No products in the cart.
Coldact with vitamin C, 10 pcs.
€11.51 €10.75
Description
Pharmacological properties
Combined drug, has antipyretic, anti-inflammatory, anti-edema, analgesic and anti-allergic effect, eliminates the symptoms of “colds”.
Pharmacodynamics
Paracetamol. It has analgesic and antipyretic effect similar to that of salicylates. Paracetamol also has weak anti-inflammatory activity. In equal doses, the degree of analgesic and antipyretic effect is comparable to that of aspirin.
Paracetamol reduces body temperature in patients with fever, but rarely reduces the normal temperature. The antipyretic effect is through the hypothalamus. Fever reduction is achieved due to vasodilation and increased peripheral blood flow.
Phenylephrine hydrochloride. It is a vasoconstrictor of sympathomimetics group. It has direct effect on a-adrenergic receptors. In therapeutic doses it does not affect β1-adrenergic receptors of the heart. Phenylephrine does not stimulate β2-adrenergic receptors of the bronchi or peripheral blood vessels.
α-adrenergic effects are thought to result in suppression of cyclic adenosine-3,5-monophosphate (cAMP) production by inhibiting adenyl cyclase, whereas β-adrenergic effects are caused by increased adenyl cyclase activity.
Phenylephrine indirectly promotes noradrenaline release. Vasoconstriction is the main effect of phenylephrine in therapeutic doses.
Chlorphenamine maleate. It has a pronounced antagonistic effect on H1-receptors of histamine. Antihistamines reduce or eliminate the effects of histamine through reversible binding of H1-receptor histamine in tissues.
Chlorphenamine also has anticholinergic activity. Antihistamines inhibit the release of histamine, prostaglandins, leukotrienes, and migration of inflammatory mediators.
The action of chlorpheiamine includes inhibition of histamine in smooth muscle tissue, reduction of capillary permeability and thereby reducing edema in allergic reactions.
Ascorbic acid (vitamin C). It replenishes the increased need for vitamin C during colds and flu, especially in the initial stages of the disease. Increases the body’s resistance to infections, improves the tolerance of paracetamol. Participates in various biochemical oxidation-reduction reactions.
It is an effective antioxidant. Taking ascorbic acid soothes the course of the disease and shortens its duration.
Pharmacokinetics:
Paracetamol. It is rapidly and almost completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Maximum plasma concentrations are reached 10-60 minutes after oral administration.
Paracetamol is widely distributed in all body tissues. It penetrates the placental barrier and is secreted with breast milk. Binding to plasma proteins is low at normal therapeutic concentrations, but increases with increasing concentrations.
Paracetamol is metabolized in the liver primarily by two pathways: glucuronidation and sulfation. Excreted by the kidneys, mainly as conjugates of glucuronide and sulfate. The elimination half-life is from 1 to 3 hours.
In severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance less than 30 ml/min) excretion of paracetamol and its metabolites is delayed.
Phenylephrine hydrochloride. Absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and metabolized by monoamine oxidase during primary passage through the intestinal wall and in the liver, so when ingested phenylephrine hydrochloride has limited bioavailability. It is excreted by the kidneys almost completely in the form of sulfate conjugate.
Maximal concentration of the drug in plasma is reached within 45 minutes to 2 hours and half-life period of the drug from plasma is 2-3 hours.
Chlorphenamine maleate. It is relatively slowly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, maximum concentrations of chlorphenamine in plasma are achieved 2.5-6 hours after taking the drug.
The substance has low bioavailability of 25-50%. About 70% of chlorphenamine in bloodstream is bound to plasma proteins. It is widely distributed in body tissues including central nervous system (CNS).
Chlorphenamine undergoes significant metabolism during primary passage. The duration of action is 4-6 hours. In children, faster and more complete absorption, faster clearance, and a shorter half-life were noted.
The half-life is 2 to 43 hours, even with an average duration of action of 4-6 hours. Part of chlorphenamine unchanged with metabolites was excreted by the kidneys.
Ascorbic acid. It is easily absorbed after oral administration. Under normal dosing regimen (30-180 mg/day) about 70-90% of the vitamin is absorbed; further increasing the dose reduces absorption (50-20%).
