No products in the cart.
Description
Dacarbazine is an alkylating antitumor agent with a chemical composition of 5-(3,3-dimethyl-1-triazeno)-imidazole-4-carboxamide. The drug becomes active after metabolism in the liver.
The three pathways of action of dacarbazine are thought to exist: alkylation due to carbonium ions, inhibition of purine bases and interaction with SH groups. The drug is phase specific.
The maximum plasma concentration is usually reached immediately after intravenous administration of the drug. Binding with plasma proteins is very low (about 5%). It passes through the blood-brain barrier in insignificant amounts. There is no data on its penetration into the placenta and the mother’s milk.
The drug is excreted from the body in two phases with the initial half-life of about 20 minutes and the final one – about 5 hours; in case of liver or kidney function disorders these indices are about 55 minutes and 7 hours respectively.
The drug undergoes dimethylation by hepatic microsomal enzymes to form carbon dioxide, which is excreted with exhaled air and aminoimidazolcarboxamide, which is excreted with urine. 40% of the drug is excreted unchanged by kidneys mainly due to glomerular filtration.
.
Indications
Indications
• Melanoma
• Lymphogranulomatosis
• Soft tissue sarcoma (excluding Kaposi’s sarcoma).
There are reports of the effectiveness of dacarbazine in combination with other cytostatics in the treatment of osteogenic sarcoma, uterine sarcoma, pleural and peritoneal mesothelioma, small cell lung cancer, thyroid cancer, carcinoid, pheochromocytoma, insulinoma, neuroblastoma and gliomas.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Dacarbazine is an antitumor agent with alkylating action and its chemical composition is 5-(3,3-dimethyl-1-triazeno)-imidazole-4-carboxamide. The drug becomes active after metabolism in the liver.
It is believed that there are three ways of the mechanism of action of dacarbazine: alkylation due to carbonium ions, inhibition of purine bases and interaction with SH groups. The drug is phase-nonspecific.
The maximum plasma concentration is usually achieved immediately immediately after intravenous administration of the drug. Communication with plasma proteins is very low (about 5%). Penetrates the blood-brain barrier in small quantities. There is no data on its penetration into the placenta and breast milk.
The drug is eliminated from the body in two phases with an initial half-life of about 20 minutes and a final half-life of approximately 5 hours; if liver or kidney function is impaired, these figures are approximately 55 minutes and 7 hours, respectively.
The drug undergoes dimethylation by liver microsomal enzymes to form carbon dioxide, which is excreted in exhaled air, and aminoimidazole carboxamide, excreted in the urine. 40% of the drug is excreted unchanged by the kidneys, mainly due to glomerular filtration.
Special instructions
Special instructions
Dacarbazine should be used under the supervision of a physician experienced in working with anticancer drugs. During and after treatment, careful monitoring of the peripheral blood picture, liver function and its size is necessary.
If abnormal liver or renal function, symptoms of hypersensitivity to the drug, or hepatic vein thrombosis occur, treatment with dacarbazine should be discontinued immediately.
When the first signs of extravasation of dacarbazine appear (burning or pain at the injection site), administration should be stopped immediately.
The remaining dose should be injected into another vein. During treatment and for 6 months after, reliable methods of contraception should be used. During therapy with dacarbazine, vaccination with vaccines containing live pathogens should not be performed.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
