No products in the cart.
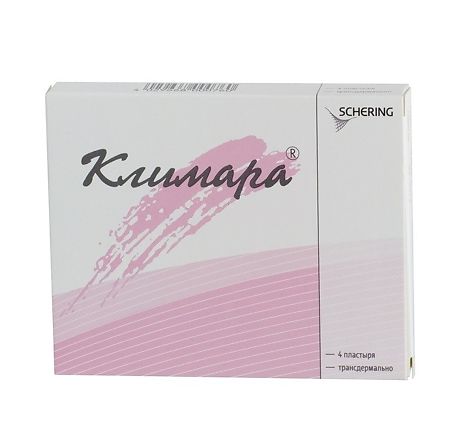
Climara, 3.9mg/12, 5 cm 4 pcs
€1.00
Out of stock
(E-mail when Stock is available)
Description
Climara is estrogenic.
Pharmacokinetics
Estradiol is released from the patch (50 mcg daily) and is transdermally delivered to the bloodstream at a constant rate, maintaining the target plasma level of the hormone.
Indications
Indications
Hormone replacement therapy for disorders caused by natural or surgical menopause (only for non-cancerous diseases): vasomotor symptoms (hot flashes, sweating), sleep disorders, atrophic processes.
Prevent postmenopausal osteoporosis.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Composition
Composition
1 patch contains:
The active ingredient:
Estradiol hemihydrate;
Excipients:
Ethyloleate – 19.25 mg,
Isopropyl myristate – 9.65 mg,
Glyceryl monolaurate – 4.8 mg,
acrylate copolymer – 99 mg.
How to take, the dosage
How to take, the dosage
When performing HRT to reduce symptoms of estrogen deficiency due to natural menopause or surgical removal of the ovaries, PTC containing the lowest dose of estradiol should be used. If necessary, TTS with a higher dose of estradiol can be used. Subsequently, Climara should be used with the lowest effective dose of the active ingredient.
In order to prevent osteoporosis, treatment should be started immediately after the onset of menopause. Long-term treatment is recommended; the regimen is tailored individually.
The treatment should be given either in a continuous or cyclic regimen.
The estrogen therapy alone is used if the woman has had a hysterectomy. In all other cases therapy with corresponding doses of gestagens is prescribed for 10-14 days each month.
The TTCs should be applied weekly in a continuous regimen. Each used patch should be removed after 7 days, after which a new patch is reattached.
Cyclical use of Climar may also be recommended. In this case, the TTC is attached weekly for 3 consecutive weeks, followed by a 7-day interval without the patch until the next course of treatment.
Menstrual-like bleeding normally occurs 2-3 days after discontinuation of gestagens.
TTC Method of Use
After removing the protective film, the TTC (patch) is applied with the adhesive side on a clean, dry, undamaged area of skin (without signs of irritation) along the spine or on the buttocks. The TTS is not attached in or near the mammary glands. The area selected for patch fixation should not be greasy; attachment to the waist area should be avoided, as the patch may peel off if tight clothing rubs against it.
The patch should be applied immediately after opening the package and removing the protective film. Press firmly on the band-aid with the palm of your hand for approximately 10 seconds. Make sure that there is good contact with the skin, especially around the edges.
The application site should be changed at 1 week intervals.
If the patch is applied correctly, you can take a bath and shower as usual. Keep in mind, however, that the patch may peel off the skin when exposed to very hot water or in a sauna.
If the patch does come off, a new patch should be applied for the remaining days of the 7-day interval.
Interaction
Interaction
In long-term concomitant use of Climar with inducers of microsomal liver enzymes (e.g. hydantoin derivatives, barbiturates, primidone, carbamazepine, rifampicin, and also, apparently, with oxcarbamazepine, topiramate, felbamate and griseofulvin) an increase in clearance of sex hormones and reduction of clinical effectiveness is possible. Maximum enzyme induction is generally not seen for 2-3 weeks, but may then persist for at least 4 weeks after discontinuation of drug therapy.
Significant alcohol consumption while on MHT may result in elevated circulating estradiol levels.
Special Instructions
Special Instructions
Before starting treatment, during or repeated prescription of ZGT a woman is recommended to undergo a thorough general medical and gynecological examination, including examination of pelvic organs (with cytological examination of cervical mucus), abdomen, breast, BP control, examination of the coagulation system and blood lipid spectrum. In patients with diabetes, blood glucose control is required (at least once a year).
Hormonal contraception should be discontinued at the start of MHT; if necessary, non-hormonal contraception should be recommended to the patient.
If any of the conditions/risk factors listed below are present before initiating therapy or are progressing, the potential risks and expected benefits of Climar therapy should be considered on a case-by-case basis before initiating or continuing on MHT.
Cardiovascular disease. Several epidemiological studies have found some increased incidence of venous thromboembolism (VTE), such as deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism, in women who have received MHT. If MHT is recommended for women with risk factors for VTE, the risk/benefit ratio of the therapy should be carefully weighed.
Risk factors for VTE include individual and family history (the development of VTE in direct relatives at a relatively young age may indicate a genetic predisposition), and severe obesity. The risk of VTE also increases with age. There is no consensus on the possible role of varicose veins in the development of VTE.