Ascorbic acid is widely distributed in tissues. High concentrations of the vitamin are found in the liver, white blood cells, platelets, glandular tissue and the lens of the eye. About 25% of the vitamin is bound to plasma proteins. Ascorbic acid passes through the placental barrier. The concentration in umbilical cord blood is usually 2-4 times higher than in maternal blood.
Ascorbic acid is reversibly oxidized to dehydroascorbic acid. Some amount is metabolized to inactive derivatives (sulfates and oxalates) and excreted in the urine.
Indications
Indications
Elimination of cold symptoms and
flu, such as fever, headache, chills, sore throat
joints and muscles, feeling of nasal congestion, runny nose, sneezing, pain in
sinuses and throat.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological properties
A combined drug that has antipyretic, anti-inflammatory, decongestant, analgesic and antiallergic effects, eliminates the symptoms of “colds”.
Pharmacodynamics
Paracetamol. It has analgesic and antipyretic effects similar to those of salicylates. Paracetamol also exhibits weak anti-inflammatory activity. In the same doses, the degree of analgesic and antipyretic effect is comparable to the effect of aspirin.
Paracetamol reduces body temperature in patients with fever, but rarely reduces normal temperature. The antipyretic effect is carried out through the hypothalamus. Reduction of fever is achieved due to vasodilation and increased peripheral blood flow.
Phenylephrine hydrochloride. It is a vasoconstrictor from the group of sympathomimetics. Has a direct effect on a-adrenergic receptors. In therapeutic doses it does not affect β1-adrenergic receptors of the heart. Phenylephrine does not stimulate β2-adrenergic receptors in the bronchi or peripheral blood vessels.
It is believed that α-adrenergic effects lead to suppression of cyclic adenosine 3,5-monophosphate (cAMP) production by inhibiting adenyl cyclase, while β-adrenergic effects are caused by increasing adenyl cyclase activity.
Phenylephrine indirectly promotes the release of norepinephrine. Vasoconstriction is the main effect of phenylephrine at therapeutic doses.
Chlorphenamine maleate. It has a pronounced antagonistic effect on histamine H1 receptors. Antihistamines reduce or eliminate the effects of histamine by reversibly binding to histamine H1 receptors in tissues.
Chlorphenamine also has anticholinergic activity. Antihistamines prevent the release of histamine, prostaglandins, leukotrienes, as well as the migration of inflammatory mediators.
The effects of chlorpheniamine include inhibition of histamine in smooth muscle tissue, reduction of capillary permeability and, consequently, reduction of swelling in allergic reactions.
Ascorbic acid (vitamin C). Replenishes the increased need for vitamin C during colds and flu, especially in the initial stages of the disease. Increases the body’s resistance to infections and improves paracetamol tolerance. Participates in various biochemical oxidation-reduction reactions.
Is an effective antioxidant. Taking ascorbic acid softens the course of the disease and shortens its duration.
Pharmacokinetics:
Paracetamol. Quickly and almost completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Maximum plasma concentrations are achieved 10-60 minutes after oral administration.
Paracetamol is widely distributed in all tissues of the body. Penetrates the placental barrier and is secreted into breast milk. Plasma protein binding is negligible at normal therapeutic concentrations, but increases with increasing concentrations.
Paracetamol is metabolized in the liver primarily in two ways: glucuronidation and sulfation. It is excreted by the kidneys, mainly in the form of glucuronide and sulfate conjugates. The half-life ranges from 1 to 3 hours.
In case of severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance less than 30 ml/min), the elimination of paracetamol and its metabolites is delayed.
Phenylephrine hydrochloride. Absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and metabolized by monoamine oxidase during the initial passage through the intestinal wall and in the liver, therefore, when taken orally, phenylephrine hydrochloride has limited bioavailability. It is excreted almost entirely by the kidneys in the form of a sulfate conjugate.
Maximum concentrations of the drug in the blood plasma are achieved within 45 minutes – 2 hours, and the half-life of the drug from the plasma is 2-3 hours.
Chlorphenamine maleate. Relatively slowly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, maximum concentrations of chlorphenamine in the blood plasma are achieved 2.5-6 hours after taking the drug.
The substance has low bioavailability at 25-50%. About 70% of chlorphenamine in the bloodstream is bound to plasma proteins. It is widely distributed in body tissues, including the central nervous system (CNS).
