No products in the cart.
Diclofenac, 100 mg 20 pcs
€2.96 €2.69
Description
A nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), a derivative of phenylacetic acid.
Diclofenac has anti-inflammatory, analgesic, antiaggregant and antipyretic effects.
Indiscriminately inhibiting cyclooxygenase 1 and 2 (COX1 and COX2), disrupts arachidonic acid metabolism, reduces the number of prostaglandins in the focus of inflammation. It is most effective for pain of inflammatory nature.
In rheumatic diseases the anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect of diclofenac significantly reduces the severity of pain, morning stiffness and joint swelling and improves the functional state of the joint.
In case of injury and in the postoperative period diclofenac reduces pain and inflammatory swelling.
Absorption is fast and complete, food slows the rate of absorption by 1-4 hours and reduces the maximum concentration (Cmax) by 40%.
After oral administration of 100 mg tablets, Cmax – 0.5 mcg/ml is reached after -4-5 hours. Plasma concentrations are linearly related to the amount of the administered dose.
There is no change in pharmacokinetics of diclofenac on repeated administration. It does not cumulate if the recommended interval between doses is observed.
The bioavailability is 50%. Binding with plasma proteins is more than 99% (most of it is bound with albumin). It penetrates into synovial fluid; Cmax in synovial fluid is observed 2-4 hours later than in plasma.
The half-life (T½) of synovial fluid is 3-6 h (the concentration of the active substance in synovial fluid is higher in synovial fluid 4-6 h after administration than in plasma and stays higher for 12 h).
The relationship between the concentration of the drug in synovial fluid and the clinical efficacy of the drug has not been elucidated.
Metabolism: 50% of the active substance is metabolized during the “first passage” through the liver.
Metabolism occurs as a result of multiple or single hydroxylation and conjugation with glucuronic acid.
The CYP2C9 isoenzyme is involved in metabolism of the drug. The pharmacological activity of the metabolites is lower than that of diclofenac.
The systemic clearance is about 260±50 ml/min, the volume of distribution is 550 ml/kg.
T½ from plasma averages about 2.5 hours. 65% of the administered dose is excreted as metabolites by the kidneys; less than 1% is excreted unchanged, the rest of the dose is excreted as metabolites in the bile.
In patients with severe renal insufficiency (creatinine clearance (CK) less than 10 ml/min) excretion of metabolites in bile is increased, while there is no increase in their blood concentrations.
In patients with chronic hepatitis or compensated liver cirrhosis pharmacokinetic parameters of diclofenac are not changed.
Diclofenac penetrates into breast milk.
Indications
Indications
Symptomatic treatment of diseases of the musculoskeletal system (rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, juvenile chronic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis (ankylosing spondylitis);
gouty arthritis, rheumatic soft tissue lesions, osteoarthritis of peripheral joints and spine, including radicular syndrome, tenosynovitis, bursitis).
The drug relieves or reduces pain and inflammation during the treatment period, but does not affect the progression of the disease.
Pain syndrome of mild or moderate severity: neuralgia, myalgia, lumboischialgia, post-traumatic pain syndrome accompanied by inflammation, postoperative pain, headache, migraine, algomenorrhea, adnexitis, proctitis, toothache.
As part of complex therapy for infectious and inflammatory diseases of the ear, nose and throat with severe pain (pharyngitis, tonsillitis, otitis media).
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), a derivative of phenylacetic acid.
Diclofenac has anti-inflammatory, analgesic, antiplatelet and antipyretic effects.
By indiscriminately inhibiting cyclooxygenase 1 and 2 (COX1 and COX2), it disrupts the metabolism of arachidonic acid and reduces the amount of prostaglandins at the site of inflammation. Most effective for inflammatory pain.
In rheumatic diseases, the anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect of diclofenac helps to significantly reduce the severity of pain, morning stiffness, and swelling of the joints, which improves the functional state of the joint.
For injuries, in the postoperative period, diclofenac reduces pain and inflammatory swelling.
Absorption is rapid and complete, food slows the rate of absorption by 1-4 hours and reduces the maximum concentration (Cmax) by 40%.
