No products in the cart.
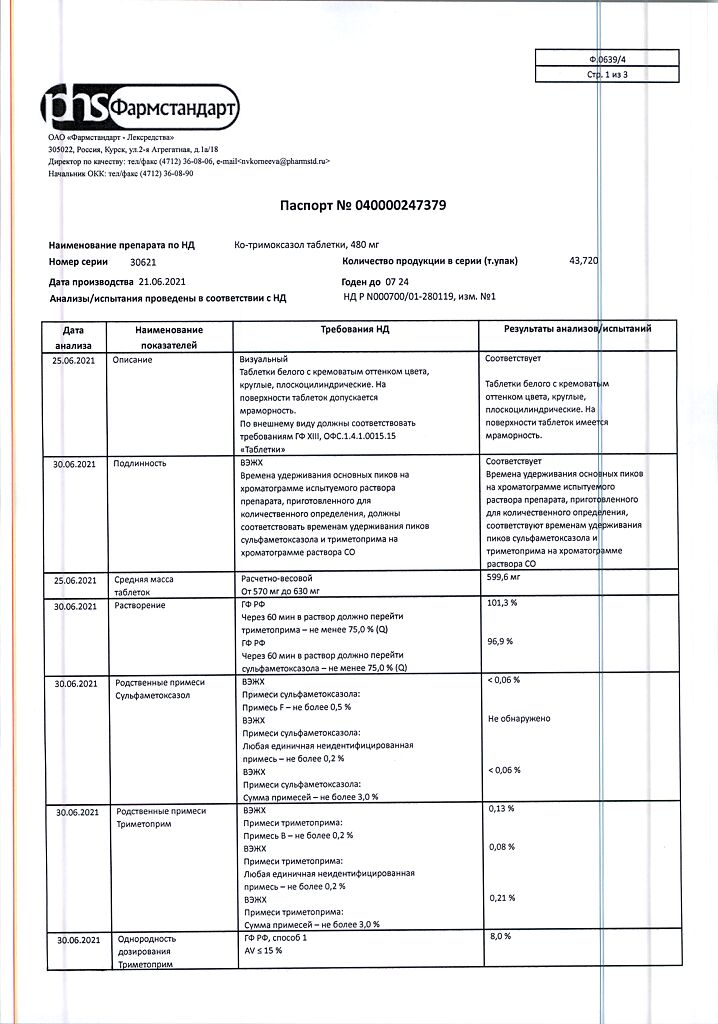
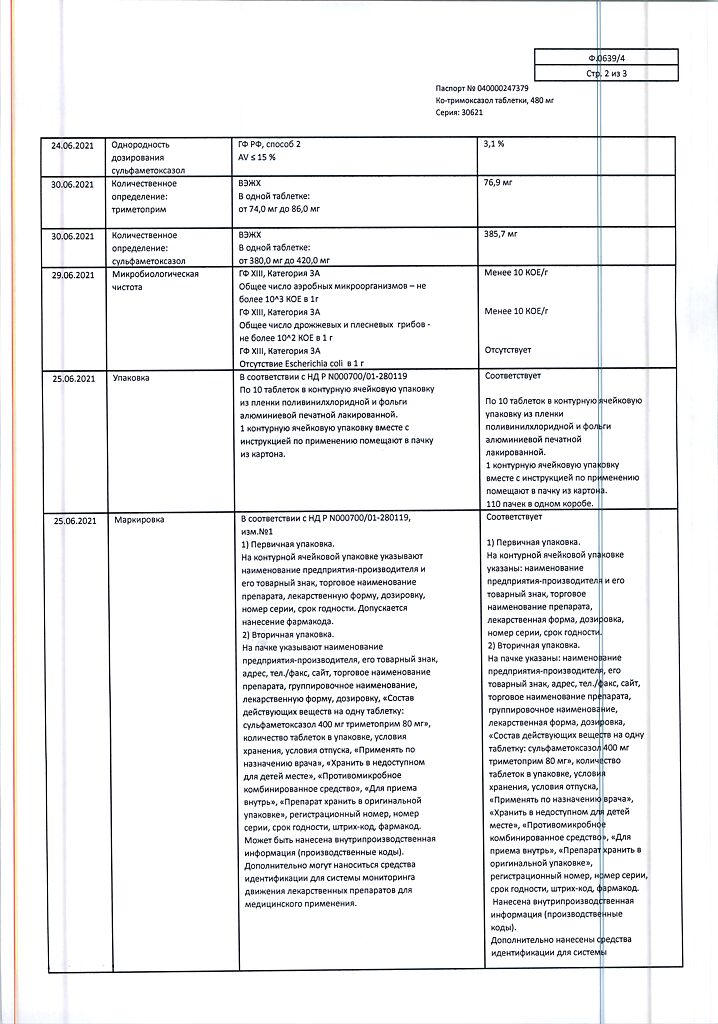
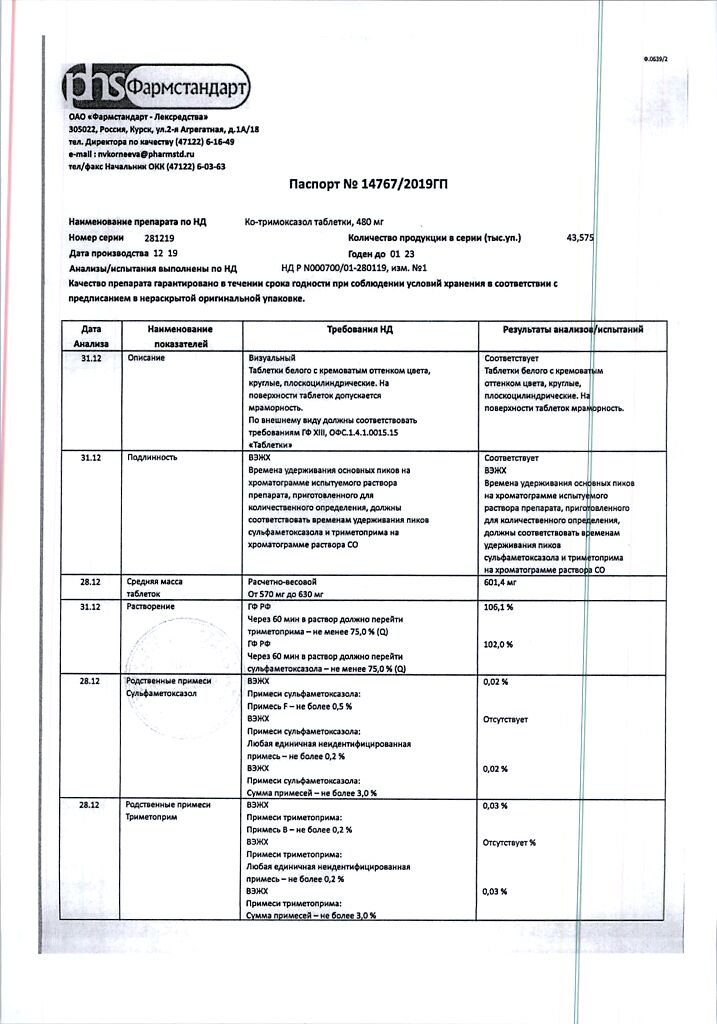
Co-trimoxazole, tablets 400 mg+80 mg mg 10 pcs
€1.00
Out of stock
(E-mail when Stock is available)
Description
Pharmacotherapeutic group
Antimicrobial combination drug
ATX code: J01EE01
Pharmacokinetics
When taken orally both components of the drug are completely absorbed from ‑the gastrointestinal ‑tract. Maximum concentration of the active components of the drug is observed after 1-4 hours.
Trimethoprim penetrates well into cells and through tissue barriers – lungs, kidneys, prostate, bile, saliva, sputum, cerebrospinal fluid. Protein binding is 50%. The normal elimination half-life is 8.6-17 hours. It is excreted mainly by kidneys, 50% – unchanged.
Sulfamethoxazole is 66% bound to plasma proteins; standard half-life is 9-11 hours. It is eliminated mainly by kidneys, 15-30% – in active form.