Chlorphenamine undergoes significant first pass metabolism. The duration of action is 4-6 hours. In children, there was faster and more complete absorption, faster clearance, and a shorter half-life.
The half-life ranges from 2 to 43 hours, even with an average duration of action of 4-6 hours. Part of chlorphenamine unchanged with metabolites was excreted by the kidneys.
Ascorbic acid. Easily absorbed after oral administration. With the usual dosing regimen (30-180 mg/day), about 70-90% of the vitamin is absorbed; with a further increase in dose, absorption decreases (50-20%).
Ascorbic acid is widely distributed in tissues. High concentrations of the vitamin are found in the liver, white blood cells, platelets, glandular tissue and the lens of the eye. About 25% of the vitamin is bound to plasma proteins. Ascorbic acid passes through the placental barrier. The concentration in cord blood is usually 2-4 times higher than in maternal blood.
Ascorbic acid is reversibly oxidized to dehydroascorbic acid.
Some is metabolized to inactive derivatives
(sulfates and oxalates) and is excreted in the urine.
Special instructions
Special instructions
To avoid toxic liver damage, the drug should not be combined with alcoholic beverages.
Due to the stimulating effect of ascorbic acid on the synthesis of corticosteroid hormones, it is necessary to monitor renal function and blood pressure. With long-term use of large doses, the function of the insular apparatus of the pancreas may be suppressed, so it must be regularly monitored during treatment.
In patients with high iron levels in the body, ascorbic acid should be used in minimal doses.
Prescribing ascorbic acid to patients with rapidly proliferating and intensively metastasizing tumors can aggravate the process.
Ascorbic acid as a reducing agent can distort the results of laboratory tests (blood glucose, bilirubin, liver transaminase and LDH activity).
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles. Wed and fur.:
During treatment, it is not recommended to drive a vehicle or other mechanisms that require concentration and high speed of psychomotor reactions.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
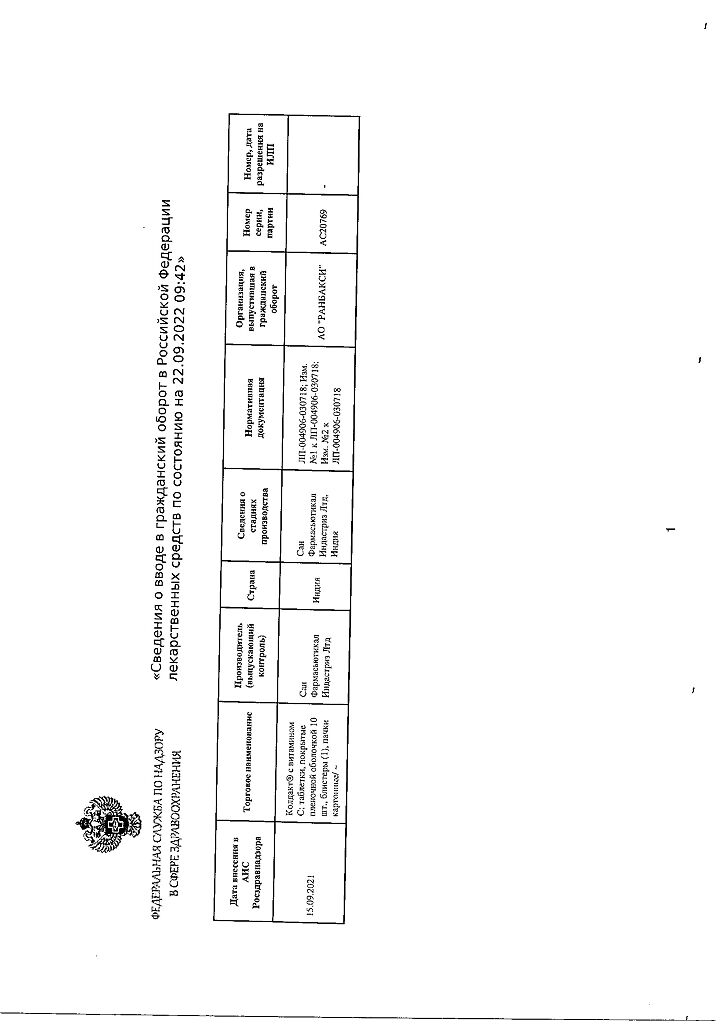
Paracetamol, Phenylephrine, Chlorphenamine, [Ascorbic Acid]
Composition
Composition
Each film-coated tablet contains:
active substance:
paracetamol 650.00 mg,
phenylephrine hydrochloride 10.00 mg,
chlorphenamine maleate 4.00 mg,
coated ascorbic acid**, 31.35 mg, equivalent to Ascorbic acid 30.00 mg**: contains 1.35 mg stearyl alcohol
excipients:
colloidal silicon dioxide 15.00 mg, pregelatinized starch 50.00 mg, microcrystalline cellulose 95.65 mg, sodium carboxymethyl starch 30.00 mg, povidone K30 30.00 mg, talc 5.00 mg, magnesium stearate 9.00 mg.
