No products in the cart.
Diclofenac, 25 mg/ml 3 ml 5 pcs
€1.00
Description
Pharmgroup:
NSAIDs.
Pharmacological action:
Penylacetic acid derivative; anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic effect.
Inhibiting COX1 and COX2 indiscriminately, disrupts arachidonic acid metabolism, reduces the amount of Pg in the focus of inflammation.
The drug is most effective for pain of inflammatory nature. Like all NSAIDs, the drug has antiaggregant activity.
Pharmacokinetics:
Absorption is rapid and complete, food slows the rate of absorption. After oral administration of 50 mg, Cmax is 1.5 mcg/ml, TCmax is 2-3 h.
Diclofenac prolonged action: as a result of slow release of the drug, Cmax in plasma is lower than that produced by administration of short-acting drugs; however, it remains high for a long time after administration.
Cmax is 0.5-1 mcg/ml, TCmax is 5 h after administration of 100 mg sustained release tablets.
After 75 mg IV drip administration, Cmax is 1.9 mcg/ml (5.9 µmol/L). After intravenous administration, Cmax is 2.5 µg/mL (8 µmol/L), TCmax is 20 min.
With rectal administration, TCmax is 30 min.
Plasma concentration is in linear relationship to the amount of dose administered.
No changes in pharmacokinetics of diclofenac on repeated administration. It does not cumulate if the recommended interval between meals is observed.
The bioavailability is 50%. Binding with plasma proteins is more than 99% (most of it is bound with albumin).
Transfers to breast milk, synovial fluid; Cmax in synovial fluid is observed 2-4 hours later than in plasma.
The T1/2 from synovial fluid is 3-6 h (the drug concentrations in synovial fluid are higher 4-6 h after administration than in plasma and remain higher for 12 h).
50% of the drug is metabolized during “first passage” through the liver; AUC is half as much after oral administration of the drug as after parenteral administration of the same dose.
Metabolism occurs as a result of multiple or single hydroxylation and conjugation with glucuronic acid. The CYP2C9 isoenzyme is also involved in the metabolism of the drug.
The pharmacological activity of metabolites is less than that of diclofenac.
The systemic clearance is 260 ml/min. T1/2 from plasma is 1-2 hours. 60% of the administered dose is excreted as metabolites through the kidneys; less than 1% is excreted unchanged, the rest of the dose is excreted as metabolites in the bile.
In patients with significant renal insufficiency (CKD less than 10 ml/min) excretion of metabolites in bile is increased, while there is no increase of their concentrations in blood.
In patients with chronic hepatitis or compensated liver cirrhosis pharmacokinetic parameters do not change.
Indications
Indications
For short-term symptomatic treatment of pain of various origins of moderate intensity:
Inflammatory and degenerative diseases of the musculoskeletal system:
rheumatoid, psoriatic, juvenile chronic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis (ankylosing spondylitis); gouty arthritis, rheumatic soft tissue lesions, osteoarthritis of peripheral joints and spine (including with radicular syndrome);
lumbago, sciatica, neuralgia;
algodismenorrhea, inflammatory processes of the pelvic organs, including adnexitis;
post-traumatic pain syndrome accompanied by inflammation;
renal colic;
postoperative pain.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Pharmaceutical group:
NSAIDs.
Pharmaceutical action:
NSAID, phenylacetic acid derivative; has anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic effects.
By indiscriminately inhibiting COX1 and COX2, it disrupts the metabolism of arachidonic acid and reduces the amount of Pg at the site of inflammation.
Most effective for inflammatory pain. Like all NSAIDs, the drug has antiplatelet activity.
Pharmacokinetics:
Absorption is rapid and complete; food slows down the rate of absorption. After oral administration of 50 mg, Cmax is 1.5 mcg/ml, TCmax is 2-3 hours.
Long-acting diclofenac: as a result of the delayed release of the drug, Cmax in plasma is lower than that created by the administration of short-acting drugs; however, it remains high for a long time after administration.
Cmax – 0.5-1 mcg/ml, TCmax – 5 hours after taking 100 mg extended-release tablets.
After intravenous drip administration of 75 mg, Cmax is 1.9 μg/ml (5.9 μmol/l). After intramuscular administration, Cmax is 2.5 mcg/ml (8 μmol/l), TCmax is 20 minutes.
For rectal administration TCmax – 30 min.
Plasma concentration is linearly dependent on the administered dose.
There are no changes in the pharmacokinetics of diclofenac following repeated administration. Does not accumulate if the recommended interval between meals is observed.
Bioavailability – 50%. Communication with plasma proteins is more than 99% (most of it is associated with albumin).