After oral administration of 100 mg tablets, Cmax – 0.5 mcg/ml is achieved after -4-5 hours. Plasma concentration is linearly dependent on the administered dose.
There are no changes in the pharmacokinetics of diclofenac following repeated administration. Does not accumulate if the recommended interval between doses is observed.
Bioavailability – 50%. Communication with plasma proteins is more than 99% (most of it is associated with albumin). Penetrates into synovial fluid; Cmax in synovial fluid is observed 2-4 hours later than in plasma.
The half-life (T½) from the synovial fluid is 3-6 hours (the concentration of the active substance in the synovial fluid 4-6 hours after administration of the drug is higher than in plasma, and remains higher for another 12 hours).
The relationship between the concentration of the drug in the synovial fluid and the clinical effectiveness of the drug has not been clarified.
Metabolism: 50% of the active substance is metabolized during the “first pass” through the liver.
Metabolism occurs as a result of multiple or single hydroxylation and conjugation with glucuronic acid.
The CYP2C9 isoenzyme takes part in the metabolism of the drug. The pharmacological activity of the metabolites is lower than that of diclofenac.
Systemic clearance is approximately 260 ± 50 ml/min, volume of distribution is 550 ml/kg.
T½ from plasma averages about 2.5 hours. 65% of the administered dose is excreted in the form of metabolites by the kidneys; less than 1% is excreted unchanged, the rest of the dose is excreted as metabolites in the bile.
In patients with severe renal failure (creatinine clearance (CC) less than 10 ml/min), the excretion of metabolites in bile increases, but no increase in their concentration in the blood is observed.
In patients with chronic hepatitis or compensated liver cirrhosis, the pharmacokinetic parameters of diclofenac do not change.
Diclofenac passes into breast milk.
Special instructions
Special instructions
In order to reduce the risk of adverse events, the drug should be used at the lowest effective dose for the shortest period necessary to relieve symptoms.
Therapy with NSAIDs, including diclofenac, particularly long-term and high-dose therapy, may be associated with a small increased risk of serious cardiovascular thrombotic events (including myocardial infarction and stroke).
In patients with significant risk factors for cardiovascular events (eg hypertension, hyperlipoproteinemia, diabetes mellitus and smoking), treatment with diclofenac-containing products should only be initiated after careful evaluation and analysis.
Due to the important role of prostaglandins in maintaining renal blood flow, special caution should be exercised when prescribing the drug to patients with cardiac or renal failure, hypertension,
elderly patients, patients taking diuretics or other drugs that affect renal function, as well as patients who have a decrease in circulating blood volume for any reason (for example, after major surgery).
If diclofenac is prescribed in such cases, monitoring of renal function is recommended as a precaution.
After discontinuation of drug therapy, normalization of renal function indicators to initial values is usually observed.
When using diclofenac, phenomena such as bleeding or ulceration/perforation of the gastrointestinal tract, in some cases fatal, were observed.
These phenomena may occur at any time when using the drug in patients with or without previous symptoms and a history of serious gastrointestinal diseases.
In elderly patients, such complications can have serious consequences.
If patients receiving diclofenac develop bleeding or ulceration of the gastrointestinal tract, the drug should be discontinued.
To reduce the risk of toxic effects on the gastrointestinal tract, the drug should be used in the minimum effective dose for the shortest possible time, especially with regard to
patients with ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract, especially those complicated by bleeding or perforation in history, as well as elderly patients.
Patients with an increased risk of developing gastrointestinal complications, as well as those receiving therapy with low doses of acetylsalicylic acid or other drugs that can increase the risk of damage to the gastrointestinal tract, should take gastroprotectors.
Patients with a history of gastrointestinal disorders, especially the elderly, should report all symptoms of the digestive system to their doctor.
When carrying out long-term therapy, it is necessary to monitor liver function, peripheral blood patterns, and stool analysis for occult blood.
With long-term use of diclofenac, there may be an increase in the activity of one or more liver enzymes.
