No products in the cart.
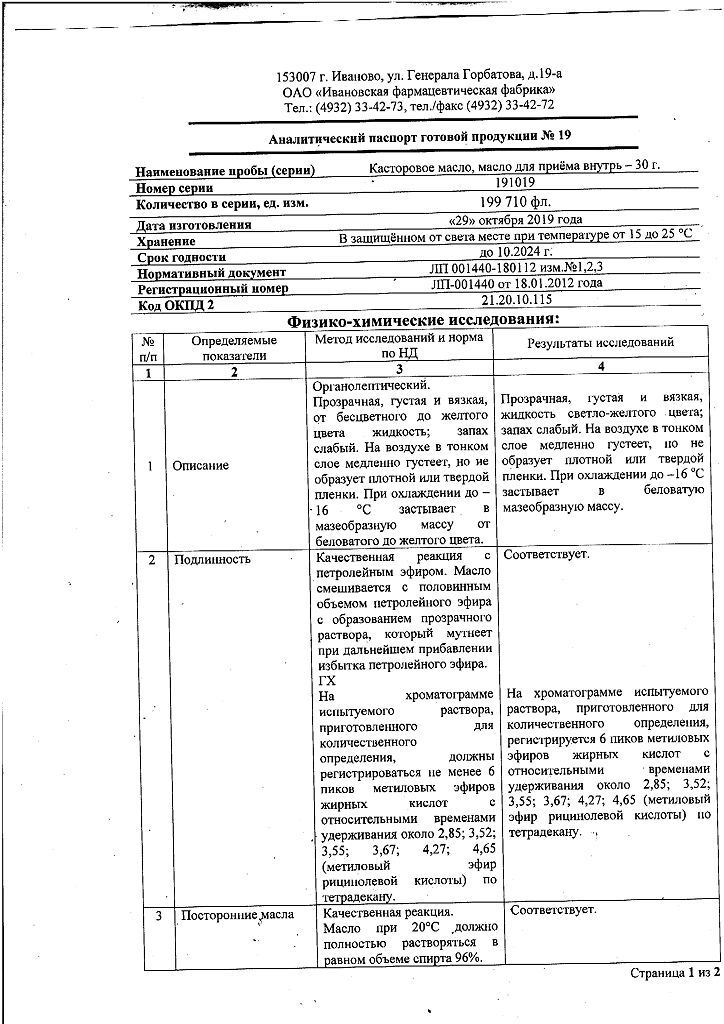
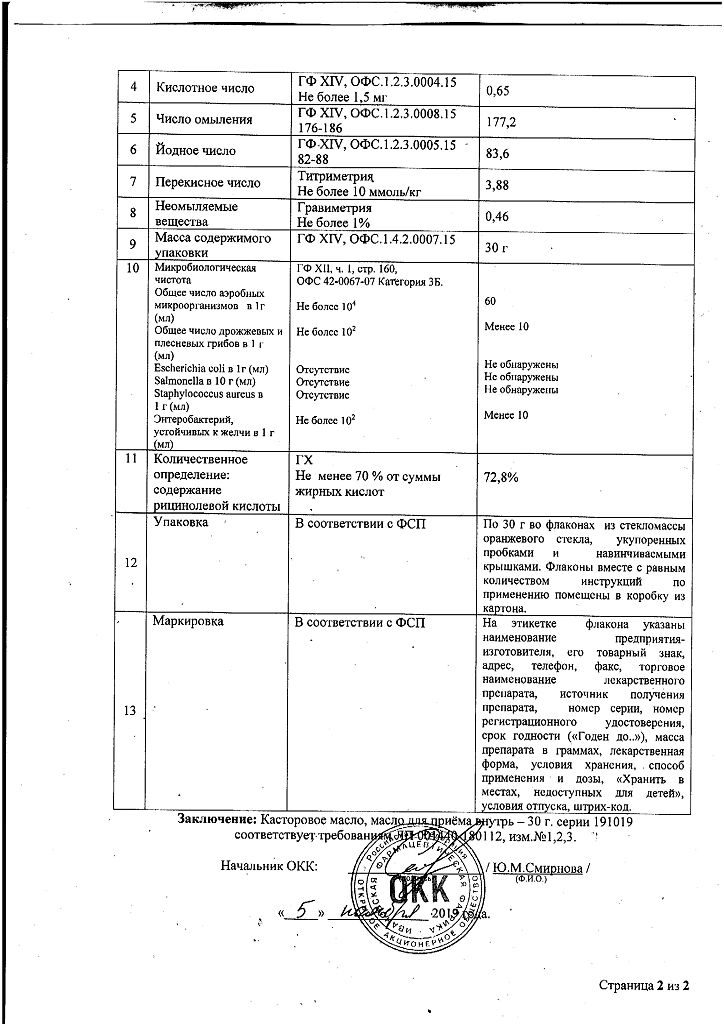
Castor oil for oral administration 30 g
€3.64 €3.31
Description
Castor oil is a laxative of vegetable origin.