Film coating: Opadry brown OY56524 27.90 mg.
Composition of Opadry brown OY56524: hypromellose 63.650%, titanium dioxide (E171) 20.140%, iron oxide dye (red) (E172) 8.860%, macrogol 6000 6.300%, iron oxide dye (yellow) (E172) 1.050%.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
The use of the drug is not recommended during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Safety during use during pregnancy and breastfeeding has not been specifically studied. Data on the potential effects of each active ingredient on pregnancy and breastfeeding are presented below.
Pregnancy
Epidemiological studies in pregnancy have shown no adverse effects when using oral paracetamol at the recommended dose. Reproductive studies evaluating the oral drug did not reveal signs of malformations or fetotoxicity.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to the components of the drug.
Taking monoamine oxidase inhibitors (simultaneously or in the previous 14 days), tricyclic antidepressants, beta-blockers, and other sympathomimetics.
Severe cardiovascular diseases, arterial hypertension, hyperthyroidism, closed-angle glaucoma, pheochromocytoma.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding period.
Children’s age up to 12 years.
With caution:
Diabetes mellitus, liver dysfunction, kidney dysfunction, prostatic hyperplasia, hemolytic anemia, bronchial asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (chronic bronchitis), emphysema, acute hepatitis, chronic exhaustion or dehydration, pyloroduodenal stenosis, epilepsy, cardiovascular diseases, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency, congenital hyperbilirubinemia.
You should not simultaneously take other drugs containing paracetamol, as well as other drugs that affect liver function.
It should be taken with caution in patients with alcohol dependence, as well as with recurrent kidney stones.
Side Effects
Side Effects
Classification of the frequency of occurrence of adverse reactions: very often (≥ 1/10); often (≥ 1/100, < 1/10); uncommon (≥ 1/1000, < 1/100); rare (≥ 1/10000, < 1/1000); very rare (< 1/10000), frequency unknown (it is not possible to determine the frequency of occurrence based on available data).From the blood and lymphatic system:Very rare: thrombocytopenia, agranulocytosis, leukopenia, pancytopenia.From the immune system:Rare: hypersensitivity, angioedema.Not known: anaphylactic reaction, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis.Mental disorders:Rarely: nervousness, insomnia.From the nervous system:Common: drowsiness.Rarely: dizziness, headache.From the side of the heart:Rarely: tachycardia, rapid heartbeat.From the side of blood vessels:Rare: arterial hypertension.From the gastrointestinal tract:Often: nausea, vomiting.Rarely: constipation, dry oral mucosa.From the liver and biliary tract:Rarely: increased activity of liver transaminases.From the skin and subcutaneous tissues:Rarely: skin rash, itching, erythema, urticaria.Ascorbic acidAscorbic acid is usually well tolerated. Large doses can cause diarrhea and other gastrointestinal disorders, as well as hyperoxaluria and the formation of kidney stones.
Interaction
Interaction
Paracetamol
The anticoagulant effect of warfarin and other coumarins may be enhanced by long-term regular use of paracetamol, and the risk of bleeding increases. Periodic use of paracetamol has no significant effect.
Hepatotoxic substances can lead to accumulation of paracetamol and overdose.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms
Overdose symptoms are mainly due to the presence of paracetamol.
In acute overdose, paracetamol can have a hepatotoxic effect and even cause liver necrosis.
Overdose of paracetamol, including a general high dose level after a long period of therapy, can lead to analgesic-induced nephropathy with irreversible liver failure.