Penetrates into breast milk and synovial fluid; Cmax in synovial fluid is observed 2-4 hours later than in plasma.
T1/2 from synovial fluid – 3-6 hours (concentrations of the drug in synovial fluid 4-6 hours after its administration are higher than in plasma, and remain higher for another 12 hours).
50% of the drug is metabolized during the “first pass” through the liver; AUC is 2 times less after oral administration of the drug than after parenteral administration of the same dose.
Metabolism occurs as a result of multiple or single hydroxylation and conjugation with glucuronic acid. The CYP2C9 isoenzyme is also involved in the metabolism of the drug.
The pharmacological activity of the metabolites is less than that of diclofenac.
Systemic clearance is 260 ml/min. T1/2 from plasma – 1-2 hours. 60% of the administered dose is excreted in the form of metabolites through the kidneys; less than 1% is excreted unchanged, the rest of the dose is excreted as metabolites in the bile.
In patients with severe renal failure (creatinine clearance less than 10 ml/min), the excretion of metabolites in bile increases, but no increase in their concentration in the blood is observed.
In patients with chronic hepatitis or compensated liver cirrhosis, pharmacokinetic parameters do not change.
Special instructions
Special instructions
The risk of adverse reactions when using diclofenac increases with increasing dose and duration of treatment.
In order to reduce the risk of adverse events, the drug should be used at the minimum effective dose for the shortest period necessary to relieve symptoms.
With regular use of the drug, the need for symptom relief, response to treatment should be periodically assessed and the dose adjusted in a timely manner.
Damage to the gastrointestinal tract
When using diclofenac, phenomena such as bleeding or ulceration/perforation of the gastrointestinal tract, in some cases with fatal outcome, were observed.
These events may occur at any time when using drugs in patients with or without previous symptoms and a history of serious gastrointestinal diseases.
In older patients, such complications can have serious consequences. If bleeding or gastrointestinal ulceration develops in patients receiving diclofenac, the drug should be discontinued.
To reduce the risk of toxic effects on the gastrointestinal tract in patients with gastrointestinal ulcers. especially with a history of complicated bleeding or perforation, as well as in elderly patients, the drug should be used in the minimum effective dose.
Patients with an increased risk of developing gastrointestinal complications, as well as patients receiving therapy with low doses of acetylsalicylic acid (Aspirin), should take gastroprotectors
(proton pump inhibitors or misoprostol) or other medications to reduce the risk of adverse gastrointestinal effects.
Patients with a history of gastrointestinal lesions, especially the elderly, should report all abdominal symptoms to the doctor.
Patients with bronchial asthma
Exacerbation of bronchial asthma (NSAID intolerance/bronchial asthma provoked by taking NSAIDs), angioedema and urticaria are most often observed in patients with bronchial asthma, seasonal
allergic rhinitis, nasal polyps, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or chronic respiratory infections (especially those associated with allergic rhinitis-like symptoms).
In this group of patients, as well as in patients with allergies to other drugs (rash, itching or urticaria), special caution should be observed when using diclofenac (preparedness for resuscitation measures).
Skin reactions
Serious dermatological reactions such as exfoliative dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, in some cases fatal, have been reported very rarely with the use of diclofenac.
The highest risk and incidence of severe dermatological reactions were observed in the first month of treatment with diclofenac.
If patients receiving diclofenac develop the first signs of skin rash, damage to the mucous membranes or other symptoms of hypersensitivity, the drug should be discontinued.
In rare cases, anaphylactic/anaphylactoid reactions may develop in patients who are not allergic to diclofenac.
Effects on the liver
Since during the period of use of diclofenac there may be an increase in the activity of one or more liver enzymes, monitoring of liver function is indicated as a precautionary measure during long-term therapy with the drug.
If liver dysfunction persists or progresses or signs of liver disease or other symptoms occur (for example, eosinophilia, rash, etc.), the drug should be discontinued.
It should be borne in mind that hepatitis during the use of diclofenac can develop without prodromal phenomena.
Effects on the kidneys
During therapy with diclofenac, it is recommended to monitor renal function in patients with hypertension, impaired cardiac or renal function, the elderly, patients receiving diuretics or other
drugs affecting renal function, as well as in patients with a significant decrease in the volume of circulating blood plasma of any etiology, for example, in the period before and after major surgical interventions.
After discontinuation of drug therapy, normalization of renal function indicators to initial values is usually observed.
Effects on the cardiovascular system
Therapy with NSAIDs, including diclofenac, particularly long-term therapy and high-dose therapy, may be associated with a small increase in the risk of serious cardiovascular thrombotic complications (including myocardial infarction and stroke).
