No products in the cart.
Calcium-D3 Nicomed Strawberry-Amelon, 60 pcs.
€12.48 €10.40
Description
Calcium-phosphorus metabolism regulator. ATX code: A12AX
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
A combination drug that regulates calcium and phosphorus metabolism in the body (bones, teeth, nails, hair, muscles). It reduces resorption (resorption) and increases bone density, making up for the lack of calcium and vitamin D3 in the body. Calcium is involved in the regulation of nerve conduction, muscle contractions, hormone production and is a component of the blood clotting system.
The adequate intake of calcium is especially important during growth, pregnancy and lactation.
Vitamin D3 increases the absorption of calcium in the intestine.
The use of calcium and vitamin D3 inhibits increased production of parathyroid hormone (PTH), which is a stimulant of increased bone resorption (leaching of calcium from bones).
Pharmacokinetics
Calcium
Intake: Normally, the amount of calcium absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract is about 30% of the dose taken.
Distribution and metabolism: 99% of calcium in the body is concentrated in the hard structure of the bones and teeth. The remaining 1% is in intra- and extracellular fluids. About 50% of the total calcium content of the blood is in the physiologically active ionized form, of which about 10% is complexed with citrate, phosphate or other anions; the remaining 40% is associated with proteins, primarily with albumin.
Excretion: Calcium is excreted by the intestines, kidneys, and sweat glands. Renal excretion depends on glomerular filtration and tubular reabsorption of calcium.
Vitamin D3
Intake: Vitamin D3 is readily absorbed in the small intestine (about 80% of the dose taken).
Distribution and metabolism: Colecalciferol and its metabolites circulate in the blood associated with specific globulin. Colecalciferol is converted in the liver by hydroxylation to 25-hydroxycolecalciferol. It is then converted in the kidneys to the active form 1,25-hydroxycolecalciferol. 1,25-hydroxycalciferol is the metabolite responsible for increasing calcium absorption. Non-metabolized vitamin D3 is deposited in fat and muscle tissue.
Excretion: Vitamin D3 is excreted by the intestines and kidneys.
Indications
Indications
Prevention and treatment of calcium and/or vitamin D3 deficiency.
Addition to specific therapy and prevention of osteoporosis and its complications (bone fractures).
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Calcium-phosphorus metabolism regulator. ATX code: A12AX
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
A combined drug that regulates the exchange of calcium and phosphorus in the body (bones, teeth, nails, hair, muscles). Reduces resorption (resorption) and increases bone density, replenishing the lack of calcium and vitamin D3 in the body, necessary for the mineralization of teeth. Calcium is involved in the regulation of nerve conduction, muscle contractions, hormone production and is a component of the blood coagulation system.
Adequate calcium intake is especially important during growth, pregnancy and lactation.
Vitamin D3 increases calcium absorption in the intestines.
The use of calcium and vitamin D3 prevents an increase in the production of parathyroid hormone (PTH), which is a stimulator of increased bone resorption (leaching of calcium from the bones).
Pharmacokinetics
Calcium
Absorption: Typically, the amount of calcium absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract is approximately 30% of the dose taken.
Distribution and Metabolism: 99% of calcium in the body is concentrated in the rigid structure of bones and teeth. The remaining 1% is found in intra- and extracellular fluids. About 50% of the total calcium content in the blood is in a physiologically active ionized form, of which approximately 10% is complexed with citrate, phosphate or other anions, the remaining 40% is associated with proteins, primarily albumin.
Excretion: Calcium is excreted by the intestines, kidneys and sweat glands. Renal excretion depends on glomerular filtration and tubular reabsorption of calcium.
Vitamin D3
Absorption: Vitamin D3 is easily absorbed in the small intestine (about 80% of the dose taken).
Distribution and metabolism: colecalciferol and its metabolites circulate in the blood bound to a specific globulin. Colecalciferol is converted in the liver by hydroxylation to 25-hydroxycolecalciferol. It is then converted in the kidneys to the active form 1,25-hydroxycolecalciferol. 1,25-hydroxycolecalciferol is a metabolite responsible for increasing calcium absorption. Unmetabolized vitamin D3 is stored in adipose and muscle tissue.
Excretion: Vitamin D3 is excreted by the intestines and kidneys.
Special instructions
Special instructions
During long-term therapy, serum calcium and creatinine levels should be monitored. Monitoring is especially important in elderly patients during concomitant treatment with cardiac glycosides and diuretics (see section “Interactions with other drugs and foods”) and in patients with an increased tendency to form kidney stones. In cases of hypercalcemia or signs of renal impairment, reduce the dose or discontinue treatment.
Vitamin D3 should be taken with caution in patients with renal failure. In this case, it is necessary to monitor the calcium and phosphate levels in the blood serum. The risk of soft tissue calcification must also be considered.
To avoid overdose, additional intake of vitamin D and calcium from other sources must be taken into account.
Calcium and vitamin D3 should be used with caution in immobilized patients with osteoporosis due to the risk of hypercalcemia.
Concomitant use with tetracycline or quinolone antibiotics is usually not recommended, or should be done with caution (see section “Interaction with other drugs and foods”).
