No products in the cart.
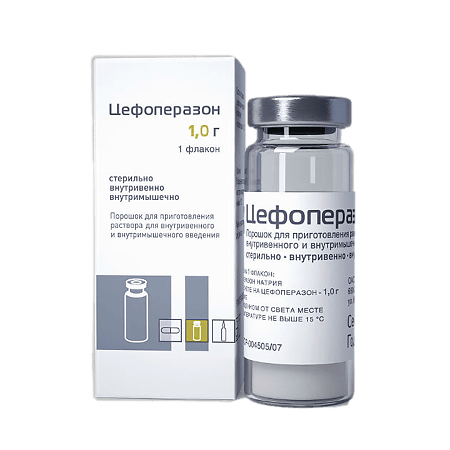
Cefoperazone, 1 g
€1.00
Out of stock
(E-mail when Stock is available)
Description
Pharmacotherapeutic group
Cephalosporin antibiotic
ATX code: J01DD12
Pharmacokinetics
The binding to plasma proteins is 82-93%. Time of reaching maximum concentration after intramuscular administration – 1-2 hours, after intravenous – at the end of infusion, maximum concentration after intramuscular administration of 1 and 2 g is 65-75 and 97 mcg/ml respectively; after single intravenous administration of 1, 2, 3 and 4 g maximum concentration is 153, 252, 340, and 506 mcg/ml respectively. Maximum concentration in urine after intramuscular and intravenous administration of 2 g is 1 and more than 2.2 mg/ml, respectively. Reaches therapeutic concentrations in such tissues and body fluids as peritoneal, ascitic fluid and cerebrospinal fluid (in meningitis), urine, bile, gallbladder walls, lungs, sputum, palatine tonsils and sinus mucosa, atria, kidneys, ureters, prostate, testicles, uterus, fallopian tubes, bone, cord blood and amniotic fluid.
The volume of distribution is 0.14-2 l/kg. Period of semiejection – 1.6-2.4 hours, regardless of method of administration, 2.8-4.2 hours – in hemodialysis, 2.2 hours – in infants and children from 2 months to 11 years. It is excreted 70-80% in bile, 20-30% unchanged in the kidneys. Half-life of patients with impaired liver function and biliary obstruction is 3-7 hours; renal excretion is 90% or more. Even with severe liver damage, therapeutic concentrations are achieved in bile, and the elimination half-life is only 2-4 times longer. In patients with renal-hepatic insufficiency may cumulate.
Pharmacodynamics
The semisynthetic cephalosporin antibiotic of the III generation of a broad spectrum of antibacterial action. It has a bactericidal effect caused by inhibition of the synthesis of the bacterial cell wall.
It is active in vitro against a large number of clinically relevant microorganisms.
It is resistant to the action of many beta-lactamases.
The following microorganisms are sensitive to cefoperazone: Gram-positive – Staphylococcus aureus (penicillinase-producing and non-producing strains), Staphylococcus epidermidis, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus pyogenes (beta-hemolytic Streptococcus group A), Streptococcus agalactiae (beta-hemolytic Streptococcus group B), Enterococcus (Streptococcus faecalis, S. faecium and S. durans); Gram-negative – Escherichia coli, Klebsiella species (including K. pneumoniae), Enterobacter spp, Citrobacter spp., Haemophilus influenzae, Proteus mirabilis, Proteus vulgaris, Morganella morganii, Providencia stuartii, Providencia rettgeri, Serratia marcescens, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Pseudomonas spp, some strains of Acinetobacter calcoaceticus, Neisseria gonorrhoeae; anaerobic microorganisms: gram-positive cocci (including Peptococcus spp., Peptostreptococcus spp.), Clostridium spp., Bacteroides fragilis and other strains of Bacteroides spp. Cefoperazone is also active in vitro against a wide range of other pathogens; however, the clinical significance of this is unknown: Salmonella spp. and Shigella spp, Serratia liquefaciens, Neisseria meningitidis, Bordetella pertussis, Yersinia enterocolitica, Clostridium difficile, Fusobacterium spp, Eubacterium spp. and betalactamase-producing strains of Haemophilus influenzae and Neisseria gonorrhoeae‑.