If liver dysfunction persists or progresses or signs of liver disease or other symptoms occur (for example, eosinophilia, rash, etc.), the drug should be discontinued.
It should be borne in mind that hepatitis during the use of diclofenac can develop without prodromal phenomena.
Caution must be exercised when using diclofenac in patients with hepatic porphyria, since the drug can provoke attacks of porphyria.
Diclofenac can reversibly inhibit platelet aggregation, therefore, in patients with hemostasis disorders with long-term use, careful monitoring of relevant laboratory parameters is necessary.
In patients with bronchial asthma, seasonal allergic rhinitis, swelling of the nasal mucosa (including nasal polyps), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, chronic respiratory tract infections
(especially associated with allergic rhinitis-like symptoms), as well as in patients with allergies to other drugs (rash, itching, urticaria), special caution should be observed when prescribing diclofenac (preparedness for resuscitation measures).
Severe, in some cases fatal, skin reactions, including exfoliative dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, have been very rarely reported with the use of diclofenac.
The highest risk and incidence of severe dermatological reactions were observed in the first month of treatment with diclofenac.
If patients receiving the drug develop the first signs of skin rash, damage to the mucous membranes or other symptoms of hypersensitivity, diclofenac should be discontinued.
The anti-inflammatory effect of NSAIDs, including diclofenac, may complicate the diagnosis of infectious processes.
Due to the negative effect on fertility, the drug is not recommended for women planning pregnancy. In patients with infertility (including those undergoing examination), it is recommended to discontinue the drug.
When taking 100 mg tablets, patients with diabetes should take into account the sucrose content in the drug (1 tablet contains 94.7880 mg of sucrose).
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery
Patients who experience visual disturbances, dizziness, drowsiness or other disorders of the central nervous system while using diclofenac should not drive vehicles or operate machinery.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Diclofenac
Composition
Composition
One extended-release film-coated tablet contains:
Active ingredient:
Diclofenac sodium 100.0000 mg;
Excipients:
Sucrose – 94.7880 mg,
Cetyl alcohol – 54.8200 mg,
Colloidal silicon dioxide – 0.7900 mg,
Talc – 3.9500 mg,
Povidone K-25 – 1.0530 mg,
Magnesium stearate – 7.8990 mg;
Shell:
Hypromelose – 3.4355 mg,
Titanium dioxide E 171 CI 77891 – 0.8649 mg,
Talc – 2.4178 mg,
Polysorbate 80 – 0.3826 mg,
Macrogol 6000 – 0.6894 mg,
Crimson dye [Ponceau 4R] [E124] – 0.0441 mg, brown dye [sunset yellow dye [E110] + azorubine dye [E122] + brilliant black dye [E151]] – 0.0147 mg, aluminum varnish based on sunset yellow dye [E110] – 0.0500 mg.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
There is insufficient data on the safety of diclofenac in pregnant women.
Therefore, diclofenac should be prescribed in the first and second trimesters of pregnancy only in cases where the expected benefit to the mother outweighs the potential risk to the fetus.
Diclofenac, like other inhibitors of prostaglandin synthesis, is contraindicated in the last 3 months of pregnancy (possible suppression of uterine contractility and premature closure of the ductus arteriosus in the fetus).
Diclofenac passes into breast milk in small quantities. To prevent undesirable effects on the child, the drug should not be prescribed to nursing women.
If it is necessary to use the drug, breastfeeding should be stopped.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to the active substance (including other NSAIDs) or auxiliary components;
Complete or incomplete combination of bronchial asthma, recurrent nasal polyposis and paranasal sinuses and intolerance to acetylsalicylic acid or other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (including a history);
Erosive and ulcerative changes in the mucous membrane of the stomach or duodenum, active gastrointestinal bleeding;
Inflammatory bowel diseases (ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease) in the acute phase;
The period after coronary artery bypass surgery;
III trimester of pregnancy, breastfeeding period;
Confirmed chronic heart failure (II-IV functional class according to the NYHA classification);
Coronary heart disease;
Peripheral arterial disease or cerebrovascular disorders;
Hematopoietic disorders, hemostasis disorders (including hemophilia);
Severe liver failure or active liver disease;
Severe renal failure (creatinine clearance less than 30 ml/min); progressive kidney disease;
Confirmed hyperkalemia;
Sucrase/isomaltase deficiency, fructose intolerance, glucose-galactose malabsorption (the drug contains sucrose).
