No products in the cart.
Description
Breast Cancer
– Combination therapy with docetaxel for locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer when chemotherapy including an anthracycline drug is ineffective;
Monotherapy of locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer that is resistant to chemotherapy with taxanes or anthracycline-type drugs or if there are contraindications to them.
Colorectal cancer
– Adjuvant therapy of stage III colorectal cancer after surgical treatment;
The therapy of metastatic colorectal cancer.
Gastric cancer
– First-line therapy for advanced gastric cancer.
Indications
Indications
Breast cancer
– Combination therapy with docetaxel for locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer when chemotherapy, including an anthracycline drug, is ineffective;
– monotherapy for locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer resistant to chemotherapy with taxanes or anthracycline drugs or if there are contraindications to them.
Colorectal cancer
– Adjuvant therapy for stage III colon cancer after surgical treatment;
– therapy for metastatic colorectal cancer.
Stomach cancer
– First-line therapy for advanced gastric cancer.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacotherapeutic group:
Special instructions
Special instructions
Adverse reactions that limit the dose of the drug are diarrhea, abdominal pain, nausea, stomatitis, hand-foot syndrome.
Patients receiving capecitabine therapy should be closely monitored for toxicities.
Most adverse events are reversible and do not require complete discontinuation of the drug, although it may be necessary to adjust the dose or temporarily discontinue the drug.
Diarrhea: Treatment with capecitabine may cause diarrhea, sometimes severe.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Capecitabine
Composition
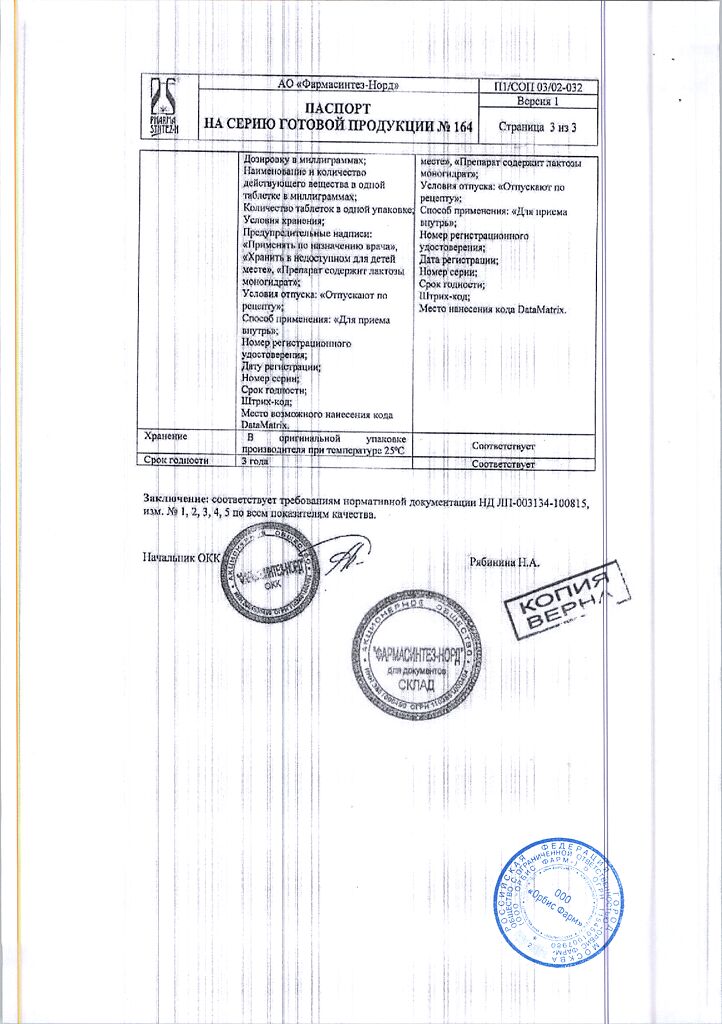
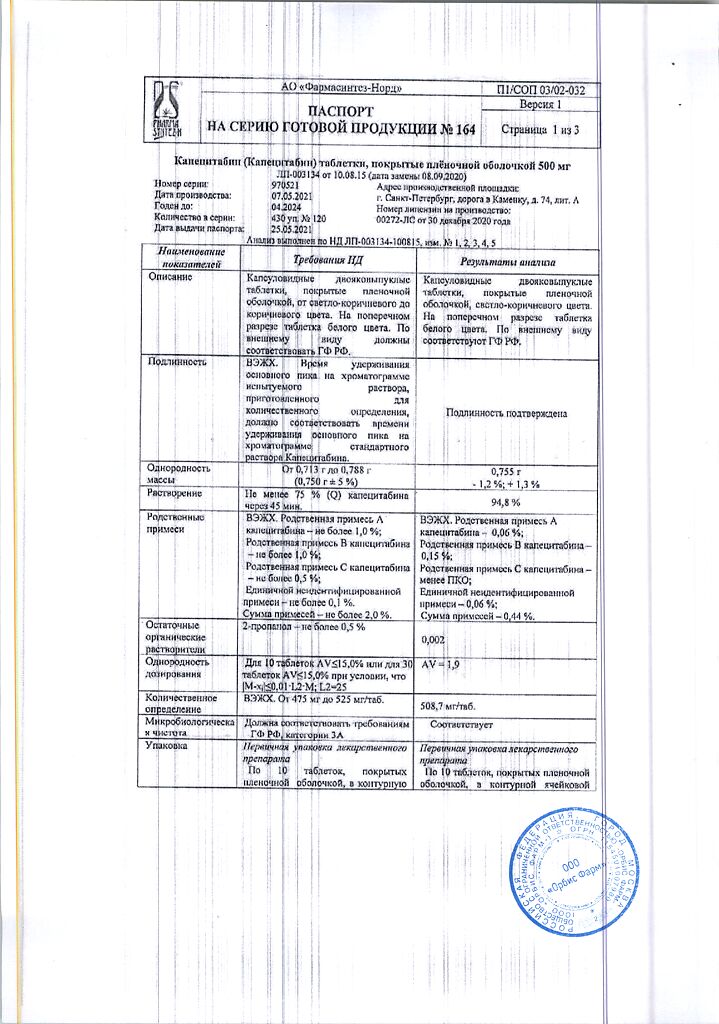
Composition
Active ingredient:
capecitabine 500.00 mg;
excipients:
lactose 91.11 mg,
microcrystalline cellulose 91.11 mg,
croscarmellose sodium 32.80 mg,
hypromellose 2.92 mg,
magnesium stearate 10.93 mg;
shell:
film coating 6.56 mg (hypromellose (38.46%),
