No products in the cart.
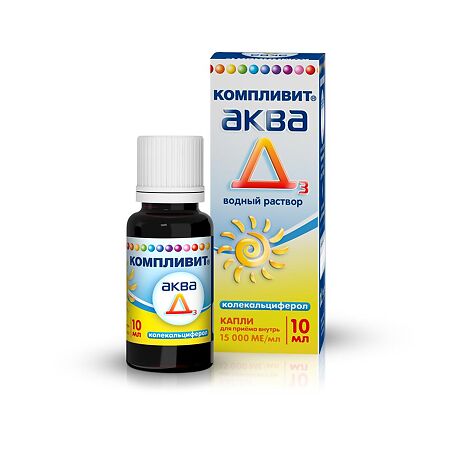
Complivit Aqua D3, drops 15000 me/ml 10 ml
€5.22 €4.35
Out of stock
(E-mail when Stock is available)
Description
Pharmacotherapeutic group
Calcium-phosphorus metabolism regulator.
The ATX code: A11CC05
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
Vitamin D3 is an active anti-rachitis factor. The most important function of vitamin D3 is to regulate calcium and phosphate metabolism, which promotes proper mineralization and skeletal growth.
Vitamin D3 is the natural form of vitamin D that is produced in humans in the skin by sunlight. Compared to vitamin D2, it has 25% higher activity.
Calciferol plays an essential role in the absorption of calcium and phosphate from the intestine, in the transport of mineral salts and in the calcification of bones, and also regulates the excretion of calcium and phosphate by the kidneys.
Deficiency of vitamin D in food, impaired absorption, calcium deficiency, and lack of exposure to sunlight leads to: in children during intensive growth – to rickets, in adults – to osteomalacia, pregnant women may experience symptoms of tetany, in newborns – disorders of calcification of bone tissue.
The increased requirement for vitamin D occurs in women during menopause due to the development of hormonal disorders leading to osteoporosis.
Pharmacokinetics.
Aqueous solution of vitamin D3 is absorbed better than the oil solution. Premature infants have insufficient bile formation and intestinal intake, which impairs absorption of vitamins in the form of oil solutions. After oral administration, colecalciferol is absorbed in the small intestine. It is metabolized in the liver and kidneys.
Half-life period of colecalciferol from blood is several days and may be prolonged in case of renal insufficiency. The drug penetrates through the placental barrier and into the mother’s milk. Vitamin D3 has the property of cumulation. It is excreted by the kidneys in small amounts, most of it is excreted with bile.
Indications
Indications
Prevention of vitamin D deficiency and diseases associated with its insufficiency (rickets, osteomalacia).
The treatment of rickets.
Comprehensive therapy of osteoporosis of different genesis.
Composition
Composition
Ingredients for 1 ml:
Active ingredient:
colecalciferol (vitamin D3) -0.375*mg (15000 IU)
Additives:
Macroglaglycerylricinoleate-75,000 mg;
sugarose(white sugar) 250,000 mg;
sodium hydrophosphate dodecahydrate-7,000 mg;
citric acid (citric acid monohydrate) -0.430 mg;
anethol – 0.825 mg;
benzyl alcohol – 15.000 mg;
purified water to 1 ml.
How to take, the dosage
How to take, the dosage
Orally.
The drug Complivit® Aqua D3 is taken by mouth in a scoop of liquid.
1 drop contains about 500 ME of vitamin D3.
Prevention of rickets:
– preterm infants from 4 weeks of life -1 drop(500ME) per day;
– premature infants from 4 weeks of life -2 drops (1000ME) per day for the first year of life, then 1 drop (500 ME) per day.
The drug should be used during the first two years of the child’s life, during periods of low insolation (especially in winter).
The treatment of rickets:
In the absence of visible deformities of the bones (mild rickets) 2-3 drops (1000-1500 ME) a day, the treatment must be continued for 30 days.
In case of presence of bone deformities typical for moderate and severe rickets 4-8 drops (2000-4000 ME) per day, the treatment should be continued for 30-45 days; the drug dose and duration of therapy depend on the intensity of changes and are determined by the doctor (see Special indications).
Prevention of vitamin D deficiency and diseases associated with its insufficiency (osteomalacia):
1 drop (500ME) per day for the duration of the period accompanied by vitamin D deficiency. The minimum duration of prophylaxis is 1 month.
In case of complex treatment of osteoporosis:
1 to 2 drops (500-1000 ME) a day for 3 months – repeated courses of therapy are possible on the recommendation of the doctor depending on the results of evaluation of markers of bone and calcium metabolism (see Special indications).
Interaction
Interaction
Antiepileptic agents (especially phenytoin and phenobarbital, primidone), rifampicin, colestiramine reduce vitamin D reabsorption3.
The use simultaneously with thiazide diuretics increases the risk of hypercalcemia. In such cases continuous monitoring of calcium concentration in blood is necessary.
In hypervitaminosis D3 there may be increased activity of cardiac glycosides and increased risk of arrhythmias due to development of hypercalcemia (monitoring of blood calcium concentration, electrocardiogram, and correction of cardiac glycoside dose are reasonable).
The concomitant therapy with glucocorticosteroids may decrease the effectiveness of vitamin D3.
Long-term use of antacids containing aluminum and magnesium in combination with vitamin D3 may increase aluminum and magnesium concentrations in the blood and as a consequence, toxic effects of aluminum on bone tissue and hypermagnesemia in patients with renal insufficiency.
Colestyramine, colestipol and mineral oils reduce gastrointestinal absorption of fat-soluble vitamins and require increasing their dose.
The concomitant use of benzodiazepines increases the risk of hypercalcemia.
Drugs containing high concentrations of calcium and phosphorus increase the risk of hyperphosphatemia.