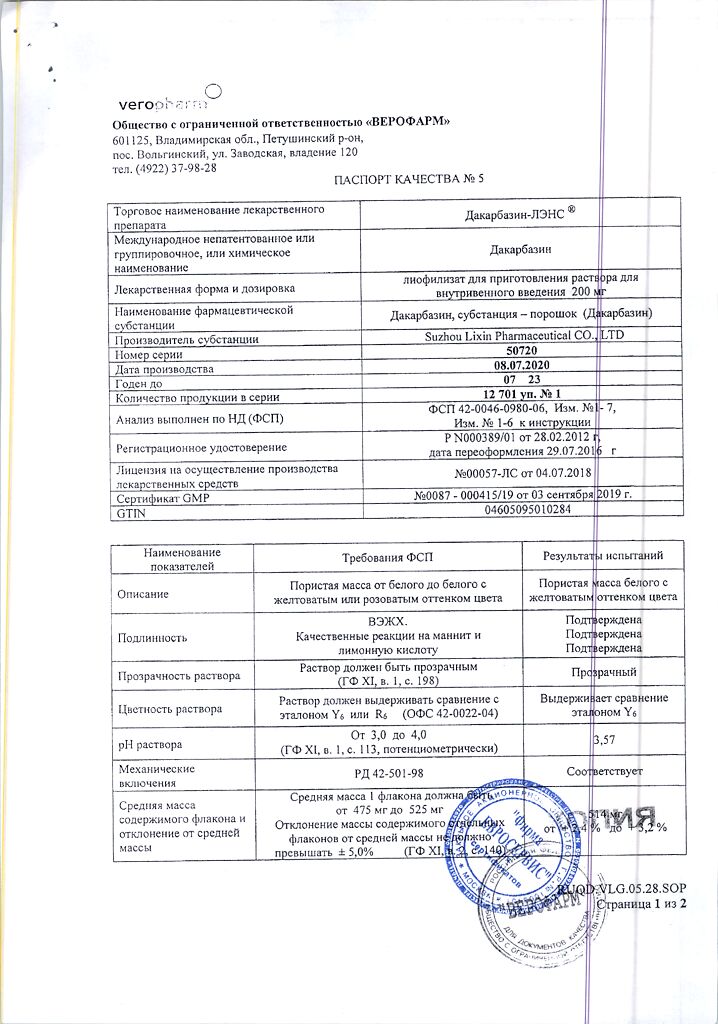
Dacarbazine
Composition
Composition
1 bottle contains:
Active substance:
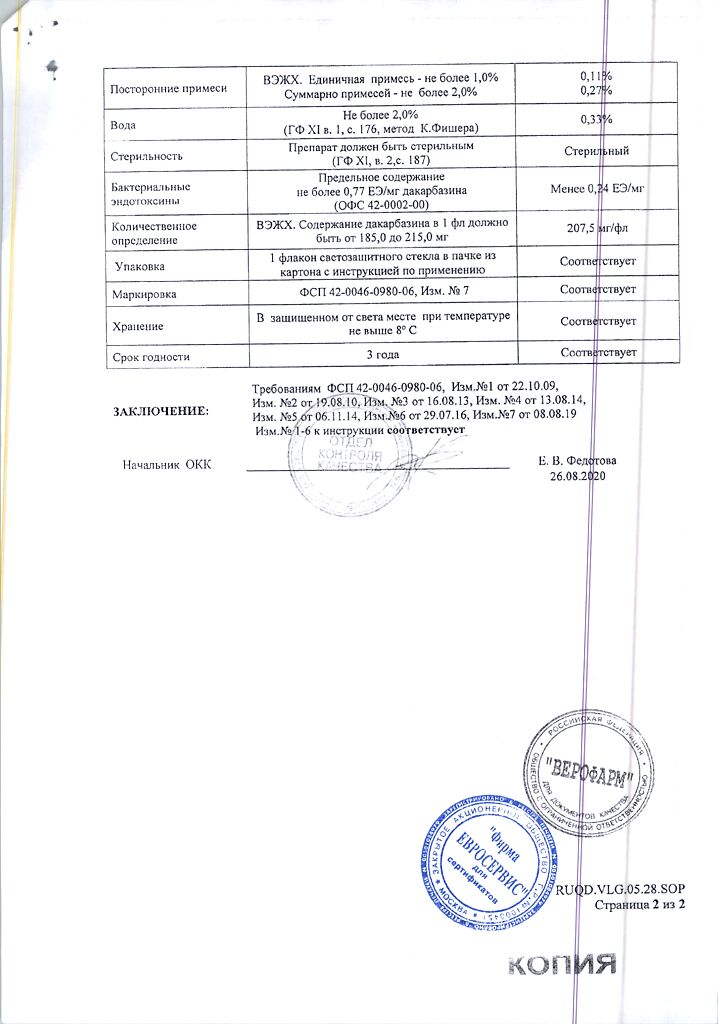
Dacarbazine 200 mg
Excipients:
citric acid 200 mg
mannitol 100 mg
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
Dacarbazine is contraindicated during pregnancy.
If use is necessary during lactation, breastfeeding should be discontinued.
Women of childbearing age should use reliable methods of contraception.
Experimental studies have revealed the toxic effect of dacarbazine on the fetus.
Contraindications
Contraindications
– hypersensitivity to dacarbazine or to any of the auxiliary components of the drug;
– pronounced inhibition of bone marrow hematopoiesis;
– severe liver or kidney failure;
– pregnancy and lactation period.
With caution: in case of myelodepression (including against the background of concomitant radiation and chemotherapy), acute infectious diseases of viral (including chickenpox, herpes zoster), fungal or bacterial nature (risk of severe complications and generalization of the process), concomitant radiation therapy.
Side Effects
Side Effects
From the hematopoietic organs: anemia, leukopenia, granulocytopenia, thrombocytopenia. Inhibition of myelopoiesis is a dose-limiting side effect. Leukocytopenia is usually observed on the 14th day, thrombocytopenia on the 18th day after the end of therapy and lasts on average up to 1 week. Blood counts are restored by the 4th week.
From the digestive system: nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, stomatitis; rarely – diarrhea, increased activity of liver enzymes. Very rarely – hepatonecrosis caused by occlusion of intrahepatic veins, possibly with a fatal outcome (as a rule, this syndrome occurred during the 2nd course of treatment). Symptoms include fever, eosinophilia, abdominal pain, liver enlargement, and shock, which rapidly increases in severity over hours or days.
From the nervous system: headache, blurred vision, confusion, severe drowsiness, convulsions, asthenic syndrome, paresthesia, facial skin hypoesthesia.
From the reproductive system: amenorrhea, azoospermia.
Allergic reactions: skin rash, facial flushing, fever, anaphylactic reactions.
From the skin and skin appendages: rarely – alopecia, hyperpigmentation and photosensitivity of the skin.
Local reactions: pain at the injection site and along the vein. If the drug gets under the skin – sharp pain, necrosis of surrounding tissues.
Other: flu-like syndrome, secondary infections, hepatic vein thrombosis, myalgia. Long-term use increases the risk of developing tumors.
Interaction
Interaction
Enhances the effect (including toxic) of phenobarbital, azathioprine, 6-mercaptopurine, allopurinol. Inducers of microsomal liver enzymes (barbiturates, rifampicin, phenytoin) enhance the toxic effect of dacarbazine.
Dacarbazine may enhance the photosensitizing effect of methoxypsoralen.
Dacarbazine solution is chemically incompatible with heparin, hydrocortisone, L-cysteine and sodium bicarbonate.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: increased inhibition of bone marrow hematopoiesis and the severity of dyspeptic disorders.
Treatment: symptomatic, specific antidote unknown.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
In a dry place, protected from light, at a temperature of 2–8 °C
Shelf life
Shelf life
2 years
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Veropharm LLC, Russia
Additional information
| Shelf life | 2 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | In a dry, light-protected place at 2-8 °C |
| Manufacturer | Veropharm AO, Russia |
| Medication form | lyophilizate |
| Brand | Veropharm AO |
Related products
Buy Dacarbazine-LENS, lyophilizate 200 mg with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.