talc (30.77%),
titanium dioxide (E 171) (29.41%),
red iron oxide dye (E 172) (0.68%),
iron oxide yellow dye (E 172) (0.68%).
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
The drug is contraindicated for use during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Reliable methods of contraception should be used during capecitabine therapy and for at least 3 months thereafter.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to capecitabine or any other components of the drug;
hypersensitivity to fluorouracil or with a history of reported cases of unexpected or severe adverse reactions to treatment with fluoropyrimidine derivatives;
established deficiency of DPD (dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase), as for other fluoropyrimidines;
simultaneous administration of sorivudine or its structural analogues such as brivudine;
severe liver failure;
severe renal failure (creatinine clearance below 30 ml/min);
severe leukopenia;
initial neutrophil content <1.5x109/l and/or platelets <100x109/l;
if there are contraindications to one of the drugs in combination therapy, it should not be used;
pregnancy and lactation;
children’s age (efficacy and safety of use have not been established).
With caution:
For coronary heart disease,
history of anemia and angina pectoris,
moderate renal failure or liver failure,
hypo- or hypercalcemia,
diseases of the central and peripheral nervous system,
diabetes mellitus and water-electrolyte imbalances,
over 60 years of age,
simultaneous use with oral coumarin anticoagulants,
hereditary lactase deficiency,
lactose intolerance,
glucose-galactose malabsorption.
Side Effects
Side Effects
The incidence of adverse reactions is stated according to WHO recommendations: very often (> 10%), often (> 1% and 0.1% and 0.01% and < 0.1%), very rarely (< 0.01%).
The most common side effects associated with capecitabine were gastrointestinal (GIT) disorders (diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, stomatitis), hand-foot syndrome, fatigue, asthenia, anorexia, cardiotoxicity, worsening renal failure in patients with a history of renal impairment, and thrombosis/embolism.