Children under 18 years of age.
With caution
Anemia, bronchial asthma, confirmed chronic heart failure of functional class I according to the NYHA classification, arterial hypertension, edema syndrome, hepatic or renal failure (creatinine clearance 30-60 ml/min), dyslipidemia, hyperlipoproteinemia, diabetes mellitus, smoking, inflammatory bowel diseases, condition after major surgical interventions, inducible porphyria, diverticulitis, systemic connective tissue diseases, pregnancy I-II trimester.
Anamnestic data on the development of peptic ulcer disease of the gastrointestinal tract, the presence of Helicobacter pylori infection, old age, long-term use of NSAIDs, frequent alcohol consumption, severe somatic diseases.
Concomitant therapy with anticoagulants (for example, warfarin), antiplatelet agents (for example, acetylsalicylic acid, clopidogrel), oral glucocorticosteroids (for example, prednisolone), selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (for example, citalopram, fluoxetine, paroxetine, sertraline).
In patients with seasonal allergic rhinitis, swelling of the nasal mucosa (including nasal polyps), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, chronic respiratory tract infections (especially those associated with allergic rhinitis-like symptoms), allergies to other drugs, and in patients with a significant decrease in circulating blood volume, diclofenac should be used with caution.
Side Effects
Side Effects
Criteria for assessing the frequency of adverse reactions: very often (>1/10), often (≥1/100, <1/10), infrequently (≥1/1000, <1/100), rarely (≥1/10000, <1/1000) and very rarely (<1/10000); frequency unknown - based on available data, it is not possible to determine the frequency of occurrence.
Gastrointestinal disorders:
often – epigastric pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, dyspepsia, flatulence, anorexia;
rarely – gastritis, proctitis, bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract (gastrointestinal tract) (vomiting with blood, melena, diarrhea mixed with blood), gastrointestinal ulcers (with or without bleeding or perforation);
very rarely – stomatitis, glossitis, esophagitis, nonspecific hemorrhagic colitis, exacerbation of ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease, the occurrence of diaphragm-like strictures in the intestine, constipation, pancreatitis.
Disorders of the liver and biliary tract:
often – increased aminotransferase activity;
rarely – hepatitis, jaundice, liver dysfunction;
very rarely – fulminant hepatitis, liver necrosis, liver failure.
Nervous system disorders:
often – headache, dizziness; rarely – drowsiness; very rarely – sensory disturbance, incl. paresthesia, memory disorders, tremor, convulsions, anxiety, cerebrovascular disorders, aseptic meningitis.
Mental disorders: very rarely – disorientation, depression, insomnia, nightmares, irritability, mental disorders.
Sensory organ disorders:
often – vertigo;
very rarely – visual impairment (blurred vision, diplopia), hearing impairment, tinnitus, impaired sense of taste.
Renal and urinary tract disorders:
very rarely – acute renal failure, hematuria, proteinuria, interstitial nephritis, nephrotic syndrome, papillary necrosis.
Blood and lymphatic system disorders:
very rarely – thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, hemolytic and aplastic anemia, agranulocytosis, eosinophilia.
Immune system disorders:
anaphylactic/anaphylactoid reactions, including a marked decrease in blood pressure (BP) and shock;
very rarely – angioedema (including the face).
Cardiovascular system disorders:
very rarely – palpitations, chest pain, increased blood pressure, vasculitis, heart failure, myocardial infarction.
Respiratory system disorders:
organs of the chest and mediastinum: rarely – exacerbation of bronchial asthma, cough, laryngeal edema; very rarely – pneumonitis.
Disorders of the skin and subcutaneous tissues:
often – skin rash; rarely – urticaria;
very rarely – bullous rashes, eczema, incl. multiforme and Stevens-Johnson syndrome, Lyell’s syndrome, exfoliative dermatitis, itching, hair loss, photosensitivity, purpura, incl. allergic.
