No products in the cart.
Codelac Neo, 1.5 mg/ml syrup 200 ml
€9.28 €8.12
Description
Pharmacotherapeutic group: central antitussive.
ATX code:R05DB13
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
Butamirate, the active ingredient of Codelac® Neo, is an anti-cough medicine of central action. It is neither chemically nor pharmacologically related to opium alkaloids. It is not addictive or addictive.
It suppresses cough having a direct effect on the coughing center. It has a bronchodilator effect (dilates the bronchi). Helps ease breathing by improving spirometry (reduces airway resistance) and blood oxygenation (saturates blood with oxygen).
Pharmacokinetics
Intake
After oral administration, butamirate is quickly and completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. After taking 150 mg of butamirate, the maximum concentration of the main metabolite (2-phenyl butyric acid) in blood plasma is reached after about 1.5 hours and is 6.4 µg/ml.
Distribution and metabolism
Hydrolysis of butamyrate initially to 2-phenyl butyric acid and diethylaminoethoxyethanol begins in the blood. These metabolites also have anti-cough activity, and, like butamirate, are largely (about 95%) bound to plasma proteins, which accounts for their long elimination half-life. 2-phenyl butyric acid is partially metabolized by hydroxylation.
There is no cumulation if the drug is taken repeatedly.
Elimation
The elimination half-life of butamirate is 6 hours. The metabolites are eliminated mainly by the kidneys. And 2-phenyl butyric acid is excreted mainly in the form bound to glucuronic acid.
Indications
Indications
Dry cough of any etiology, including whooping cough; to suppress cough in the preoperative and postoperative period, during surgical interventions and bronchoscopy.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacotherapeutic group: centrally acting antitussive.
ATX code: R05DB13
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
Butamirate, the active substance of Codelac® Neo, is a centrally acting antitussive agent. It is not classified as an opium alkaloid either chemically or pharmacologically. Does not form dependence or addiction.
Suppresses cough, having a direct effect on the cough center. Has a bronchodilator effect (expands the bronchi). Helps make breathing easier by improving spirometry (reduces airway resistance) and blood oxygenation (saturates the blood with oxygen).
Pharmacokinetics
Suction
After oral administration, butamirate is quickly and completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. After taking 150 mg of butamirate, the maximum concentration of the main metabolite (2-phenylbutyric acid) in the blood plasma is reached after approximately 1.5 hours and is 6.4 μg/ml.
Distribution and metabolism
Hydrolysis of butamirate initially to 2-phenylbutyric acid and diethylaminoethoxyethanol begins in the blood. These metabolites also have antitussive activity and, like butamirate, are highly (about 95%) bound to plasma proteins, resulting in their long half-life. 2-phenylbutyric acid is partially metabolized by hydroxylation.
When taking the drug again, no accumulation is observed.
Removal
The half-life of butamirate is 6 hours. Metabolites are excreted mainly by the kidneys. Moreover, 2-phenylbutyric acid is mainly excreted in the form associated with glucuronic acid.
Special instructions
Special instructions
The drug contains sodium saccharinate and sorbitol as sweeteners, so it can be used in patients with diabetes.
Due to the presence of ethyl alcohol in the drug, there is a danger when using the drug in patients with a tendency to develop drug dependence, with liver diseases, alcoholism, epilepsy, brain diseases, pregnant women and children.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and machinery
It is recommended to refrain from driving vehicles and engaging in other potentially hazardous activities that require increased concentration and speed of psychomotor reactions, as the drug can cause dizziness and drowsiness.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Butamirat
Composition
Composition
Composition per 1 ml:
active ingredient: butamirate citrate –1.5 mg;
excipients:
sorbitol (sorbitol syrup 70% (non-crystallizing)) – 405 mg,
glycerol – 290 mg,
ethanol 95% (ethyl alcohol 95%) – 2.538 mg,
sodium saccharinate – 0.6 mg,
benzoic acid – 1.15 mg,
vanillin – 0.6 mg,
sodium hydroxide solution 30% – 0.31 mg,
purified water – up to 1.0 ml.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
There is no data on the safety of the drug during pregnancy and its passage through the placental barrier. The use of the drug in the first trimester of pregnancy is contraindicated. In the second and third trimesters of pregnancy, the use of the drug is possible taking into account the balance of benefit for the mother and potential risk for the fetus.