Pharmacodynamics
The mechanism of action of castor oil is due to ricinolic acid released from it in the duodenal lumen. At a concentration of 0.5 mmol/l, ricinolic acid irritates receptors throughout the intestine and inhibits Na+/K+/2Cl–transporters, as a result electrolyte absorption is stopped and water absorption is secondary delayed.
In concentrations greater than 2 mmol/L ricinoleic acid increases water secretion into the intestinal lumen. Under the influence of castor oil increases the volume of intestinal contents, increases intestinal motility and accelerates its emptying. Remaining in the intestine oil facilitates the movement of feces in the large intestine. The laxative effect develops 2 to 6 hours after taking the oil and weakens after emptying the bowels.
When irritating the intestinal receptors castor oil reflexively stimulates spinal cord centers coordinating contractile activity of the myometrium. As a result, castor oil increases uterine contractions during pregnancy.
Pharmacokinetics
After oral administration in the alkaline environment of the duodenum in the presence of bile under the influence of lipase ricinolic acid is formed from the oil. Absorption of ricinoleic acid is inversely proportional to the dose taken. When oil is administered in a dose of 4 g, absorption of ricinolic acid is about 100%; when administered in a dose of 50 g, only 36% is absorbed (the rest of the acid is excreted with the feces within 24 hours); when administered in a dose of 60 g, the percentage of absorbed acid is only 10%.
The absorption rate of ricinoleic acid is half the absorption rate of oleic acid. At least 10 g of oil must be taken to develop a loosening effect. The absorbed portion of ricinolic acid undergoes β-oxidation in the liver and skeletal muscles and is included in metabolic processes.
Indications
Indications
Acute constipation; weakness of labor forces (as part of complex therapy); to stimulate hair growth; food intoxication; bowel cleansing before diagnostic procedures; poisoning; burns, wounds, skin ulcers, hyperkeratosis.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Castor oil is a herbal laxative.
Pharmacodynamics
The mechanism of action of castor oil is associated with ricinolic acid released from it in the lumen of the duodenum. At a concentration of 0.5 mmol/l, ricinolic acid irritates receptors throughout the intestine and stops the operation of Na+/K+/2Cl- transporters, as a result, the absorption of electrolytes stops and the absorption of water is secondarily delayed.
At concentrations of more than 2 mmol/l, ricinolic acid increases the secretion of water into the intestinal lumen. Under the influence of castor oil, the volume of intestinal contents increases, intestinal motility increases, and its emptying accelerates. The oil remaining in the intestines facilitates the movement of stool through the colon. The laxative effect develops 2 to 6 hours after taking the oil and weakens after bowel movement.
When irritating intestinal receptors, castor oil reflexively stimulates the centers of the spinal cord that coordinate the contractile activity of the myometrium. As a result, castor oil increases uterine contractions during pregnancy.
