No products in the cart.
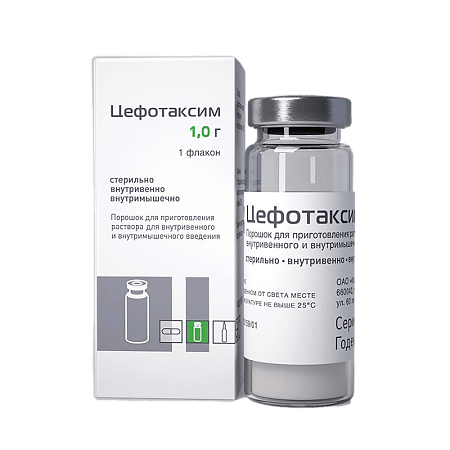
Cefotaxime, 1 g
€1.00
Out of stock
(E-mail when Stock is available)
Description
Cefotaxime is a III generation cephalosporin antibiotic for parenteral use. It acts bactericidally. It has a wide range of antimicrobial action.
Active against Gram-positive and Gram-negative microorganisms resistant to other antibiotics.
Active against Gram-positive, Gram-negative microorganisms resistant to other antibiotics: Staphylococcus spp. (including Staphylococcus aureus, including penicillinase forming strains), Staphylococcus epidermidis, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus agalactiae, Enterococcus species, Enterobacter spp, Escherichia coli, Haemophilus influenzae (including penicillinase-producing strains), Haemophilus parainfluenzae, Klebssiella spp.pneumoniae), Morganella morganii, Neisseria gonorrhoeae (including penicillinase strains), Acinetobacter species, Corynebacterium diphtheriae, Erysipelothrix insidiosa, Eubacterium spp, Propionibacterium spp, Bacillus subtilis, Clostridium spp. (including Clostridium perfringens), Escherichia coli, Citrobacter spp., Proteus mirabilis, Proteus indole, Proteus vulgaris, Providencia spp. (including Providencia rettgeri), Serratia spp, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Neisseria meningitidis, Bacteroides spp. (including some strains of Bacteroides fragilis), Fusobacterium spp. (including Fusobacterium nucleatum), Peptococcus spp.
Resistant to most beta-lactamases of Gram-positive and Gram-negative microorganisms, Staphylococcus penicillinase, Clostridium difficile.
Pharmacokinetics
After a single intravenous injection of 0.5, 1, and 2 g, the maximum concentration (Cmax) is reached in 5 min and is 39 µg/mL, 100 µg/mL, and 214 µg/mL, respectively. After 0.5 g and 1 g w/v/m, Cmax is reached after 0.5 hours and is 11 and 21 µg/ml, respectively. The binding to plasma proteins is 25-40%.
It creates therapeutic concentrations in most tissues (myocardium, bone, gallbladder, skin, soft tissue) and body fluids (synovial, pericardial, pleural, sputum, bile, urine, cerebrospinal fluid). Volume of distribution is 0.25-0.39 l/kg.
The half-life (T½) with intravenous and intramuscular administration is 1 hour.
The kidneys excreted 60% – 70% unchanged, the rest – as metabolites (the deacetylated derivative has bactericidal activity, and 2 other metabolites have no activity).
In chronic renal failure (CKD) and in elderly persons the T½ increases by 2 times. T½ in neonates is 0.75-1.5 hours, in premature infants increases to 4.6 hours. No cumulation is observed after repeated IV doses of 1 g every 6 hours for 14 days. It penetrates into breast milk.
Indications
Indications
Bacterial infections of severe course, caused by sensitive microorganisms:
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Composition
Composition
Active substance:
Cefotaxime sodium salt (in terms of the active substance) – 1.0 g
How to take, the dosage
How to take, the dosage
Intramuscularly and intravenously. For intramuscular injection, dissolve 0.5 g of the drug in 2 ml (respectively, 1 g in 4 ml) of sterile water for injection. It is injected deep into gluteal muscle. For intramuscular injection 1% lidocaine solution is also used as a solvent (for 0.5 g – 2 ml, for 1 g – 4 ml).
For intravenous administration 0.5 to 1 g of cefotaxime is dissolved in 10 ml of sterile water for injection. It is administered slowly over a period of 3 to 5 minutes.