In concomitant use with sodium fluoride, the interval between doses should be at least 2 hours; with oral forms of tetracyclines, at least 3 hours.
Simultaneous use with other analogues of vitamin D increases the risk of vitamin D hypervitaminosis.
Ketoconazole may inhibit both biosynthesis and catabolism of 1,25(OH)2-cocalciferol.
Vitamin D is an antagonist of drugs used in hypercalcemia: calcitonin, etidronate, pamidronate, plikamycin, gallium nitrate.
Isoniazid and rifampicin can decrease the effect of the drug due to increased biotransformation rate.
VitaminD3 does not interact with food.
Special Instructions
Special Instructions
Avoid overdose.
The amount of vitamin D and calcium taken with food and other medications must be taken into account when taking the drug.
High doses of vitamin D3 used for long periods or shock doses can cause chronic hypervitaminosis of D3.
Do not use high doses of calcium at the same time as vitamin D3.
The drug should be used with caution in patients with impaired urinary calcium and phosphate excretion, when treated with benzothiadiazine derivatives and in immobilized patients (risk of hypercalcemia and hypercalciuria). In these patients the plasma and urine calcium levels should be monitored.
Vitamin D3 should not be taken in pseudohypoparathyroidism because in this disease the vitamin D requirement may be reduced, which could lead to a risk of long-term overdose.
The main clinical manifestations of mild rickets include nervous excitability, restlessness, startle at loud sounds and light flashes, sleep disturbances, restless sleep, sweating, itchy skin, baldness in the back of the head, and suppleness of the edges of the great fontanelle.
The presence of visible bone deformities is common in moderate to severe rickets, which usually require hospitalization and medical therapy based on the results of the examination.
Renew courses of therapy for osteoporosis may be indicated by a physician, depending on the results of the assessment of bone and calcium metabolism markers.
If the physician prescribed a longer therapy than recommended in the instructions, the serum calcium and urine levels should be determined regularly (every three months of therapy), and renal function should be assessed by measuring serum creatinine levels. If necessary, the dose can be adjusted by the physician according to the level of serum calcium.
In case of hypercalcemia or signs of renal dysfunction, the drug dose should be reduced or treatment should be suspended. If urinary calcium levels exceed 7.5 mmol/24 h (300 mg/ 24 h), it is recommended that the drug dose be reduced or treatment withheld.
Influence on driving and operating ability
There are no data on possible effects of the drug on driving and operating ability.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to the ingredients of the drug, especially to benzyl alcohol.
Deficiency of sucrose/isomaltase, fructose intolerance, glucose-galactose malabsorption.
Vitamin D hypervitaminosis.
Elevated calcium levels in the blood (hypercalcemia), increased urinary calcium excretion (hypercalciuria), urolithiasis (formation of calcium oxalate stones) including history, renal osteodystrophy with hyperphosphatemia, pseudohypoparathyroidism.
Sarcoidosis.
Acute and chronic liver and kidney disease, renal failure.
Active form of pulmonary tuberculosis.
Children under 4 weeks of life.
With caution
In patients who are immobilized.
In patients taking thiazide diuretics and in patients with cardiovascular disease taking cardiac glycosides (see section “Interaction with other drugs”).
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms of acute vitamin D3 overdose:
The early manifestations (due to hypercalcemia) are constipation or diarrhea, dry oral mucosa, headache, thirst, pollakiuria, nycturia, polyuria, anorexia, metallic taste in the mouth, nausea, vomiting, general weakness and fatigue, hypercalcemia, hypercalciuria, dehydration;
. late manifestations – bone pain, turbidity of the urine (appearance of hyaline cylinders in the urine, proteinuria, leukocyturia), increased blood pressure, skin itching, photosensitivity of the eyes, conjunctival hyperemia, arrhythmia, somnolence, myalgia, nausea, vomiting, pancreatitis, gastralgia, weight loss, rarely – psychosis (mental changes) and mood changes.
The symptoms of chronic overdose of vitaminD3 (when taken for several weeks or months for adults at doses of 20000-60000 IU/day, children 2000-4000 IU/day): Calcinosis of soft tissues, kidneys, lungs, blood vessels, arterial hypertension, renal and chronic heart failure (these effects most often occur when combined with hypercalcemiahyperphosphatemia), growth disorder in children (long-term doses of 1800 IU/day).
Treatment: If the above symptoms occur, discontinue the drug and consult a physician. Low-calcium diet (for several weeks), large fluid intake, and assisted diuresis with furosemide, electrolytes, and administration of glucocorticosteroids,calcitonin are indicated.
With proper renal function, calcium levels can be significantly reduced by infusion of isotonic sodium chloride solution (3-6 liters over 24 hours) with furosemide and, in some cases, also sodium edetate at a dose of 15 mg/kg/h, while monitoring calcium levels and electrocardiogram data continuously. In contrast, hemodialysis (dialysate without calcium) is necessary in oligoanuria.A specific antidote is not known.
Pregnancy use
Pregnancy use
In pregnancy, the drug should not be used in doses higher than those recommended for the prevention of vitamin D deficiency (see section “Dosage and administration”) because of the possibility of teratogenic action in case of overdose.Care should be taken when prescribing vitamin D3 in women who are breast-feeding, because the drug taken in high doses by the mother may cause overdose symptoms in the baby.
Additional information
| Shelf life | 2 years. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | Store in a light-protected place at a temperature not exceeding 25 °С. Keep out of reach of children. |
| Manufacturer | Pharmstandard-Leksredstva, Russia |
| Medication form | oral drops |
| Brand | Pharmstandard-Leksredstva |
Related products
Buy Complivit Aqua D3, drops 15000 me/ml 10 ml with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.