Indications
Indications
— Infectious and inflammatory diseases caused by microorganisms sensitive to the drug:
> bacterial infections of the upper and lower respiratory tract (including bronchitis, pneumonia, pleural empyema and lung abscess);
> kidney and urinary tract infections (including pyelonephritis and cystitis);
> infections of the abdominal organs (including peritonitis, cholecystitis, cholangitis);
> sepsis, meningitis;
> infections of the skin and soft tissues;
> infections of bones and joints;
> infectious and inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs (including endometritis, gonorrhea and other genital tract infections).
– Prevention of infectious complications after abdominal, gynecological and orthopedic operations, as well as in cardiovascular surgery.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacotherapeutic group
Antibiotic-cephalosporin
ATX code: J01DD12
Pharmacokinetics
Bonding with plasma proteins is 82–93%. The time to reach the maximum concentration after intramuscular administration is 1–2 hours, after intravenous administration — at the end of the infusion, the maximum concentration after intramuscular administration of 1 and 2 g is 65–75 and 97 mcg/ml, respectively; after a single intravenous injection of 1, 2, 3 and 4 g, the maximum concentration is 153, 252, 340, and 506 mcg/ml, respectively. The maximum concentration in urine after intramuscular and intravenous administration of 2 g is 1 and more than 2.2 mg/ml, respectively. Reaches therapeutic concentrations in such tissues and body fluids as peritoneal, ascitic fluid and cerebrospinal fluid (for meningitis), urine, bile, gallbladder walls, lungs, sputum, tonsils and sinus mucosa, atria, kidneys, ureters, prostate gland, testicles, uterus, fallopian tubes, bones, umbilical cord blood and amniotic fluid.
Volume of distribution – 0.14–2 l/kg. The half-life is 1.6–2.4 hours, regardless of the route of administration, 2.8–4.2 hours during hemodialysis, 2.2 hours in newborns and children from 2 months to 11 years. Excreted with bile – 70–80%, kidneys – 20–30% unchanged. In patients with impaired liver function and biliary tract obstruction, the half-life is 3–7 hours, renal excretion is 90% or more. Even with severe liver damage, therapeutic concentrations are reached in the bile, and the half-life is only extended by 2–4 times. May accumulate in patients with renal and hepatic insufficiency.
Pharmacodynamics
Semisynthetic cephalosporin antibiotic of the third generation with a wide spectrum of antibacterial action. It has a bactericidal effect due to inhibition of bacterial cell wall synthesis.
Active in vitro against a large number of clinically significant microorganisms.
Resistant to the action of many beta-lactamases.
The following microorganisms are sensitive to cefoperazone: gram-positive – Staphylococcus aureus (strains producing and not producing penicillinase), Staphylococcus epidermidis, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus pyogenes (beta-hemolytic streptococcus of group A), Streptococcus agalactiae (beta-hemolytic streptococcus of group B), Enterococcus (Streptococcus faecalis, S. faecium and S. durans); gram-negative – Escherichia coli, Klebsiella species (including K. pneumoniae), Enterobacter spp., Citrobacter spp., Haemophilus influenzae, Proteus mirabilis, Proteus vulgaris, Morganella morganii, Providencia stuartii, Providencia rettgeri, Serratia marcescens, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Pseudomonas spp., some strains of Acinetobacter calcoaceticus, Neisseria gonorrhoeae; anaerobic microorganisms: gram-positive cocci (including Peptococcus spp., Peptostreptococcus spp.), Clostridium spp., Bacteroides fragilis and other strains of Bacteroides spp. Cefoperazone is also active in vitro against a wide range of other pathogens, however, the clinical significance of this is unknown: Salmonella spp. and Shigella spp., Serratia liquefaciens, Neisseria meningitidis, Bordetella pertussis, Yersinia enterocolitica, Clostridium difficile, Fusobacterium spp., Eubacterium spp. and strains of Haemophilus influenzae and Neisseria gonorrhoeae that produce beta-lactamases.
Special instructions
Special instructions
Before prescribing cefoperazone, it is necessary to collect a detailed allergy history in order to identify the patient’s hypersensitivity to cephalosporins, penicillins and other drugs.
If an allergic reaction occurs during treatment, the use of cefoperazone should be discontinued and appropriate treatment should be initiated.
In some patients, treatment with cefoperazone can lead to vitamin K deficiency in the body, which is associated with suppression of the intestinal flora that synthesizes this vitamin. Those most at risk are patients with malabsorption syndrome (for example, cystic fibrosis), as well as patients who adhere to an inadequate diet or
on parenteral nutrition for a long time. In such patients, prothrombin time should be monitored during treatment and, if necessary, vitamin K should be prescribed.