Side effects reported in patients taking capecitabine as monotherapy
Infectious and parasitic diseases: often – herpes viral infection, nasopharyngitis, lower respiratory tract infection; uncommon – sepsis, urinary tract infection, cellulitis, tonsillitis, pharyngitis, candidiasis of the oral mucosa, influenza, gastroenteritis, fungal infections, infections, tooth abscess.
Benign, malignant and unspecified neoplasms: uncommon – lipoma.
Disorders of the blood and lymphatic system: often – neutropenia; uncommon – febrile neutropenia, granulocytopenia, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, hemolytic anemia, increase in international normalized ratio, prolongation of prothrombin time.
Immune system disorders: uncommon – hypersensitivity. Metabolic and nutritional disorders: very often – anorexia; often – dehydration, weight loss; uncommon – diabetes mellitus, hypokalemia, indigestion, hypertriglyceridemia.
Mental disorders: infrequently – panic attacks, depressed mood, decreased libido.
Nervous system disorders: often – headache, dizziness (except vertigo), lethargy, paresthesia, dysgeusia (taste perversion): infrequently – aphasia, memory impairment, fainting, imbalance, loss of sensitivity, peripheral neuropathy.
Visual disturbances: often – increased lacrimation, conjunctivitis; infrequently – decreased visual acuity, diplopia.
Hearing and labyrinthine disorders: infrequently – vertigo, ear pain.
Cardiac disorders: uncommon – angina, including unstable, arrhythmia, sinus tachycardia, palpitations.
Vascular disorders: often – thrombophlebitis; uncommon – deep vein thrombosis, increased blood pressure, petechiae, decreased blood pressure, hot flashes, coldness of the distal extremities.
Disorders of the respiratory system, chest and mediastinal organs: often – nosebleeds, rhinorrhea; uncommon – pneumothorax, hemoptysis, bronchial asthma, shortness of breath on exertion.
Gastrointestinal disorders: very often – diarrhea, vomiting, nausea, stomatitis (including ulcerative), abdominal pain; often – constipation, epigastric pain, dyspepsia; uncommon – intestinal obstruction, ascites, enteritis, dysphagia, lower abdominal pain, abdominal discomfort, gastroesophageal reflux disease, blood in the stool.
Disorders of the liver and biliary tract: often – changes in liver function tests; infrequently – jaundice.
Disorders of the skin and subcutaneous tissues: very often – palmar-plantar syndrome (paresthesia, swelling, hyperemia, peeling of the skin, blistering), dermatitis; often – skin hyperpigmentation, macular rash, rash, alopecia, erythema, dry skin; Uncommon: blister, skin ulcers, urticaria, palmar erythema, facial edema, purpura.
Skin cracks at least thought to be related to capecitabine therapy were reported in less than 2% of patients in 7 completed clinical studies (N=949).
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders: often – pain in the limbs, back pain; Uncommon: joint swelling, bone pain, facial pain, stiffness, muscle weakness.
Renal and urinary tract disorders: uncommon – hydronephrosis, urinary incontinence, hematuria, nocturia, increased plasma creatinine.
Disorders of the genital organs and breast: infrequently – vaginal bleeding.
General disorders and disorders at the injection site: very often – fatigue, drowsiness; often – peripheral edema, malaise, chest pain, fever, weakness, asthenia; infrequently – swelling, chills, flu-like syndrome, trembling, increased body temperature.
Impact on the results of laboratory and instrumental studies: often – hyperbilirubinemia.
