No products in the cart.
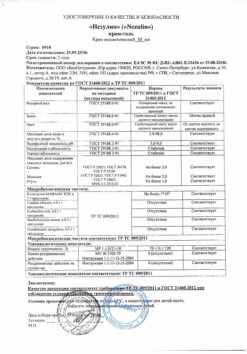
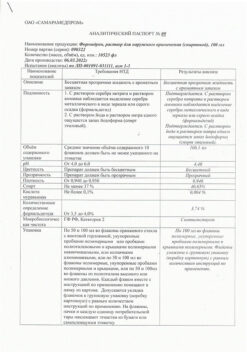
Dermazine, cream 1% 50 g
€10.59 €9.27
Description
Dermazine is a broad spectrum antibacterial.
Blocks folate synthesis in the microbial cell (sulfadiazine) and the activity of enzymes – primarily SH-containing (Ag).
Indications
Indications
Burns, bedsores, deep wounds.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Dermazin is a broad spectrum antibacterial.
Blocks the synthesis of folate in the microbial cell (sulfadiazine) and the activity of enzymes, primarily SH-containing (Ag).
Special instructions
Special instructions
Avoid getting the drug into your eyes. Dermazin cream should be used with caution in patients with hypersensitivity to sulfonamides (due to the possible occurrence of allergic reactions); with congenital deficiency of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (in the treatment of minor superficial burns); with impaired renal or liver function (cumulation may occur; for such patients, monitoring of the level of sulfonamide in the blood plasma is necessary).
Not used in patients with porphyria.
Dangerous skin reactions such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis have been reported during treatment with sulfadiazine.
The greatest risk of such reactions occurs in the first weeks of treatment. At the first manifestations of hypersensitivity (progressive skin rash, often with blisters and damage to the mucous membrane), use of the drug should be discontinued. Only for minor superficial burns can the cream be used independently. Patients with deeper burns should always consult a physician before starting treatment.
Burns affecting 2% or more of the body’s surface area (approximately 1 palm of the patient’s hand corresponds to 1% of the patient’s body surface area), as well as burns affecting the eyes, ears, face, arms, legs, and/or perineum, require medical evaluation.
Consultation with a physician is necessary for skin wounds containing foreign materials that cannot be removed; with deep puncture wounds; animal bites; for wounds with significant redness, sudden development of edema and wounds accompanied by fever. If treatment involves long-term use of Dermazin cream over large areas of skin, monitoring of blood counts is necessary, since leukopenia, thrombocytopenia and eosinophilia may occur.
When treating massive wounds, plasma concentrations of sulfadiazine can reach therapeutic levels. Systemic side effects of sulfonamides may develop. Therefore, it is recommended to monitor the concentration of sulfadiazine in the blood plasma, kidney function, and also examine the urine for the occurrence of crystalluria.
As with other local antimicrobial agents, superinfection may develop during treatment. Very rarely, an increase in body temperature is possible, which is associated with unwanted side effects. The excipients methyl parahydroxybenzoate and propyl parahydroxybenzoate can cause allergic reactions, including delayed ones, and in some cases bronchospasm. Dermazin contains peanut oil.
Patients with hypersensitivity to peanuts or soy should not use this drug. Propylene glycol, which is part of the drug, may cause skin irritation. Cetyl alcohol may also cause local skin reactions (eg contact dermatitis).
Children.
Due to the risk of kernicterus, silver sulfadiazine should not be used in premature infants, newborns and children under 3 months of age. Since the effectiveness and safety of the drug in children over 3 months of age have not been determined, it is recommended to prescribe the drug to patients in this age category after consultation with a doctor.
The ability to influence reaction speed when driving vehicles or working with other mechanisms.
There is no data regarding negative effects.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Sulfadiazine
Composition
Composition
Active ingredient:
silver sulfadiazine 10 mg;
Excipients:
cetyl alcohol;
hydrogenated peanut oil;
polysorbate 60;
propylene glycol;
methyl parahydroxybenzoate;
propyl parahydrosibenzoate;
purified water
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency, pregnancy.
Side Effects
Side Effects
Itching, burning sensation. With prolonged use on large surfaces, systemic effects characteristic of sulfonamides are possible.
Interaction
Interaction
When used simultaneously with cimetidine, the incidence of leukopenia may increase.
Silver sulfadiazine may inactivate enzyme wound cleansers when used concomitantly.
When treating extensive burns, when the concentration of silver sulfadiazine in the blood plasma reaches therapeutic values, it should be taken into account that the effect of drugs used systemically may change.
Overdose
Overdose
In case of an overdose of the cream, side effects associated with the systemic use of all sulfonamides may occur.
Long-term use of silver sulfadiazine in high doses may cause an increase in plasma silver levels.
However, these levels normalize after treatment is stopped.
In patients with severe burns during long-term treatment, a significant increase in plasma osmolarity was noted.
The reason for this may be increased resorption of propylene glycol, which is part of the drug, through the affected skin.
Treatment is symptomatic.
If necessary, kidney function and blood counts should be monitored.
Absorbed sulfadiazine is easily eliminated by hemo- and peritoneal dialysis.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
At a temperature not exceeding 25 °C.
Shelf life
Shelf life
3 years
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Salutas Pharma GmbH, Germany
Additional information
| Shelf life | 3 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | At a temperature not exceeding 25 °C. |
| Manufacturer | Salutas Pharma GmbH, Germany |
| Medication form | exterior cream |
| Brand | Salutas Pharma GmbH |
Related products
Buy Dermazine, cream 1% 50 g with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.