The risk of VTE increases with prolonged immobilization, major surgery, or extensive trauma. Depending on the etiology of the disease and the duration of immobilization, temporary discontinuation of VTE should be considered.
Treatment should be stopped immediately if symptoms of thromboembolism are present or suspected.
Endometrial cancer. Prolonged exposure to estrogen increases the risk of endometrial hyperplasia or carcinoma. Studies have confirmed that additional gestagen administration reduces the risk of endometrial hyperplasia and/or endometrial cancer.
Breast Cancer. A meta-analysis of 51 epidemiologic studies demonstrated that there is a slightly increased risk of breast cancer diagnosed in women who have received ZGT for 5 years. The increased risk observed can be a result of earlier diagnosis of breast cancer, the biological effects of MHT, or a combination of both. The relative risk increases with the duration of treatment. This compares to the increased risk of breast cancer seen in women with every year of delayed natural menopause. The increased risk gradually disappears after treatment ends in the first 5 years after cessation of MHT. Breast cancer diagnosed in women who receive MHT compared to those who did not use MHT is less likely to metastasize.
Liver tumors. In extremely rare cases, benign or even rarer malignant liver tumors have been observed following the use of hormonal drugs like Climar. Rarely, these tumors have resulted in life-threatening intra-abdominal bleeding. The main symptoms of a liver tumor are pain in the epigastric region, enlargement of the liver, and/or symptoms of intra-abdominal bleeding.
Ballbladder disease. Estrogens increase the lithogenicity of bile. In some cases, there is an increased predisposition to gallbladder disease on estrogen therapy.
Other conditions. Treatment should be discontinued immediately if migraine headaches or unusually severe headaches first develop, or other symptoms occur that are possible precursors of cerebral circulatory disorders.
If recurrent, persistent skin irritation (e.g., persistent erythema or itching at the site of application) is noted despite changes in the site of application as recommended, TTC should be discontinued.
The overall relationship between MHT and the development of clinical arterial hypertension has not been established. Although small increases in BP have been described in women treated with MHT, clinically significant increases in BP have been extremely rare. However, if, in individual cases, persistent, clinically significant hypertension develops during MHT, discontinuation of MHT should be considered.
Sex steroids can be poorly metabolized in patients with reduced liver function. In MHT with TTC, the active ingredient is not metabolized in the liver during “first pass” through the liver; in these cases, MHT should be administered with caution.
Recurrence of cholestatic jaundice or cholestatic pruritus that developed previously in pregnancy or during previous use of sex steroids requires immediate discontinuation of MHT.
Some patients receiving MHT may develop unwanted manifestations of estrogen stimulation, such as abnormal uterine bleeding. Frequent or persistent abnormal uterine bleeding during treatment is an indication for endometrial exploration.
Uterine myomas can increase in size under the influence of estrogen. If this is observed, treatment should be discontinued.
If endometriosis worsens during treatment, stopping therapy is recommended.
If prolactinoma is suspected, the diagnosis should be ruled out before starting therapy.
Chloasma may sometimes develop, especially in women with a history of chloasma in pregnancy. Women with a tendency to develop chloasma should avoid prolonged sun exposure and exposure to UV radiation during MHT.
The following conditions occur or worsen during MHT: epilepsy, benign breast disease, asthma, migraine, porphyria, otosclerosis, SLE, and minor chorea. Although their association with MHT has not been conclusively proven, in such cases women receiving MHT should be closely monitored.
Laboratory tests. MHT medications can affect the results of several laboratory tests, including liver function tests, thyroid, adrenal and kidney function parameters, plasma levels of transport proteins such as corticosteroid-binding globulin and lipid and lipoprotein fractions, carbohydrate metabolism parameters, and coagulation and fibrinolysis parameters.
Influence on driving and operating ability
There was no effect observed.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity, breast tumors, endometriosis, liver tumors, tumors dependent on sex steroid hormones, vaginal bleeding of unknown etiology, thromboembolic processes (thrombophlebitis, thrombosis), pregnancy, breastfeeding.
Side effects
Side effects
Local reactions: most often – skin irritation at the application site.
Perior genital system disorders: breakthrough bleeding and oozing from the vagina, increased size of uterine myoma, changes in the amount of vaginal secretion, painfulness and enlargement of the mammary glands.
In the digestive system: nausea, vomiting, stomach pain, pain in the epigastric region, flatulence, cholestatic jaundice.
Dermatological reactions: chloasma, melanoderma, which may be persistent.
Allergic reactions: in some cases – allergic contact dermatitis, pruritus, generalized exanthema.
CNS disorders: headache, migraine, dizziness, depression.
Others: change in body weight, worsening of the course of porphyria, edema, changes in libido, muscle cramps.
Overdose
Overdose
In application of Climar, overdose is unlikely.
Symptoms: nausea, vomiting; in some cases – bleeding withdrawal.
Treatment: removal of the patch, symptomatic therapy. A specific antidote is unknown.
Additional information
| Shelf life | Shelf life – 3 years. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | The drug should be kept out of reach of children at a temperature not exceeding 30°C. |
| Manufacturer | Bayer Bitterfeld GmbH, Germany |
| Medication form | transdermal therapeutic system |
| Brand | Bayer Bitterfeld GmbH |
Related products
Buy Climara, 3.9mg/12, 5 cm 4 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.