Pharmacological properties.
Pharmacodynamics
The active ingredient diclofenac is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) with pronounced analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antipyretic properties. Indiscriminately inhibiting cyclooxygenase 1 and 2 types, disrupts the metabolism of arachidonic acid and the synthesis of prostaglandins in the inflammation focus. Diclofenac gel for external use is used to eliminate pain and inflammation in joints, muscles and ligaments of traumatic or rheumatic origin, helping to reduce pain and swelling associated with the inflammatory process, increasing joint mobility.
Pharmacokinetics
Assimilation. The amount of diclofenac absorbed through the skin is proportional to the surface area treated and depends on both the total dose of the drug applied and the degree of hydration of the skin. With the recommended method of application no more than 6% of diclofenac is absorbed.
Distribution The concentration of diclofenac in plasma, synovial membrane and synovial fluid was measured when the drug was applied to the area of the affected joint. Maximum concentrations in plasma were approximately 100 times lower than after oral administration of the same amount of diclofenac. Binding with plasma proteins is 99% (predominantly with albumin). Diclofenac is mainly distributed and retained deep in the tissues subject to inflammation, such as joints, where its concentration is 20 times higher than in plasma.
Biotransformation / metabolism
Diclofenac is metabolized partly by glucuronidation of the unchanged molecule, but predominantly by single and multiple hydroxylation, resulting in several phenolic metabolites, most of which are converted to glucuronide conjugates. Two phenolic metabolites are biologically active, but to a much lesser extent than diclofenac.
Extractions. Total systemic plasma clearance of diclofenac is 263±56 ml/min. Final elimination half-life is 1-2 hours. Half-life of metabolites, including two pharmacologically active ones, is also short and is 1-3 hours. One of the metabolites (3′-hydroxy-4′-methoxydiclofenac) has a longer half-life, however, this metabolite is completely inactive. It is excreted by the kidneys (about 65%) and with the bile (about 35%) in the form of inactive compounds with glucuronic acid.
Indications
Indications
Back pain due to inflammatory and degenerative diseases of the spine (sciatica, osteoarthritis, lumbago, sciatica).
Pain in joints (fingers, knees, etc.) due to osteoarthritis. Muscle pain (due to sprains, strains, bruises, injuries).
Inflammation and swelling of soft tissues and joints due to injuries and rheumatic diseases (tenosynovitis, bursitis, lesions of periarticular tissues, wrist syndrome).
The drug is intended for symptomatic therapy, reducing pain and inflammation at the time of use, and does not affect the progression of the disease.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacotherapeutic group: non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID)
ATX code: M02AA15
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
The active component diclofenac is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) with pronounced analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antipyretic properties. Indiscriminately inhibiting cyclooxygenase types 1 and 2, it disrupts the metabolism of arachidonic acid and the synthesis of prostaglandins at the site of inflammation. Diclofenac gel for external use is used to eliminate pain and inflammation in joints, muscles and ligaments of traumatic or rheumatic origin, helping to reduce pain and swelling associated with the inflammatory process, increasing joint mobility.
Pharmacokinetics
Suction. The amount of diclofenac absorbed through the skin is proportional to the area of the treated surface and depends on both the total dose of the drug applied and the degree of skin hydration. With the recommended method of applying the drug, no more than 6% of diclofenac is absorbed.
Distribution. The concentration of diclofenac in plasma, synovial membrane and synovial fluid was measured when the drug was applied to the area of the affected joint. Maximum plasma concentrations were approximately 100 times lower than after oral administration of the same amount of diclofenac. Communication with plasma proteins is 99% (mainly with albumin). Diclofenac is preferentially distributed and retained deep in tissues prone to inflammation, such as joints, where its concentration is 20 times higher than in blood plasma.
Biotransformation/metabolism
The metabolism of diclofenac is carried out partly by glucuronidation of the unchanged molecule, but mainly through single and multiple hydroxylation, which leads to the formation of several phenolic metabolites, most of which are converted to glucuronide conjugates. Two phenolic metabolites are biologically active, but to a much lesser extent than diclofenac.
Excretion. The total systemic plasma clearance of diclofenac is 263±56 ml/min. The terminal half-life is 1-2 hours. The half-life of metabolites, including two pharmacologically active ones, is also short and amounts to 1-3 hours. One of the metabolites (3′-hydroxy-4′-methoxydiclofenac) has a longer half-life, however, this metabolite is completely inactive. Excreted by the kidneys (about 65%) and bile (about 35%) in the form of inactive compounds with glucuronic acid.
Special instructions
Special instructions
Use externally only.
Avoid contact of the drug with the eyes, mucous membranes or open wounds.
Diclofenac-Teva gel should be applied only to intact areas of the skin. After applying the drug, a bandage may be applied, but airtight occlusive dressings should not be applied. Before use, patients with gastric and duodenal ulcers, impaired liver, kidney or hematopoietic function, as well as concomitant use of other NSAIDs, should consult a doctor.
