No products in the cart.
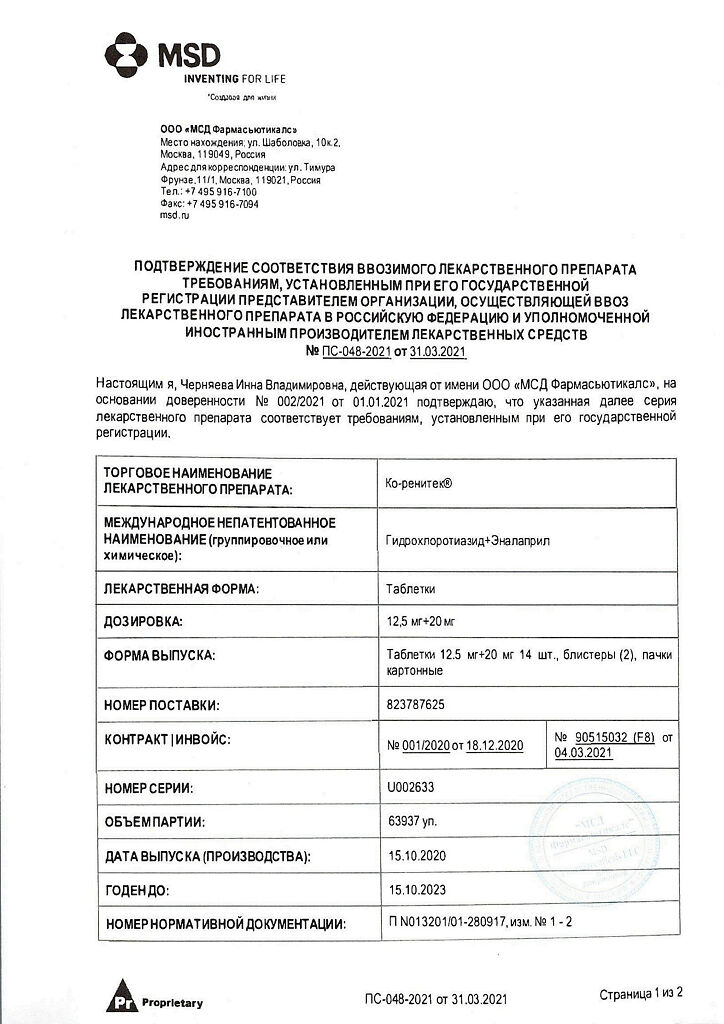
Co-renitec, 20 mg+12, 5 mg tablets 28 pcs
€20.48 €17.07
Description
Co-renitec – hypotensive, diuretic.
Inhibits ACE, reduces reabsorption of ions and water in the convoluted tubules.
Reduces the content of sodium ions in the vascular wall, reduces arterial vascular tone, BP, and PPS, increases diuresis. The hypotensive effect lasts for 24 hours.
Indications
Indications
Arterial hypertension; chronic heart failure.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Ko-Renitek – hypotensive, diuretic.
Inhibits ACE, reduces the reabsorption of ions and water in convoluted tubules.
Reduces the content of sodium ions in the vascular wall, reduces the tone of arterial vessels, blood pressure, peripheral vascular resistance, and increases diuresis. The hypotensive effect lasts for 24 hours.
Special instructions
Special instructions
Hypotension and electrolyte imbalance: As with any antihypertensive therapy, some patients may develop symptomatic hypotension. Patients should be examined to identify clinical signs of fluid and electrolyte imbalance, i.e. hypovolemia, hyponatremia, hypochloremic alkalosis, hypomagnesemia or hypokalemia, which may occur due to diarrhea or vomiting. In such patients, periodic determination of serum electrolytes should be carried out at certain intervals. The drug should be prescribed with extreme caution to patients with coronary heart disease or cerebrovascular diseases, since an excessive decrease in blood pressure can lead to the development of myocardial infarction or stroke. If arterial hypotension occurs, the patient should be laid down and, if necessary, administered a 0.9% sodium chloride solution. Transient arterial hypotension, when the drug is prescribed, is not a contraindication to its further use. After normalization of blood pressure and replenishment of circulating blood volume, therapy can be resumed in smaller doses or each of the components of the drug can be used separately.
Aortic Stenosis/Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: As with all drugs that have a vasodilating effect, ACE inhibitors should be administered with caution to patients with left ventricular outflow tract obstruction.