The following adverse reactions are toxicities known to occur with fluoropyrimidine therapy; At least an indirect association between the development of such reactions and the use of capecitabine was reported in less than 5% of patients participating in 7 completed clinical studies (N=949):
disorders of the gastrointestinal tract: dry mouth, flatulence, adverse reactions associated with inflammation/ulceration of the mucous membranes, such as esophagitis, gastritis, duodenitis, colitis, gastrointestinal bleeding;
disorders of the cardiovascular system: edema of the lower extremities, cardialgia, including angina pectoris, cardiomyopathy, myocardial ischemia, myocardial infarction, heart failure, sudden death, tachycardia, supraventricular arrhythmias, including atrial fibrillation, ventricular extrasystoles;
disorders of the nervous system: taste disturbance, insomnia, confusion, encephalopathy, symptoms of cerebellar disorders (ataxia, dysarthria, impaired balance and coordination);
mental disorders: depression;
infectious and parasitic diseases: infectious complications associated with myelosuppression, immunosuppression and/or mucositis, such as local and fatal systemic infections (bacterial, viral or fungal etiology) and sepsis;
disorders of the blood and lymphatic system: anemia, myelosuppression/pancytopenia;
disorders of the skin and subcutaneous tissues: itching, focal peeling of the skin, hyperpigmentation of the skin, changes in the nails, photosensitivity reactions, radiation dermatitis;
visual disturbances: eye irritation;
disorders of the respiratory system, chest and mediastinal organs: shortness of breath, cough;
musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders: arthralgia, myalgia, back pain;
general disorders and disorders at the injection site: chest pain (non-cardiac etiology), pain in the extremities.
Use of capecitabine in combination therapy
The safety profile did not differ between indications and combinations, but the adverse reactions listed with monotherapy may occur with greater frequency when capecitabine is used in combination therapy.
The following are undesirable reactions that were observed in addition to those with monotherapy:
Infectious and parasitic diseases: often – candidiasis of the oral mucosa, herpes zoster, urinary tract infections, upper respiratory tract infections, rhinitis, influenza, infection, oral herpes;
Disorders of the blood and lymphatic system: very often – neutropenia, anemia, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, febrile neutropenia; often – myelosuppression;
Immune system disorders: often – hypersensitivity;
Metabolic and nutritional disorders: very often – weight loss, loss of appetite; often – hypokalemia, hyponatremia, hypomagnesemia, hypocalcemia, hyperglycemia;
Mental disorders: often – sleep disorders, anxiety;
Nervous system disorders: very often – paresthesia, dysgeusia, headache, peripheral neuropathy, peripheral sensory neuropathy, dysesthesia; often – neurotoxicity, tremor, neuralgia, hypoesthesia;
Visual disturbances: very often – lacrimation; often – visual disturbances, dry eyes, eye pain, blurred vision;
Hearing disorders and labyrinthine disorders: often – tinnitus, hearing loss;
Cardiac disorders: often – atrial fibrillation;
Vascular disorders: very often – thrombosis/embolism, increased blood pressure (BP), edema of the lower extremities; often – hyperemia, decreased blood pressure, hypertensive crisis, hot flashes, phlebitis;
Disorders of the respiratory system, chest and mediastinal organs: very often – pharyngeal dysesthesia, sore throat; often – nosebleeds, dysphonia, rhinorrhea, hiccups, pain in the pharynx and larynx;
Gastrointestinal disorders: very often – constipation, dyspepsia; often – bleeding from the upper gastrointestinal tract, oral ulcers, gastritis, bloating, gastroesophageal reflux disease, oral pain, dysphagia, rectal bleeding, lower abdominal pain, dysesthesia, paresthesia and hypoesthesia in the mouth, abdominal discomfort;
Disorders of the liver and biliary tract: often – impaired liver function;
Disorders of the skin and subcutaneous tissues: very often – alopecia, changes in nails; often – hyperhidrosis, erythematous rash, urticaria, night sweats;
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders: very often – myalgia, arthralgia, pain in the extremities; often – jaw pain, muscle spasms, trismus, muscle weakness;
Renal and urinary tract disorders: often – hematuria, proteinuria, decreased creatinine clearance, dysuria;
General disorders and disorders at the injection site: very often – weakness, lethargy, increased sensitivity to high and low temperatures; often – fever, pain, inflammation of the mucous membrane, chills, chest pain, flu-like syndrome, contusion.
Cases of liver failure and cholestatic hepatitis have been reported both in and outside of clinical studies. A cause-and-effect relationship with capecitabine has not been established.
Hypersensitivity reactions (2%) and myocardial ischemia/infarction (3%) have been reported frequently (but in less than 5% of patients) during capecitabine therapy in combination with other chemotherapy drugs.