General disorders and disorders at the injection site:
rarely – swelling.
Interaction
Interaction
Lithium preparations, digoxin: diclofenac may increase the concentrations of lithium and digoxin in the blood plasma.
Monitoring of plasma lithium and digoxin concentrations is recommended during concomitant use with diclofenac.
Methotrexate: caution is required when prescribing diclofenac less than 24 hours before or 24 hours after taking methotrexate, because in such cases, the concentration of methotrexate in the blood may increase and its toxic effect may increase.
Cyclosporine: The effect of diclofenac on the synthesis of prostaglandins in the kidneys may enhance the nephrotoxicity of cyclosporine. Therefore, the doses of diclofenac used should be lower than in patients not using cyclosporine.
Diuretics and antihypertensive drugs: diclofenac may reduce the hypotensive effect of diuretics and antihypertensive drugs (for example, beta-blockers, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors – ACE inhibitors).
In patients, especially elderly patients, these combinations should be prescribed with caution and blood pressure should be regularly monitored.
Patients should be adequately hydrated. After initiation and periodically during treatment, especially when diuretics and ACE inhibitors are coadministered, renal function should be monitored due to the increased risk of nephrotoxicity.
Drugs that can cause hyperkalemia: simultaneous use of diclofenac with potassium-sparing diuretics, cyclosporine, tacrolimus or trimethoprim may lead to increased concentrations of
potassium in the blood serum (if this combination of drugs is used, this indicator should be regularly monitored).
Antibacterial agents – quinolone derivatives: there are isolated reports of the development of seizures in patients receiving concomitant quinolone derivatives and diclofenac.
Anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents: it is necessary to combine diclofenac with drugs of these groups with caution due to the risk of bleeding.
Although clinical studies have not established the effect of diclofenac on the action of anticoagulants, there are isolated reports of an increased risk of bleeding in patients taking this combination of drugs.
Therefore, in the case of this combination of drugs, regular and careful monitoring of patients is recommended.
Acetylsalicylic acid reduces the concentration of diclofenac in the blood.
NSAIDs and corticosteroids: Concomitant use of systemic diclofenac and other systemic NSAIDs or corticosteroids may increase the incidence of side effects (particularly gastrointestinal).
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs): simultaneous use of diclofenac and drugs from the SSRI group increases the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding.
Hypoglycemic drugs: clinical studies have shown that when used together, diclofenac does not affect the effectiveness of hypoglycemic drugs.
However, there are isolated reports of the development of both hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia in such cases, which required changing the dose of hypoglycemic drugs during diclofenac therapy.
Therefore, during the combined use of diclofenac and hypoglycemic drugs, it is recommended to monitor blood glucose concentrations.
Phenytoin: with simultaneous use of phenytoin and diclofenac, it is necessary to monitor the concentration of phenytoin in the blood plasma due to a possible increase in its systemic exposure.
Tacrolimus: increased nephrotoxicity is possible when used concomitantly with diclofenac.
Cefamandole, cefoperazone, cefotetan, valproic acid and plicamycin increase the incidence of hypoprothrombinemia.
The effect of diclofenac on the synthesis of prostaglandins in the kidneys may enhance the toxic effect of gold preparations.
Simultaneous use with ethanol, colchicine, corticotropin and St. John’s wort preparations increases the risk of bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract.
Potent CYP2C9 inhibitors: Caution should be exercised when co-administering diclofenac and strong CYP2C9 inhibitors (such as voriconazole) due to the possible increase in diclofenac serum concentrations and increased systemic effects.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms:
vomiting, bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract, epigastric pain, diarrhea, dizziness, tinnitus, lethargy, convulsions, rarely – increased blood pressure, acute renal failure, hepatotoxic effect, respiratory depression, coma.
Treatment:
gastric lavage, activated charcoal, symptomatic therapy aimed at eliminating increased blood pressure, renal dysfunction, convulsions, gastrointestinal irritation, respiratory depression. Forced diuresis and hemodialysis are ineffective (due to the significant connection with proteins and intensive metabolism).