Patients with diseases of the cardiovascular system and a high risk of developing diseases of the cardiovascular system (for example, with arterial hypertension, hyperlipidemia, diabetes mellitus, smokers)
the drug should be prescribed only after careful consideration and used with extreme caution, at the lowest effective dose for the shortest possible duration of treatment, since the risk of thrombotic complications increases with increasing dose and duration of treatment.
With long-term therapy (more than 4 weeks), the daily dose of diclofenac in such patients should not exceed 100 mg. The effectiveness of treatment and the patient’s need for symptomatic therapy should be periodically assessed, especially in cases where its duration is more than 4 weeks.
The patient should be instructed to immediately seek medical attention if the first symptoms of thrombotic disorders (eg, chest pain, shortness of breath, weakness, speech disturbances) appear. Impact on the hematopoietic system
Diclofenac may temporarily inhibit platelet aggregation. Therefore, in patients with hemostasis disorders, it is necessary to carefully monitor relevant laboratory parameters.
With long-term use of diclofenac, it is recommended to conduct regular clinical tests of peripheral blood.
Masking signs of an infectious process
The anti-inflammatory effect of diclofenac may complicate the diagnosis of infectious processes.
Use simultaneously with other NSAIDs
Diclofenac should not be used concomitantly with other NSAIDs, including selective COX-2 inhibitors, due to the risk of increased adverse events.
Impact on women’s fertility
Diclofenac may have a negative effect on women’s fertility, so diclofenac is not recommended for women wishing to become pregnant.
In women experiencing difficulty conceiving (including those undergoing testing), the possibility of discontinuing the use of diclofenac should be considered.
Metabisulfite, which is part of the drug, can rarely cause severe hypersensitivity reactions and bronchospasm.
Information for Patients on a Sodium Controlled Diet
The sodium content in one ampoule (3 ml) of Diclofenac solution for injection does not exceed 1 mmol (23 mg), i.e. practically “sodium-free”.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Diclofenac
Composition
Composition
Composition per 1 ml of the drug:
active ingredient:
Diclofenac sodium 25.0 mg;
Excipients:
benzyl alcohol,
Sodium metabisulfite,
Mannitol,
Sodium hydroxide,
Propylene glycol,
Water for injection.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
Contraindicated.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity (including to other NSAIDs), complete or incomplete combination of bronchial asthma, recurrent polyposis of the nose and paranasal sinuses and intolerance to ASA or others.
NSAIDs (including a history), erosive and ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract and duodenum, active gastrointestinal bleeding, inflammatory bowel diseases, severe liver and heart failure;
period after coronary artery bypass surgery; severe renal failure (creatinine clearance less than 30 ml/min), progressive kidney disease, active liver disease, confirmed hyperkalemia,
pregnancy (III trimester), lactation period, children’s age (up to 14 years – for enteric-coated tablets 50 mg and rectal suppositories 50 mg, up to 18 years – for extended-release tablets and suppositories 100 mg).
For rectal use (additionally): proctitis.
For dosage forms containing lactose (additionally): hereditary lactose intolerance, impaired absorption of glucose-galactose, lactase deficiency.
With caution.
Peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum, ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease, history of liver disease, hepatic porphyria, chronic renal failure, heart failure, arterial hypertension, significant decrease in blood volume (including after extensive surgery),
elderly patients (including those receiving diuretics, debilitated patients and those with low body weight),
bronchial asthma, simultaneous use of corticosteroids (including prednisolone), anticoagulants (including warfarin), antiplatelet agents (including ASA, clopidogrel), selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (including citalopram, fluoxetine, paroxetine, sertraline),
IHD, cerebrovascular diseases, dyslipidemia/hyperlipidemia,
diabetes mellitus, peripheral artery disease, smoking, chronic renal failure (creatinine clearance 30-60 ml/min), the presence of Helicobacter pylori infection, long-term use of NSAIDs, alcoholism, severe somatic diseases.
Side Effects
Side Effects
From the digestive system: nausea, vomiting, epigastric pain, anorexia, flatulence, constipation, gastritis up to erosive with bleeding, increased transaminase activity, drug-induced hepatitis, pancreatitis.
From the urinary system: interstitial nephritis.
From the side of the central nervous system: headache, dizziness, disorientation, agitation, insomnia, irritability, fatigue, aseptic meningitis.
From the respiratory system: bronchospasm.
From the hematopoietic system: anemia, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, agranulocytosis.
Dermatological reactions: exanthema, erythema, eczema, hyperemia, erythroderma, photosensitivity.