During long-term therapy, it is recommended to periodically monitor the function of the kidneys, liver and hematopoietic organs. This is especially important for newborns, incl. premature
Clostridium difficile associated diarrhea is observed during the use of almost all antibacterial drugs, including cefoperazone, and manifests itself from mild forms of diarrhea to severe colitis. with fatal outcome. Treatment with antibacterial drugs leads to disruption of the normal microflora of the colon, resulting in increased growth of Clostridium difficile, production of toxins A and B, which lead to the development of Clostridium difficile associated diarrhea. Hypertoxin-producing strains of Clostridium difficile lead to increased morbidity and mortality because they may be resistant to antibiotic therapy. All cases of diarrhea in patients during antibiotic therapy should be considered suspicious for the development of Clostridium difficile associated diarrhea.
During the treatment period, a false positive reaction to glucose in the urine is possible when conducting tests using Benedict’s or Fehling’s solutions.
If necessary, use the drug in newborns, incl. prematurity, the expected positive effects of therapy and the possible risks associated with treatment should be taken into account. In newborns with kernicterus, cefoperazone does not displace bilirubin from the binding sites of plasma proteins.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery
Use with caution.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Cefoperazone
Composition
Composition
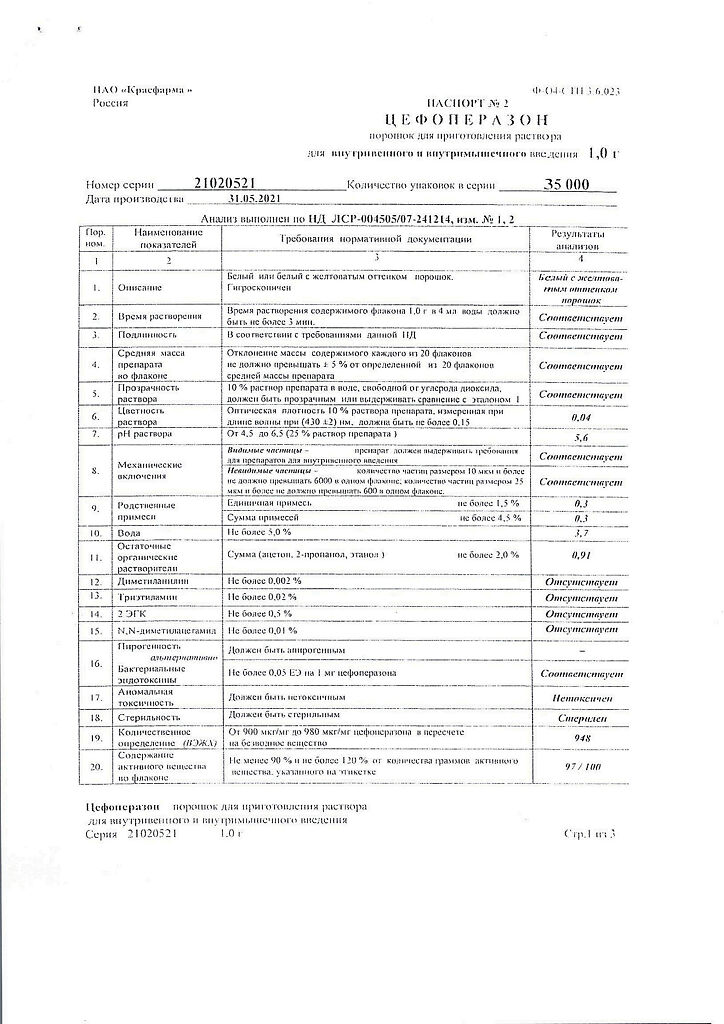
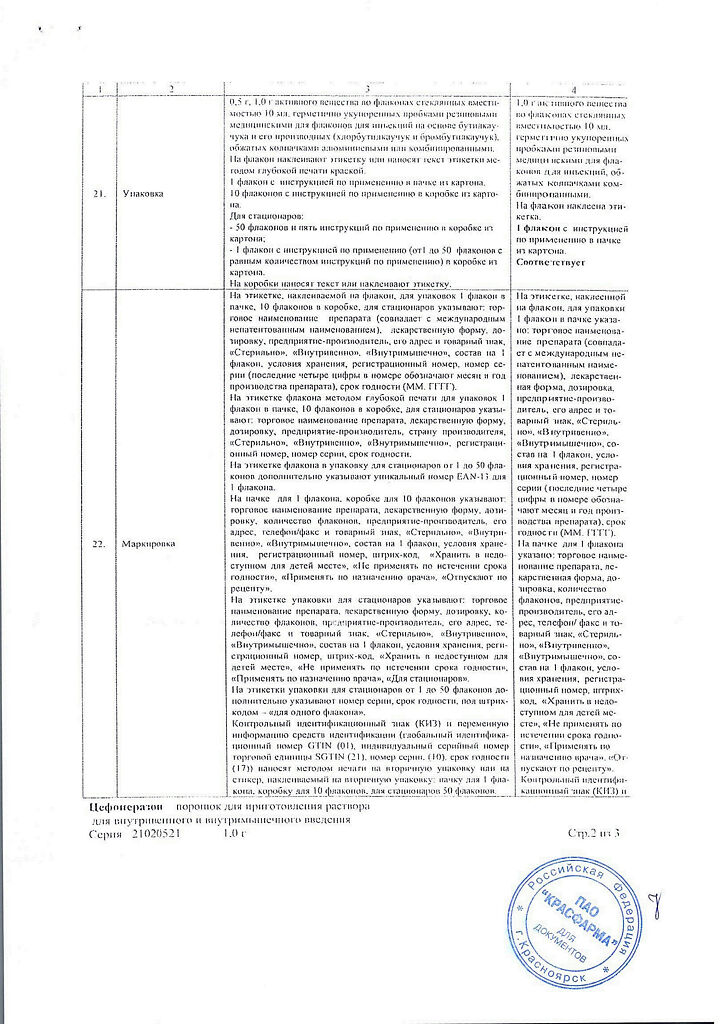
Composition of the drug for 1 bottle
Active substance:
Cefoperazone sodium in terms of cefoperazone – 1.0 g.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to cefoperazone and other beta-lactam antibiotics.
With caution
Renal and hepatic failure, history of colitis, children under 1 year of age, obstruction of the biliary tract.
Side Effects
Side Effects
Allergic reactions: urticaria, skin itching, maculopapular rash, fever, eosinophilia, exudative erythema multiforme (including Stevens-Johnson syndrome), rarely – anaphylactic shock.