Recommendations for use
Recommendations for use
In all patients receiving diclofenac, it should be used at the minimum effective dose for the shortest time required to reduce symptoms.
Orally, without chewing, during or after meals, with plenty of water.
1 tablet 1 time per day. If additional drug intake is necessary, use 50 mg tablets. The maximum daily dose is 150 mg.
Prescribing
Prescribing
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID)
Complete set of goods
Complete set of goods
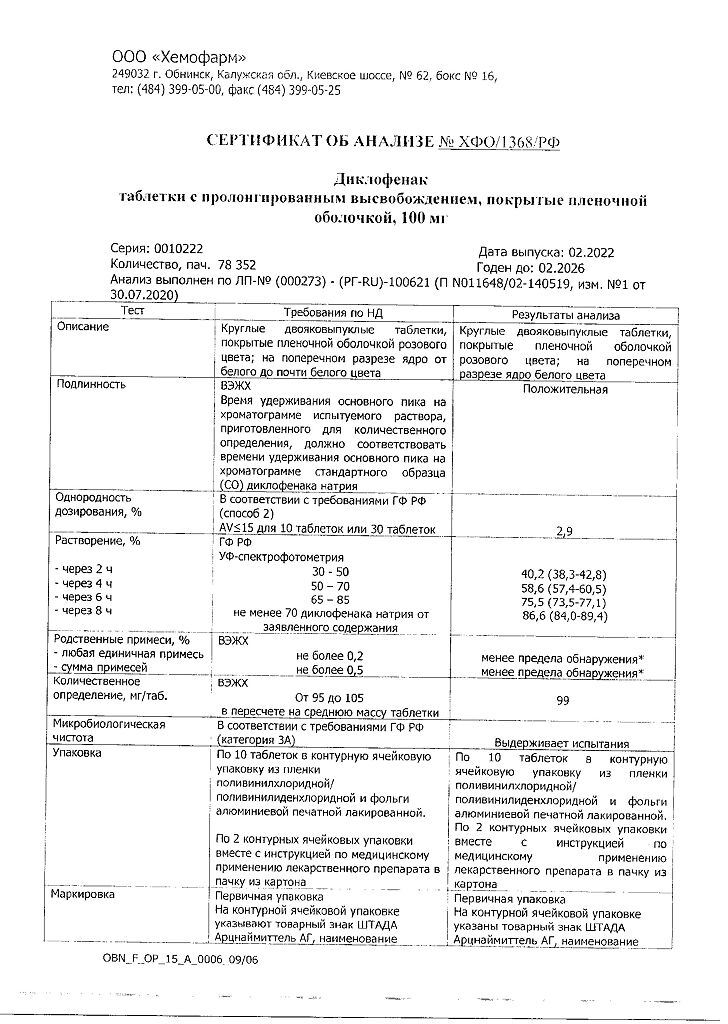
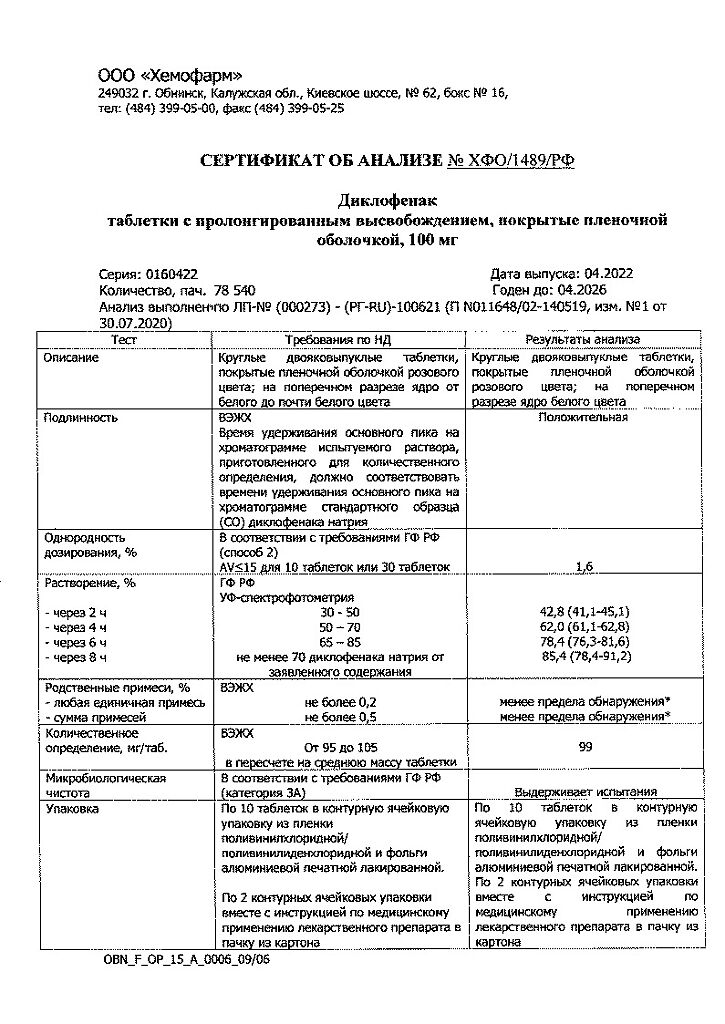
Extended-release film-coated tablets, 100 mg.
10 tablets per blister pack (blister) made of polyvinyl chloride/polyvinylidene chloride film and printed varnished aluminum foil.
2 blister packs along with instructions for use in a cardboard pack.
Functional features
Functional features
Absorption is rapid and complete, food slows the rate of absorption by 1-4 hours and reduces the maximum concentration (Cmax) by 40%.
After oral administration of 100 mg tablets, Cmax – 0.5 mcg / ml is achieved after – 4-5 hours. Plasma concentration is linearly dependent on the size of the administered dose.
There are no changes in the pharmacokinetics of diclofenac following repeated administration. Does not accumulate if the recommended interval between doses is observed.
Bioavailability – 50%. Communication with plasma proteins is more than 99% (most of it is associated with albumin).
Penetrates into synovial fluid; Cmax in synovial fluid is observed 2-4 hours later than in plasma. The half-life (T½) from synovial fluid is 3-6 hours (the concentration of the active substance in synovial fluid 4-6 hours after administration of the drug is higher than in plasma, and remains higher for another 12 hours).
The relationship between the concentration of the drug in the synovial fluid and the clinical effectiveness of the drug has not been clarified.