Laboratory and instrumental data:
The following are changes in laboratory parameters observed in clinical studies in patients undergoing adjuvant therapy for colon cancer and in patients undergoing treatment for metastatic breast cancer and metastatic colorectal cancer, regardless of their relationship with capecitabine: neutropenia, granulocytopenia, lymphocytopenia, thrombocytopenia, anemia, hyperbilirubinemia, increased activity of ALT, AST, alkaline phosphatase, hypercreatininemia, hyperglycemia, hypo-/hypercalcemia, hyponatremia, hypokalemia.
Post-registration experience with capecitabine
rarely – acute renal failure as a result of dehydration, including fatal outcome, punctate keratitis, ventricular fibrillation, prolongation of the QT interval, ventricular tachysystolic arrhythmia “pirouette”, bradycardia, vasospasm; very rarely – cutaneous lupus erythematosus, severe skin reactions such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, unspecified lacrimal duct stenosis, corneal damage, including keratitis; very rarely, in clinical studies and outside of their framework, cases of liver failure and cholestatic hepatitis were recorded.
Diarrhea
Diarrhea was observed in 50% of patients during capecitabine therapy.
A meta-analysis of 14 clinical trials involving more than 4,700 patients treated with capecitabine identified covariates that were statistically associated with an increased risk of developing diarrhea: increasing the initial dose of capecitabine (in grams), increasing the study period of treatment (in weeks), increasing the patient’s age (every 10 years), and female gender.
Covariates statistically associated with a reduced risk of diarrhea: increasing the cumulative dose of capecitabine (0.1 – kg) and increasing the relative dose intensity in the first 6 weeks of treatment.
Patients with severe diarrhea should be closely monitored with rehydration and restoration of fluid and electrolyte balance if dehydration occurs. According to indications, it is recommended to take standard antidiarrheal drugs (for example, loperamide) as early as possible.
Cardiotoxicity
In addition to the side effects presented in Tables 4 and 5, the following adverse reactions were observed with capecitabine monotherapy with an incidence of less than 0.1%: cardiomyopathy, heart failure, sudden death and ventricular extrasystoles.
Encephalopathy
During monotherapy with capecitabine, the development of encephalopathy was observed with an incidence of less than 0.1%.
Adverse reactions in special patient groups
Elderly patients
Elderly patients aged >60 years receiving capecitabine alone or in combination with docetaxel experienced an increased incidence of grade 3, 4 and serious adverse reactions compared with patients aged <60 years.
The majority of patients aged >60 years receiving combination therapy with docetaxel experienced earlier discontinuation of treatment due to adverse reactions compared with patients aged <60 years.
A meta-analysis of 14 clinical studies involving more than 4,700 patients treated with capecitabine found that as the patient’s age increased (every 10 years), the risk of developing hand-foot syndrome and diarrhea increased, while the risk of developing neutropenia, on the contrary, decreased.
Floor
In female patients, there is a statistically significant increase in the risk of developing hand-foot syndrome and diarrhea; the risk of developing neutropenia is reduced.
Patients with impaired renal function
Patients with pre-treatment renal impairment who received capecitabine monotherapy experienced an increased incidence of treatment-related grade 3 and 4 adverse reactions compared with patients with normal renal function (36% in patients without renal impairment, 41% in those with mild renal impairment and 54% in those with moderate renal impairment).
Patients with moderate renal impairment were more likely to require dose reductions (44%) compared with 33% and 32% of patients without renal impairment with mild renal impairment, respectively, and were more likely to have premature treatment discontinuation.
Interaction
Interaction
Coumarin anticoagulants
In patients taking capecitabine concomitantly with coumarin anticoagulants (warfarin and phenprocoumon), coagulation abnormalities and/or bleeding have been reported several days to months after the start of capecitabine therapy, and in some cases within one month after its completion.
In a drug interaction study, after a single dose of 20 mg warfarin, capecitabine increased the AUC of S-warfarin by 57% and the international normalized ratio (INR) by 91%.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms of acute overdose include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, inflammation of the mucous membrane (mucositis), gastrointestinal irritation and bleeding, and suppression of bone marrow function.
Treatment of overdose should include a standard set of therapeutic and supportive measures aimed at correcting clinical symptoms and preventing possible complications.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Pharmasyntez-Nord JSC, Russia
Additional information
| Manufacturer | Pharmasintez JSC, Russia |
|---|---|
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Pharmasintez JSC |
Related products
Buy Capecitabine, 500 mg 120 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.