From the gastrointestinal tract: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, pseudomembranous colitis.
From the hematopoietic organs and hemostasis system: bleeding (vitamin K deficiency), anemia, reversible neutropenia (with long-term use).
Laboratory indicators: hypoprothrombinemia, increased prothrombin time, increased activity of liver transaminases and alkaline phosphatase, hypercreatininemia, positive Coombs test.
Local reactions: with intravenous administration – phlebitis; with intramuscular injection – pain at the injection site.
Interaction
Interaction
Pharmaceutically incompatible with aminoglycosides (if combination therapy with cefoperazone and an aminoglycoside is necessary, drugs are prescribed in the form of sequential fractional IV administration of drugs using 2 separate IV catheters).
Indirect anticoagulants, heparin, thrombolytics, antiplatelet agents, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs increase the risk of hypoprothrombinemia and bleeding.
Aminoglycosides and loop diuretics increase the risk of nephrotoxicity, especially in persons with renal impairment.
Medicines that reduce tubular secretion increase the concentration of the drug in the blood and slow down its elimination.
Not compatible with ethanol; disulfiram-like reactions may develop in the form of hyperemia, nausea, vomiting, headache, shortness of breath, tachycardia, decreased blood pressure, and abdominal cramps.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: neurological disorders; including seizures.
Treatment: symptomatic therapy. Hemodialysis is effective.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
Store in a dry place, protected from light, at a temperature not exceeding 25°C. Keep out of the reach of children.
Shelf life
Shelf life
2 years
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Kraspharma PJSC, Russia
Additional information
| Shelf life | 2 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | Store in a dry, light-protected place at a temperature not exceeding 25°C. Keep out of reach of children. |
| Manufacturer | Kraspharma PJSC, Russia |
| Medication form | Powder for preparation of solution |
| Brand | Kraspharma PJSC |
Related products
Buy Cefoperazone, 1 g with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.