Metabolism: 50% of the active substance is metabolized during the “first pass” through the liver.
Metabolism occurs as a result of multiple or single hydroxylation and conjugation with glucuronic acid.
The CYP2C9 isoenzyme takes part in the metabolism of the drug. The pharmacological activity of the metabolites is lower than that of diclofenac.
Systemic clearance is approximately 260 ± 50 ml/min, volume of distribution is 550 ml/kg.
T½ from plasma averages about 2.5 hours. 65% of the administered dose is excreted in the form of metabolites by the kidneys; less than 1% is excreted unchanged, the rest of the dose is excreted as metabolites in bile.
In patients with severe renal failure (creatinine clearance (CC) less than 10 ml/min), the excretion of metabolites in bile increases, but no increase in their concentration in the blood is observed.
In patients with chronic hepatitis or compensated liver cirrhosis, the pharmacokinetic parameters of diclofenac do not change.
Diclofenac passes into breast milk.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
Store in a dry place, protected from light at a temperature not exceeding 25 C.
Keep out of the reach of children.
Shelf life
Shelf life
4 years. Do not use after the expiration date stated on the package.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Hemofarm LLC, Russia
Additional information
| Shelf life | 4 years. Do not use after the expiration date printed on the package. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | Store in a dry, dark place at temperatures under 25 C. Keep out of the reach of children. |
| Manufacturer | Chemopharm LLC, Russia |
| Medication form | sustained release tablets |
| Brand | Chemopharm LLC |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Diclofenac, 100 mg 20 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.