Renal impairment: Thiazide diuretics may not be effective in patients with impaired renal function and may not be effective in patients with creatinine clearance levels of 30 mL/min or less (ie, moderate to severe renal impairment). The drug should not be prescribed to patients with renal failure (creatinine clearance less than 80 ml/min) until the selection of individual components of the drug shows that the required doses are present in this dosage form. In some patients without any evidence of renal disease before treatment, usually slight and transient increases in blood urea and serum creatinine levels occurred when treated with enalapril in combination with a diuretic. In such cases, treatment with the drug should be discontinued. In the future, it is possible to resume therapy in smaller doses, or prescribe each of the components of the drug separately. In some patients with bilateral renal artery stenosis or arterial stenosis of a solitary kidney, increases in blood urea and serum creatinine were observed when treated with ACE inhibitors. These changes were reversible; as a rule, the indicators returned to normal after cessation of treatment.
Liver disease Thiazide diuretics should be used with caution in patients with impaired liver function or progressive liver disease, since even minor changes in fluid and electrolyte balance can lead to hepatic coma.
Surgery/General anesthesia: During major surgery or general anesthesia using agents that cause hypotensive effects, enalaprilat blocks the formation of angiotensin II, which is caused by compensatory release of renin. If a pronounced decrease in blood pressure develops, explained by a similar mechanism, it can be corrected by increasing the volume of circulating blood.
Metabolic and endocrine effects: Thiazide diuretics may cause impaired glucose tolerance. Dosage adjustments of hypoglycemic agents, including insulin, may be required. Thiazide diuretics may decrease urinary calcium excretion and may also cause a slight and transient increase in serum calcium concentrations. Severe hypercalcemia may be a sign of hidden hyperparathyroidism. Thiazide diuretics should be discontinued before testing parathyroid function. Increases in cholesterol and triglyceride levels may also be associated with thiazide diuretic therapy, however, at the 12.5 mg dose of hydrochlorothiazide contained in the CO-RENITEC tablet, such effects were not observed or were insignificant. Thiazide diuretic therapy may lead to hyperuricemia and/or gout in some patients. However, enalapril may increase uric acid levels in the urine and thereby reduce the hyperuricemic effect of hydrochlorothiazide.
Allergic reactions/Angioedema: Rare cases of angioedema of the face, extremities, lips, tongue, glottis and/or larynx have been described during treatment with ACE inhibitors, including enalapril. These phenomena can occur in any phase of therapy. In such cases, it is necessary to immediately stop taking enalapril and carefully monitor the patient’s condition in order to control and correct clinical symptoms. Even in cases where there is only swelling of the tongue without swelling of the respiratory organs, patients may require long-term observation as therapy with antihistamines and corticosteroids may not be sufficient. There are rare reports of death due to angioedema associated with laryngeal edema or tongue edema. Swelling of the tongue, glottis, or larynx can lead to airway obstruction, especially in patients who have undergone respiratory surgery. In cases where swelling is localized in the area of the tongue, glottis or larynx, which can lead to airway obstruction, 0.3-0.5 ml of a 0.1% solution of epinephrine (adrenaline) should be immediately administered subcutaneously and quickly ensure airway patency. In black patients taking ACE inhibitors, angioedema was observed more often than in other patients. Patients with a history of angioedema not associated with ACE inhibitors may be at greater risk of developing angioedema during ACE inhibitor therapy (see also CONTRAINDICATIONS). In patients receiving thiazides, allergic reactions may occur regardless of a history of allergic conditions and bronchial asthma. Relapses or worsening of the severity of systemic lupus erythematosus have been reported in patients receiving thiazides.
Anaphylactoid reactions during hyposensitization with Hymenoptera venom allergen: In rare cases, patients receiving ACE inhibitors have developed life-threatening anaphylactoid reactions during hyposensitization with Hymenoptera venom allergen. Such reactions can be avoided if you temporarily stop taking the ACE inhibitor before starting hyposensitization.
Patients on hemodialysis: The use of CO-RENITEC is not indicated for patients with renal failure undergoing hemodialysis. Anaphylactoid reactions have been observed in patients on dialysis using high-flux membranes (such as AN 69s) concomitantly receiving treatment with ACE inhibitors. In these patients, it is necessary to use a different type of dialysis membrane or other classes of antihypertensive agents.
Cough: There have been cases of cough during therapy with ACE inhibitors. As a rule, the cough is dry, persistent and disappears after the end of therapy. Cough associated with the use of ACE inhibitors should be considered as part of the differential diagnosis of cough.
Use in Elderly Patients: In clinical studies, the efficacy and tolerability of enalapril and hydrochlorothiazide when administered together were similar in elderly and younger patients with hypertension.