Allergic reactions: erythema multiforme, Lyell’s syndrome, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, anaphylactic reactions, including shock.
Local reactions: burning, formation of infiltrate, and necrosis of adipose tissue are possible at the injection site.
Other: fluid retention in the body, edema, increased blood pressure.
Interaction
Interaction
Diclofenac may enhance the toxic effect of cyclosporine on the kidneys.
When used simultaneously with anticoagulants, regular monitoring of blood clotting parameters is necessary.
With the simultaneous use of Diclofenac with digoxin, phenytoin or lithium preparations, it is possible to increase the plasma concentrations of these drugs; with diuretics and antihypertensives
means – it is possible to reduce the effect of these drugs; with potassium-sparing diuretics – hyperkalemia may develop; with acetisalicylic acid – a decrease in the concentration of diclofenac in the blood plasma and an increased risk of side effects.
When using methotrexate within 24 hours before or after taking Diclofenac, the concentration of methotrexate may increase and its toxic effect may increase.
Diclofenc can cause hypo- or hyperglycemia, therefore, when used simultaneously with hypoglycemic agents, monitoring of blood glucose concentrations is required.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms:
bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract, diarrhea, vomiting, epigastric pain, dizziness, tinnitus, lethargy, convulsions, rarely – increased blood pressure, acute renal failure, hepatotoxic effect, respiratory depression, coma.
Treatment:
gastric lavage, activated charcoal, symptomatic therapy aimed at eliminating increased blood pressure, renal dysfunction, convulsions, gastrointestinal irritation, respiratory depression.
Forced diuresis and hemodialysis are ineffective (due to the significant connection with proteins and intensive metabolism).
Prescribing
Prescribing
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID)
Complete set of goods
Complete set of goods
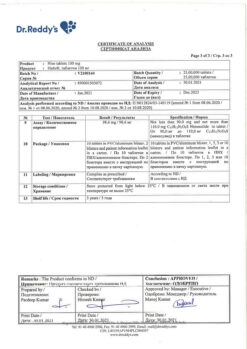
Solution for intramuscular administration 25 mg/ml.
3 ml of the drug in colorless glass ampoules of hydrolytic class I.
A dot and a ring are applied to the ampoule with brown paint.
5 ampoules per blister pack made of polyvinyl chloride film and aluminum foil.
The contour blister packaging along with instructions for use is placed in a cardboard pack.
Functional features
Functional features
Suction
The time to reach the maximum concentration when administered intramuscularly at a dose of 75 mg is 15-30 minutes, the value of the maximum concentration is 1.9-4.8 (average 2.7) mcg/ml.
3 hours after administration, plasma concentrations average 10% of the maximum.
Distribution
Communication with blood plasma proteins is more than 99% (most of it is associated with albumin). Volume of distribution – 550 ml/kg.
Diclofenac penetrates into the synovial fluid, where its maximum concentration is reached 2-4 hours later than in the blood plasma. The apparent half-life from synovial fluid is 3-6 hours.
2 hours after reaching the maximum plasma concentration, the concentration of diclofenac in the synovial fluid is higher than in the plasma, and its values remain higher for a period of time up to 12 hours.
Metabolism
Metabolism occurs as a result of multiple or single hydroxylation and conjugation with glucuronic acid.
The CYP2C9 isoenzyme of cytochrome P450 takes part in the metabolism of the drug. The pharmacological activity of the metabolites is lower than that of diclofenac.
Removal
Systemic clearance is 350 ml/min. The half-life from plasma is 2 hours. 65% of the administered dose is excreted in the form of metabolites by the kidneys; less than 1% is excreted unchanged, the rest of the dose is excreted as metabolites in the bile. Diclofenac passes into breast milk.
Pharmacokinetics in certain groups of patients
In patients with severe renal failure (creatinine clearance less than 10 ml/min), the excretion of metabolites in bile increases, but no increase in their concentration in the blood is observed.
In patients with chronic hepatitis or compensated liver cirrhosis, the pharmacokinetic parameters of diclofenac do not change.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
Store in a dry place, protected from light at a temperature not exceeding 25 C.
Keep out of the reach of children.
Shelf life
Shelf life
At temperatures between 15 and 25 °C.
Keep out of the reach of children!
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Hemofarm A.D., Serbia
Additional information
| Shelf life | At the temperature from 15 to 25 °C. Keep out of reach of children! |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | Store in a dry, dark place at temperatures under 25 C. Keep out of the reach of children. |
| Manufacturer | Chemopharm A.D., Serbia |
| Medication form | solution |
| Brand | Chemopharm A.D. |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Diclofenac, 25 mg/ml 3 ml 5 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.