Pharmacokinetics
After ingestion in the alkaline environment of the duodenum in the presence of bile, ricinolic acid is formed from the oil under the influence of lipase. Absorption of ricinolic acid is inversely proportional to the dose taken. When the oil is administered in a dose of 4 g, the absorption of ricinolic acid is about 100%; when administered in a dose of 50 g, only 36% is absorbed (the rest of the acid is excreted in the feces within 24 hours); when administered in a dose of 60 g, the proportion of absorbed acid is only 10%.
The absorption rate of ricinolic acid is half the absorption rate of oleic acid. To develop a laxative effect, you need to take at least 10 g of oil. The absorbed portion of ricinolic acid undergoes β-oxidation in the liver and skeletal muscles and is included in metabolic processes.
Special instructions
Special instructions
Caution when using.
It is not recommended to use castor oil as a laxative for more than 3 days, since digestion may be impaired, as well as the absorption of vitamins A and D, with the development of corresponding hypovitaminosis.
It is unacceptable to use castor oil when treating with medicines obtained from male fern, because in this case, their systemic absorption and the development of neurotoxic effects are possible.
Influence on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery.
While taking castor oil, it is not recommended to drive a vehicle; you should refrain from other operator activities due to possible impairment of concentration during the onset of the effect.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Castor bean seed oil
Composition
Composition
Castor oil 100%
Contraindications
Contraindications
Acute inflammatory bowel diseases (including appendicitis);
individual intolerance;
chronic constipation;
acute and chronic glomerulonephritis;
mechanical intestinal obstruction;
abdominal pain of unknown origin;
intestinal and uterine bleeding;
poisoning with fat-soluble poisons (including gasoline, carbon tetrachloride, male fern extract);
tubulointerstitial nephritis;
children’s age (up to 12 years);
pregnancy and lactation period.
Side Effects
Side Effects
Hypovitaminosis A and D with repeated use;
abdominal pain, nausea;
digestive disorders, enterocolitis with repeated use;
addiction with repeated use;
rush of blood to the pelvic organs.
Interaction
Interaction
When applied topically, it increases the percutaneous absorption of drugs applied together with it to the skin.
When used simultaneously, it reduces the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins A, D and K. In doses of up to 4 g/day, it increases the absorption of fat-soluble drugs – male fern extract, mebendazole, griseofulvin, probucol.
When used simultaneously with saline laxatives, a sharp increase in the laxative effect is possible.
M-anticholinergic drugs (atropine sulfate, platifilin, pirenzepine), antispasmodics (papaverine, drotaverine) weaken the effect of castor oil.
Strengthens the effect of drugs that stimulate the contractile activity of the myometrium (methylergometrine, ergometrine, oxytocin, prostaglandins) up to the risk of uterine rupture during childbirth.
Anticholinesterase agents (neostigmine, pyridostigmine, rivastigmine) and glycerin enhance the laxative effect of castor oil.
Overdose
Overdose
Specific antidotes are atropine sulfate and loperamide.
Assistance measures include discontinuation of the drug, replenishment of fluid and electrolyte losses (combined oral and intravenous administration is preferable), supportive and symptomatic therapy aimed at eliminating the disorders that have arisen.
If neurotoxic effects develop, diazepam 5–10 mg is administered intravenously.
Develops when taking castor oil at a dose of more than 7 g/kg body weight. Characteristic symptoms include diarrhea, severe abdominal cramps, impaired renal function, dizziness, hallucinations, and loss of consciousness.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
In a place protected from light, at a temperature not exceeding 25 ºС.
Shelf life
Shelf life
5 years
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Ivanovo pharmaceutical factory, Russia
Additional information
| Shelf life | 5 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | In the light-protected place at a temperature not exceeding 25 ºC. |
| Manufacturer | Ivanovskaya Pharmfabrika, Russia |
| Medication form | oil for oral administration |
| Brand | Ivanovskaya Pharmfabrika |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Castor oil for oral administration 30 g with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.