Use in pediatrics: The safety and effectiveness of the drug in children have not been established. Therefore, the use of CO-RENITEC in pediatrics is not recommended.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Hydrochlorothiazide, Enalapril
Composition
Composition
Active ingredients:
Enalapril maleate 20 mg;
Hydrochlorothiazide 12.5 mg
Excipients:
Sodium bicarbonate;
Lactose aqueous;
Corn starch;
Pregelatinized corn starch;
Iron oxide yellow dye;
Magnesium stearate.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity (including to other ACE inhibitors and sulfonamide derivatives), anuria, childhood.
Side Effects
Side Effects
In clinical studies, side effects were usually mild, transient, and in most cases did not require treatment interruption.
From the cardiovascular system: 1-2% – orthostatic effects, including arterial hypotension; rarely – fainting, arterial hypotension regardless of body position, palpitations, tachycardia, chest pain.
From the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system:
often – dizziness, increased fatigue (usually resolved with dose reduction and rarely required discontinuation of the drug); 1-2% – asthenia, headaches; rarely – insomnia, drowsiness, systemic dizziness, paresthesia, increased excitability.
From the respiratory system: 1-2% – cough; rarely – shortness of breath.
From the digestive system: 1-2% – nausea; rarely – pancreatitis, diarrhea, vomiting, dyspepsia, abdominal pain, flatulence, constipation, dry mouth.
From the musculoskeletal system: 1-2% – muscle cramps; rarely – arthralgia.
Allergic reactions:
rarely – angioedema of the face, limbs, lips, tongue, glottis and/or larynx. There are rare reports of the development of angioedema of the intestine in connection with taking ACE inhibitors, including enalapril.
Dermatological reactions: rarely – Stevens-Johnson syndrome, hyperhidrosis, skin rash, itching.
From the urinary system: rarely – impaired renal function, renal failure.
From the reproductive system: 1-2% – impotence; rarely – decreased libido.
From laboratory parameters: possible hyperglycemia, hyperuricemia, hypo- or hyperkalemia, increased concentrations of urea, serum creatinine in the blood, increased activity of liver enzymes and/or increased serum bilirubin (these indicators usually returned to normal after cessation of therapy with Korenitek); in some cases – a decrease in hemoglobin and hematocrit.
Other: rarely – tinnitus, gout. A symptom complex is described, the possible manifestations of which are fever, serositis, vasculitis, myalgia, myositis, arthralgia/arthritis, a positive test for antinuclear antibodies, accelerated ESR, eosinophilia and leukocytosis; photosensitivity may develop.
Interaction
Interaction
Other antihypertensive drugs: When enalapril is prescribed in combination with other antihypertensive drugs, additive effects may occur.
Serum potassium: Potassium loss due to thiazide diuretics is generally reduced by enalapril. Serum potassium concentrations usually remain within normal limits. The use of potassium supplements, potassium-sparing agents or potassium-containing salts, especially in patients with renal failure, can lead to a significant increase in serum potassium levels.
Lithium preparations: Diuretics and ACE inhibitors reduce the excretion of lithium by the kidneys and increase the risk of developing lithium intoxication. Before using lithium preparations, you must read the instructions for use of this drug.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, including selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors, may reduce the effect of diuretics and other antihypertensive drugs. Therefore, the hypotensive effect of ACE inhibitors may be reduced by concomitant administration of NSAIDs, including COX-2 inhibitors. In some patients with impaired renal function taking NSAIDs, including selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors, concomitant use of ACE inhibitors may lead to a further deterioration of renal function. These changes are usually reversible.
Non-depolarizing muscle relaxants: Thiazide diuretics may enhance the effect of tubocurarine.
Other drugs: The hypotensive effect is reduced by estrogens and ethanol. Immunosuppressants, allopurinol, and cytostatics increase the risk of developing hematotoxicity.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms:
Enalapril – a pronounced decrease in blood pressure, starting approximately six hours after taking the drug, stupor. Enalaprilat serum concentrations 100-200 times higher than those observed at therapeutic doses occurred after taking 300 and 440 mg of enalapril, respectively.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
At a temperature not exceeding 30 °C
Shelf life
Shelf life
2 years
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Organon Pharma (UK) Limited, UK
Additional information
| Shelf life | 2 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | At a temperature not exceeding 30 °C |
| Manufacturer | Organon Pharma (UK) Limited, United Kingdom |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Organon Pharma (UK) Limited |
Related products
Buy Co-renitec, 20 mg+12, 5 mg tablets 28 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.