Pharmacodynamics
A combined antimicrobial drug consisting of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim. Sulfamethoxazole, which is similar in structure to para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA), disrupts the synthesis of dihydrofolic acid in bacterial cells, preventing the incorporation of PABA into its molecule. Trimethoprim enhances the effect of sulfamethoxazole by disrupting the reduction of dihydrofolic acid to tetrahydrofolic acid, the active form of folic acid responsible for protein metabolism and microbial cell division.
It is a broad spectrum bactericidal drug, active against the following microorganisms: Streptococcus spp. (hemolytic strains are more sensitive to penicillin), Staphylococcus spp, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Neisseria meningitidis, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Escherichia coli (including enterotoxigenic strains), Salmonella spp. (including Salmonella typhi and Salmonella paratyphi), Vibrio cholerae, Bacillus anthracis, Haemophilus influenzae (including ampicillin resistant strains), Listeria spp, Nocardia asteroides, Bordetella pertussis, Enterococcus faecalis, Klebsiella spp., Proteus spp., Pasteurella spp., Francisella tularensis, Brucella spp, Mycobacterium spp. (including Mycobacterium leprae), Citrobacter, Enterobacter spp., Legionella pneumophila, Providencia, some Pseudomonas species (except Pseudomonas aeruginosa), Serratia marcescens, Shigella spp, Yersinia spp., Morganella spp., Pneumocystis carinii; Chlamydia spp. (including Chlamydia trachomatis, Chlamydia psittaci); protozoa: Plasmodium spp., Toxoplasma gondii, pathogenic fungi, Actinomyces israelii, Coccidioides immitis, Histoplasma capsulatum, Leishmania spp.
Resistant to the drug: Corynebacterium spp., Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Treponema spp., Leptospira spp., viruses. Inhibits the activity of E. coli, which leads to a decrease in the synthesis of thymine, riboflavin, nicotinic acid and other B vitamins in the intestine. Duration of therapeutic effect is 7 hours.
Indications
Indications
Urogenital organ infections: urethritis, cystitis, pyelitis, pyelonephritis, prostatitis, epididymitis, gonorrhea (male and female), soft chancre, venereal lymphogranuloma, inguinal granuloma;
Respiratory infections: bronchitis (acute and chronic), bronchiectatic disease, lumpy pneumonia, bronchopneumonia, pneumocystis pneumonia;
Infections of ENT organs: otitis media, sinusitis, laryngitis, sore throat; scarlatina;
Gastrointestinal infections: typhoid, paratyphoid, salmonellosis, cholera, dysentery, cholecystitis, cholangitis, gastroenteritis caused by enterotoxic strains of Escherichia coli;
Infections of skin and soft tissue: acne, furunculosis, pyoderma, wound infections; osteomyelitis (acute and chronic), etc. osteoarticular infections, brucellosis (acute), South American blastomycosis, malaria (Plasmodium falciparum), toxoplasmosis (in complex therapy).
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Composition
Composition
1 tablet contains
Active substance:
Sulfamethoxazole – 400.00 mg,
Trimethoprim – 80.00 mg,
Auxiliary substances:
Microcrystalline cellulose, potato starch, povidone (polyvinylpyrrolidone low molecular weight medical 12600 ± 2700), crosspovidone (collidone CL), magnesium stearate.
How to take, the dosage
How to take, the dosage
Overly, after meals, with plenty of liquid.
The dose is set individually.
Children: 3 to 5 years old: 240 mg (2 tablets of 120 mg) 2 times a day; 6 to 12 years old: 480 mg (4 tablets of 120 mg or 1 tablet of 480 mg) 2 times a day.
Adults and children over 12 years of age: 960 mg 2 times a day, in long-term therapy – 480 mg 2 times a day. The course of therapy is 5-14 days; in case of severe course and/or in chronic form of the disease the single dose may be increased by 30-50%.
In case of pneumonia – 0.1 g/kg/day (in terms of sulfamethoxazole), the interval between doses is 6 hours, the course is 14 days.
In gonorrhea – 2 g (per sulfamethoxazole) 2 times a day with an interval of 12 hours. If the course of treatment exceeds 5 days and/or if it is necessary to increase the dose, the therapy should be carried out under hematologic control; in case of changes in blood picture it is necessary to prescribe folic acid 5-10 mg/day.
Interaction
Interaction
It is not recommended for use with thiazide diuretics because of the risk of thrombocytopenia (bleeding).