The penetration of the drug into breast milk has not been studied, therefore the use of the drug during breastfeeding is not recommended.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to the components of the drug, fructose intolerance, pregnancy (first trimester), breastfeeding period. Children under 3 years of age.
With caution
Pregnancy (II and III trimesters).
Due to the presence of ethyl alcohol in the drug, use with caution in patients with a tendency to develop drug dependence, liver diseases, alcoholism, epilepsy, brain diseases, pregnant women and children.
Side Effects
Side Effects
Classification of the frequency of adverse reactions: very common (≥1/10), common (≥1/100, <1/10), uncommon (≥1/1000, <1/100), rare (≥1/10000, <1/1000), very rare (<1/10000), including individual reports.
From the nervous system:
Rarely: drowsiness, dizziness, which goes away when the drug is stopped or the dose is reduced.
From the gastrointestinal tract:
Rarely: nausea, diarrhea.
From the skin and subcutaneous tissues:
Rarely: urticaria, possible development of allergic reactions.
Interaction
Interaction
No drug interactions have been reported for butamirate. During treatment with the drug, it is not recommended to drink alcoholic beverages, as well as drugs that depress the central nervous system (hypnotics, antipsychotics, tranquilizers and other drugs).
Due to the fact that butamirate suppresses the cough reflex, the simultaneous use of expectorants should be avoided to avoid the accumulation of sputum in the respiratory tract with the risk of developing bronchospasm and respiratory tract infection.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: nausea, vomiting, drowsiness, diarrhea, dizziness, decreased blood pressure, impaired coordination of movements.
Treatment: activated carbon, saline laxatives, symptomatic therapy (according to indications).
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
Store at a temperature not exceeding 25 ºС.
The shelf life of an opened bottle is no more than 12 months.
Keep out of the reach of children.
Shelf life
Shelf life
3 years. Do not use after the expiration date stated on the package.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Pharmstandard-Leksredstva, Russia
Additional information
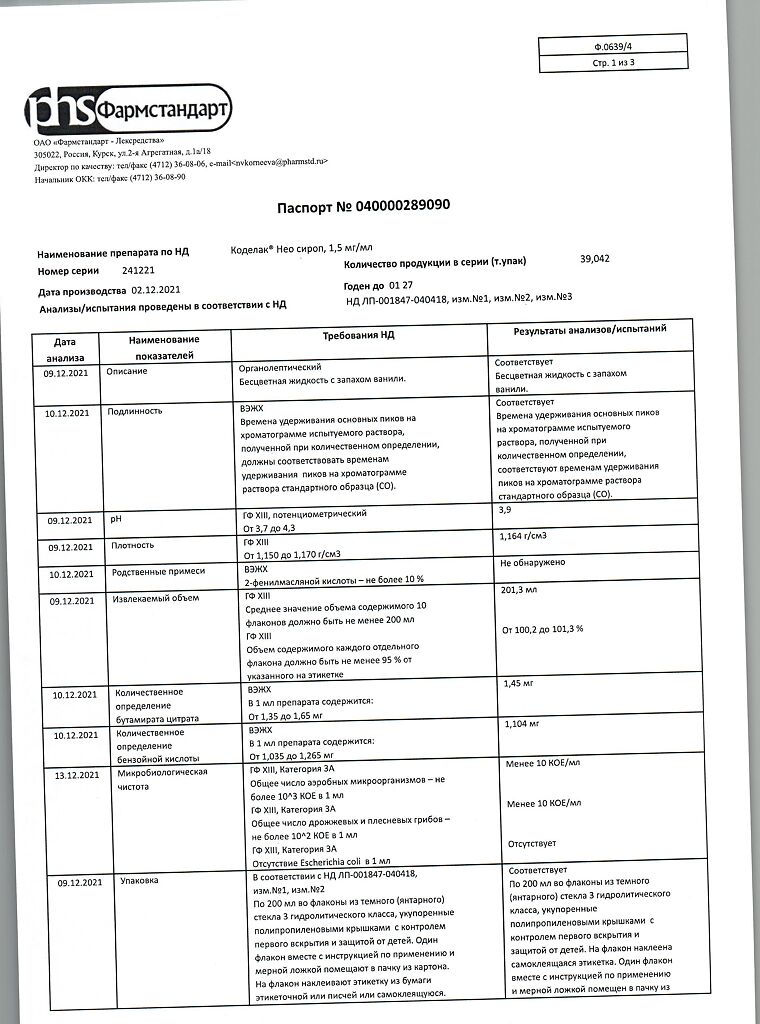
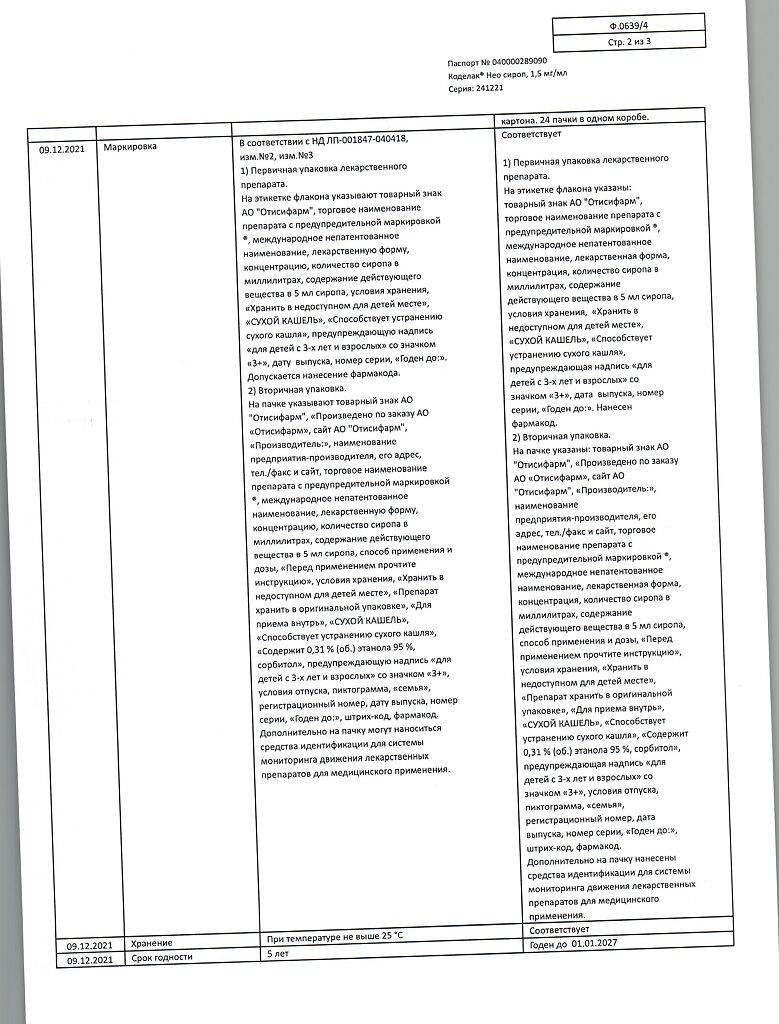
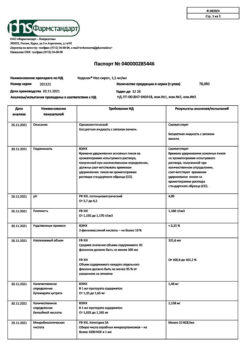
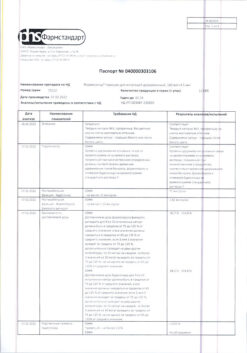
| Shelf life | 5 years. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | In a light-protected place at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C. |
| Manufacturer | Pharmstandard-Leksredstva, Russia |
| Medication form | syrup |
| Brand | Pharmstandard-Leksredstva |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Codelac Neo, 1.5 mg/ml syrup 200 ml with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.