Patients should be warned not to take other drugs containing paracetamol at the same time.
There is a risk of poisoning, especially in elderly patients and young children, persons with liver disease, in cases of chronic alcoholism, patients with chronic malnutrition and patients receiving microsomal enzyme inducers.
Overdose of paracetamol can lead to liver failure, encephalopathy, coma and death.
Symptoms of paracetamol overdose on the first day include pallor, nausea, vomiting and anorexia. Abdominal pain may be the first sign of liver damage, and it may appear only 24-48 hours, and sometimes 4-6 days after taking the drug.
Most often, signs of liver damage occur 72-96 hours after taking the drug. Impaired glucose metabolism and metabolic acidosis are possible.
Acute renal failure and acute renal tubular necrosis can develop even in the absence of severe liver damage. Cases of cardiac arrhythmia and pancreatitis have been reported.
In case of overdose, intoxication is possible, especially in elderly patients, children, patients with liver diseases (caused by chronic alcoholism), in patients with nutritional disorders, as well as in patients taking inducers of microsomal liver enzymes, in which fulminant hepatitis, liver failure, cholestatic hepatitis, cytolytic hepatitis can develop, in the above cases – sometimes with a fatal outcome.
The overdose threshold in these categories of patients may be reduced. The clinical picture of acute overdose develops within 24 hours after taking paracetamol.
Symptoms of phenylephrine overdose include hemodynamic changes and cardiovascular collapse with respiratory depression, manifested as, for example, drowsiness, which may be followed by agitation (especially in children), blurred vision, skin rash, nausea, vomiting, persistent headaches, nervousness, dizziness, insomnia, circulatory disorders (thrombocytopenia, agranulocytosis, leukopenia, pancytopenia), coma, seizures, arterial hypertension and bradycardia.
Symptoms of chlorphenamine maleate overdose include drowsiness, respiratory arrest, seizures, anticholinergic effects, dystonic reactions and cardiovascular collapse including arrhythmia.
In children, symptoms of overdose may include incoordination, agitation, tremors, behavioral changes, hallucinations, seizures, and anticholinergic effects.
Symptoms of ascorbic acid overdose: nephrolithiasis, insomnia, irritability, hypoglycemia.
Treatment
To treat an overdose of paracetamol, immediate hospitalization is necessary. Determination of the quantitative content of paracetamol in blood plasma before starting treatment as early as possible after an overdose. Laboratory studies of the activity of microsomal liver enzymes should be carried out at the beginning of treatment and then every 24 hours.
In most cases, the activity of microsomal liver enzymes returns to normal within 1-2 weeks. In very severe cases, a liver transplant may be required. The introduction of SH-group donors and precursors for glutathione synthesis – methionine and acetylcysteine - is most effective in the first 8 hours.
The need for additional therapeutic measures (further administration of methionine, intravenous administration of acetylcysteine) is determined depending on the concentration of paracetamol in the blood, as well as the time elapsed after its administration.
Symptomatic treatment.
To treat an overdose of paracetamol, treatment must be started immediately. During the first 48 hours after an overdose, it is advisable to use N-acetylcysteine intravenously or orally as an antidote to paracetamol, possibly gastric lavage and/or the use of methionine orally.
It is advisable to use activated carbon and control breathing and circulation. In case of seizures, diazepam may be used.
Treatment of phenylephrine overdose includes rapid gastric lavage, symptomatic and supportive therapy. The hypertensive effect can be reversed by intravenous administration of an alpha-receptor blocker. In case of seizures, diazepam may be used.
Treatment of an overdose of chlorphenamine maleate includes gastric lavage in case of massive overdose or induction of vomiting. After this, activated charcoal and a laxative may be prescribed to slow down absorption.
In case of seizures, sedation should be performed with intravenous diazepam or phenytoin. In severe cases, hemoperfusion may be performed.
Treatment of an overdose of ascorbic acid is symptomatic; forced diuresis may be required.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
At a temperature not exceeding 25 °C.
Keep out of the reach of children.
Shelf life
Shelf life
3 years.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd, India
Additional information
| Shelf life | 3 years. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | At a temperature not exceeding 25 ° C. Store out of the reach of children. |
| Manufacturer | Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd, India |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd |
Related products
Buy Coldact with vitamin C, 10 pcs. with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.