For drip administration (for 50-60 minutes) 2 g of the drug is dissolved in 100 ml of sodium chloride isotonic solution or 5% glucose solution.
The usual dose of cefotaxime for adults and children over 12 years of age is 1 g every 12 hours. In severe cases the dose is increased to 3 or 4 g per day, the drug is administered 3 or 4 times 1 g. Depending on the severity of the disease the daily dose may be increased to a maximum of 12 g.
The usual dose for newborns and children under 12 years of age is 50-100 mg/kg of body weight per day with administration intervals of 6 to 12 hours. For premature infants the daily dose should not exceed 50 mg/kg.
In case of impaired renal function the dose is reduced. In creatinine clearance of 10 ml/min or less the daily dose of the drug is reduced by half.
Interaction
Interaction
Increases the risk of bleeding when combined with antiaggregants, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
It does not lead to disulfiram-like reactions when combined with ethanol.
The likelihood of renal damage is increased when concomitant use with aminoglycosides, polymyxin B and “loop” diuretics.
Drugs that block tubular secretion increase plasma concentrations of cefotaxime and slow its excretion.
Pharmaceutically incompatible with other antibiotic solutions in the same syringe or dropper.
Special Instructions
Special Instructions
In the first weeks of treatment, pseudomembranous colitis may occur, manifesting as severe prolonged diarrhea. If this occurs, discontinue the drug and prescribe adequate therapy, including vancomycin or metronidazole.
An allergologic history should be taken before prescribing the drug, especially with respect to beta-lactam antibiotics. Cross-allergy between penicillins and cephalosporins is known. In patients with a history of allergic reactions to penicillin the drug is used with extreme caution (the possibility of severe anaphylactic reactions, up to and including death should be considered).
If the duration of treatment with the drug is more than 10 days it is necessary to monitor the peripheral blood count.
When determining glucose in urine by a non-enzymatic method (e.g., Benedict method), false positive results are possible.
Prescribe with caution to persons driving vehicles and engaged in activities requiring increased concentration and rapid motor reaction.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity (including to penicillins, other cephalosporins, carbapenems).
In children under 2.5 years of age intramuscular administration of the drug should not be used.
With caution
The period of infancy, lactation (in minor concentrations excreted with milk); chronic renal failure, nonspecific ulcerative colitis (including anamnesis).
Side effects
Side effects
Allergic reactions: urticaria, chills or fever, rash, itching, bronchospasm, eosinophilia, erythema malignant exudative (Stevens-Johnson syndrome), toxic epidermal necrolysis (Lyell syndrome), angioedema, anaphylactic shock.
Digestive system disorders: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea or constipation, flatulence, abdominal pain, dysbacteriosis, liver disorders (increased activity of liver transaminases, alkaline phosphatase, hypercreatininemia, hyperbilirubinemia), stomatitis, glossitis, pseudomembranous enterocolitis.
Hematopoietic disorders: leukopenia, neutropenia, granulocytopenia, thrombocytopenia, hemolytic anemia, hypocoagulation.
Urinary system disorders: impaired renal function (azotemia, increased blood urea, oliguria, anuria, interstitial nephritis).
Nervous system disorders: headache, dizziness.
Laboratory findings: false positive Coombs test.
Cardiovascular system: potentially life-threatening arrhythmias after rapid bolus injection into the central vein.
Local reactions: phlebitis, soreness along the vein, soreness and infiltration at the site of injection/injection.
Others: superinfection (in particular, candidal vaginitis).
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: convulsions, encephalopathy (in case of high doses, especially in patients with renal failure), tremor, increased neuromuscular excitability.
Treatment: symptomatic therapy.
Pregnancy use
Pregnancy use
The use of the drug during pregnancy and lactation is possible only when the estimated benefit to the mother exceeds the potential risk to the fetus.
Cefotaxime is excreted with breast milk, therefore if it is necessary to prescribe the drug during lactation, breastfeeding should be stopped.
Similarities
Similarities
Additional information
| Weight | 0.017 kg |
|---|---|
| Shelf life | 2 years |
| Conditions of storage | In a light-protected place, at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C |
| Manufacturer | Kraspharma PJSC, Russia |
| Medication form | Powder for preparation of solution |
| Brand | Kraspharma PJSC |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Cefotaxime, 1 g with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.