The concomitant administration of the drug with salicylates, butadione, naproxen and para-aminobenzoic acid derivatives is not recommended.
It potentiates the anticoagulant activity of warfarin and anticonvulsant activity of phenytoin.
Potentiates (trimethoprim) the effect of hypoglycemic drugs, sulfonylurea derivatives.
Rifampicin shortens the T1/2 of trimethoprim.
The combined administration of Co-trimoxazole and cyclosporine after renal surgery worsens the condition of patients.
Decreases the reliability of oral contraception (depresses intestinal microflora and reduces intestinal hepatic circulation of hormonal compounds).
Pyrimethamine in doses greater than 25 mg/week increases the risk of megoblastic anemia.
Benzocaine, procaine, procainamide (and other drugs whose hydrolysis produces PABA) reduce the effect.
A cross-allergic reaction may develop between diuretics (thiazides, furosemide, etc.) and oral hypoglycemic drugs (sulfonylurea derivatives) on the one hand, and antimicrobial sulfonamides on the other.
Phenytoin, barbiturates, PASC increase the manifestations of folic acid deficiency.
Salicylic acid derivatives increase the effects.
Ascorbic acid, hexamethylantetramine (and other drugs that acidify the urine) increase the risk of crystalluria.
Colestyramine decreases absorption, so it should be taken 1 hour after or 4-6 hours before taking co-trimoxazole.
The drugs that inhibit bone marrow hematopoiesis increase the risk of myelosuppression.
Special Instructions
Special Instructions
Excessive sunlight and UV exposure should be avoided.
The drug is used with caution in folic acid deficiency in the body, bronchial asthma, with a history of allergies.
Impact on driving, operating machinery
When using the drug, patients should abstain from driving and engaging in potentially hazardous activities requiring increased concentration and quick psychomotor reaction.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity (including to trimethoprim and sulfonamides), severe cardiovascular disease, hepatic, renal failure, aplastic anemia, B12-deficiency anemia, agranulocytosis, leukopenia, glucose6phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency, pregnancy, breast-feeding period, children under 3 years old, hyperbilirubinemia in children.
With caution
In folic acid deficiency, bronchial asthma, thyroid disease.
Side effects
Side effects
Digestive system disorders: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, glossitis, diarrhea, abdominal pain, lack of appetite, false diphtheria, increased liver enzymes (enzymes) and serum creatinine, oral inflammation, tongue inflammation, pancreatic inflammation, cholestatic hepatitis.
Allergic reactions: allergic myocarditis, chills, fever, photosensitization, anaphylactic symptoms, skin rash, Quincke’s edema, Stevens-Jones syndrome, Lyell syndrome,
Blood disorders: Leukopenia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, agranulocytosis, megaloblastic anemia.
Urinary system: crystalluria, hematuria, interstitial nephritis.
Metabolism: hypokalemia, hyponatremia.
Nervous system: apathy, aseptic meningitis, movement coordination disorder, headache, depression, seizures, hallucinations, nervousness, tinnitus, inflammation of spinal nerves.
Organs of internal secretion: cross-allergy, hypoglycemia, increased pyuresis.
Musculoskeletal system: joint pain, muscle pain.
Respiratory organs: choking, cough, lung infiltrates.
Other: debility, fatigue, insomnia.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms
Nausea, vomiting, intestinal colic, dizziness, headache, drowsiness, depression, fainting, confusion, visual disturbances, fever, hematuria, crystalluria; in prolonged overdose – thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, megaloblastic anemia, jaundice.
Treatment
Gastric lavage, acidification of the urine increases trimethoprim excretion, oral fluid administration, intramuscular 5-15 mg/day of calcium folinate (eliminates the effect of trimethoprim on bone marrow), if necessary – hemodialysis.
Pregnancy use
Pregnancy use
Similarities
Similarities
Additional information
| Shelf life | 3 years. Do not use after the expiration date printed on the package. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | In a light-protected place at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C. |
| Manufacturer | Pharmstandard-Leksredstva, Russia |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Pharmstandard-Leksredstva |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Co-trimoxazole, tablets 400 mg+80 mg mg 10 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.