When using the drug together with other dosage forms of diclofenac, the maximum daily dose should be taken into account.
With long-term use and/or application to large surfaces, systemic side effects may develop due to resorptive effects.
If, during treatment with Diclofenac-Teva gel, attacks of bronchial asthma, hypersensitivity reactions, swelling of the skin, mucous membranes, or skin rashes appear, treatment with the drug should be stopped.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and machinery
The drug does not affect the ability to perform potentially hazardous activities that require increased concentration of attention and speed of psychomotor reactions (driving vehicles, working with moving mechanisms).
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Diclofenac
Composition
Composition
100 g of the drug contains:
active ingredient: diclofenac sodium 1,000 g;
excipients: diisopropyl adipate 5,000 g; hyprolose 2,000 g; lactic acid 90% 0.044 g; sodium disulfite 0.050 g; isopropanol 40,000 g; purified water 51.906 g.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
Due to the lack of data on the use of diclofenac in pregnant women, the use of the drug during the first and second trimester of pregnancy is recommended only as prescribed by a doctor, weighing the benefits for the mother and the risk for the fetus.
The use of the drug in the third trimester of pregnancy is contraindicated (suppression of uterine contractility, prolongation of bleeding time, antiaggregation effect, impaired renal function in the fetus with subsequent oligohydramnios and/or premature closure of the ductus arteriosus in the fetus are possible).
Breastfeeding period
Due to evidence that diclofenac passes into breast milk in small quantities, it is not recommended to use it during breastfeeding.
During breastfeeding, you should not apply the drug to the area of the mammary glands or to a large surface of the skin and use it for a long time/
Contraindications
Contraindications
• Hypersensitivity to diclofenac or other components of the drug, as well as to acetylsalicylic acid and other NSAIDs.
• Tendency to develop attacks of bronchial asthma, skin rashes or acute rhinitis when using acetylsalicylic acid or other NSAIDs.
• Pregnancy (III trimester).
• Children’s age (up to 14 years).
• Violation of the integrity of the skin at the intended site of application.
• Breastfeeding period.
With caution
Hepatic porphyria (exacerbation), erosive and ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract, severe dysfunction of the liver and kidneys, blood clotting disorders (including hemophilia, prolonged bleeding time, bleeding tendency), chronic heart failure, bronchial asthma, old age, pregnancy (I and II trimester).
Side Effects
Side Effects
The frequency of side effects is classified according to the recommendations of the World Health Organization: very often (≥ 1/10); often (≥ 1/100, but < 1/10); uncommon (≥ 1/1000, but < 1/100); rare (≥ 1/10000, but < 1/1000); very rare (<1/10000), including isolated reports; frequency unknown - frequency cannot be estimated from available data.
Infectious and parasitic diseases: very rarely – pustular rashes.
From the immune system: very rarely – generalized skin rash, allergic reactions (urticaria, hypersensitivity (including urticaria), angioedema).
From the respiratory system: very rarely – bronchial asthma.
From the skin and subcutaneous tissue: often – erythema, dermatitis (including contact dermatitis, itching, hyperemia, swelling of the treated skin area, papular-vesicular rashes, peeling); rarely – bullous dermatitis; very rarely – photosensitivity reactions.
If any of the side effects listed in the instructions get worse, or you notice any other side effects not listed in the instructions, tell your doctor.
Interaction
Interaction
Diclofenac may enhance the effect of drugs that cause photosensitivity. Clinically significant interactions with other drugs have not been described.
Overdose
Overdose
Due to the low systemic absorption of the active component of the drug when applied externally, an overdose is unlikely. If used incorrectly or accidentally swallowed, nausea, vomiting and systemic adverse reactions characteristic of NSAIDs may develop.
Symptoms: nausea, vomiting, epigastric pain, diarrhea.
If symptoms of overdose occur, consult a doctor.
If the drug is taken orally, in order to quickly prevent the absorption of diclofenac, gastric lavage should be performed followed by the use of activated charcoal; symptomatic therapy is indicated.
Hemodialysis and forced diuresis for removing diclofenac are not effective due to the high degree of binding of diclofenac to plasma proteins (about 99%).
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
At a temperature not exceeding 25 °C.
Keep out of the reach of children!
Shelf life
Shelf life
4 years.
After opening the tube, the drug is suitable for use for 1 year.
Do not use after expiration date!
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Merkle GmbH, Germany
Additional information
| Shelf life | 4 years. After opening the tube the drug is suitable for use for 1 year. Do not use after the expiration date! |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | At a temperature not exceeding 25 ° C. Keep out of reach of children! |
| Manufacturer | Merkle GmbH, Germany |
| Medication form | gel for external use |
| Brand | Merkle GmbH |
Related products
Buy Diclofenac-Teva, gel 1% 40 g with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.