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and machinery
There is no data regarding the effect of the drug Calcium-D3 Nycomed on the ability to drive vehicles and machines.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
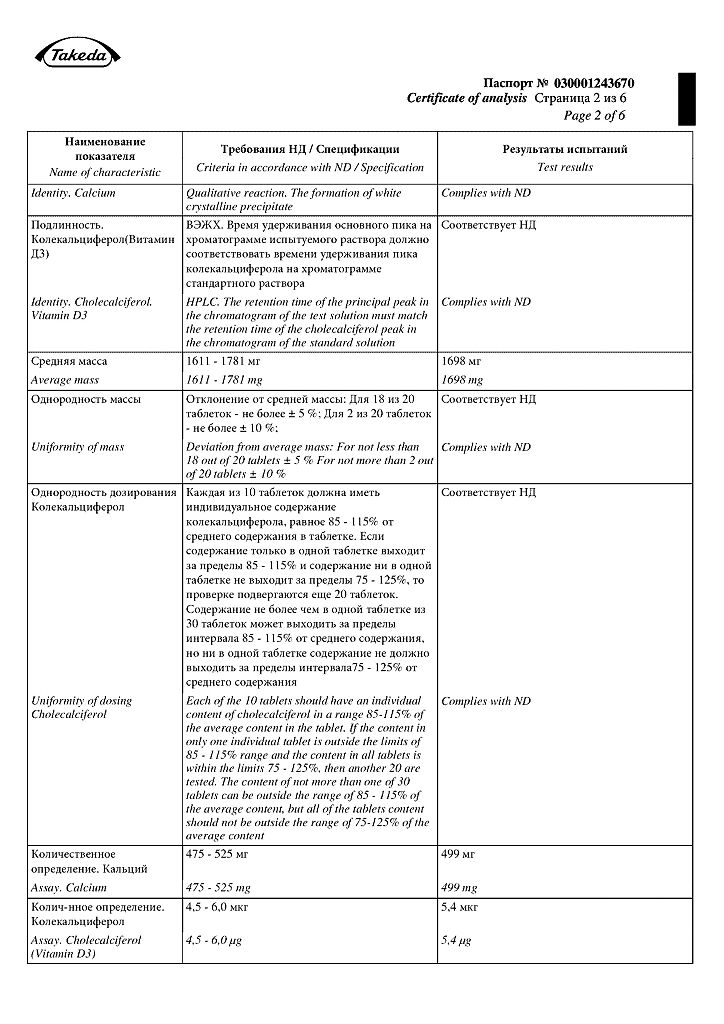
Calcium carbonate, Colecalciferol
Composition
Composition
Active components:
Calcium carbonate – 1250 mg (equivalent to elemental calcium – 500 mg)
Colecalciferol (vitamin D3) – 5.0 mcg* (200 IU) as concentrate** colecalciferol – 2.0 mg*
Auxiliary components:
Sorbitol – 390 mg
Strawberry-watermelon flavoring granulate***** – 10.2 mg
Povidone – 36.4 mg
Magnesium stearate – 6.00 mg
Aspartame – 1.00 mg.
*the amount of colecalciferol (vitamin D3), including 10% excess, is 5.5 mcg, in the form of colecalciferol concentrate – 2.2 mg.
**colecalciferol concentrate contains, including 10% excess: colecalciferol – 0.0055 mg, alpha-tocopherol – 0.022 mg, modified corn starch – 1.607 mg, sucrose – 0.385 mg, sodium ascorbate – 0.088 mg, medium chain triglycerides – 0.066 mg, silicon dioxide – 0.026 mg.
*****strawberry-watermelon flavor granules contain: maltodextrin – 8.25 mg, strawberry-watermelon flavor – 0.276 mg, triacetin – 0.163 mg, esters of glycerol and diacetyltartaric and fatty acids – 0.0918 mg, medium chain triglycerides – 0.0918 mg, water – 1.33 mg.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypercalcemia (increased concentration of calcium in the blood).
Hypercalciuria (increased calcium in urine).
Nephrolithiasis.
Hypervitaminosis D.
Hypersensitivity to the components of the drug.
Hypersensitivity to soy or peanuts.
Severe renal failure.
Active tuberculosis.
The drug in tablet form is not for use in children under 3 years of age.
Calcium-D3 Nycomed contains aspartame, which is transformed into phenylalanine in the body. Therefore, the drug should not be taken by patients with phenylketonuria.
Chewable tablets (orange, mint) contain sorbitol, isomalt and sucrose.
Chewable tablets (strawberry-watermelon) contain sorbitol and sucrose. Use is not recommended for patients with hereditary fructose intolerance, glucose-galactose malabsorption or sucrase-isomaltase deficiency.
With caution
Pregnancy, lactation, renal failure.
Calcium carbonate with colecalciferol should be administered with caution to patients with sarcoidosis, due to the risk of increasing the metabolism of vitamin D3 to its active form. In these patients, it is necessary to monitor the concentration of calcium in the blood serum and urine.
Side Effects
Side Effects
The frequency of side effects of the drug is assessed as follows:
Very common: 1/10
Frequent: 1/100, 1/10
Uncommon: 1/1000, 1/100
Rare: 1/10,000, 1/1000
Very rare: 1/10,000
Frequency unknown (cannot be calculated from available data)
Metabolic and nutritional disorders:
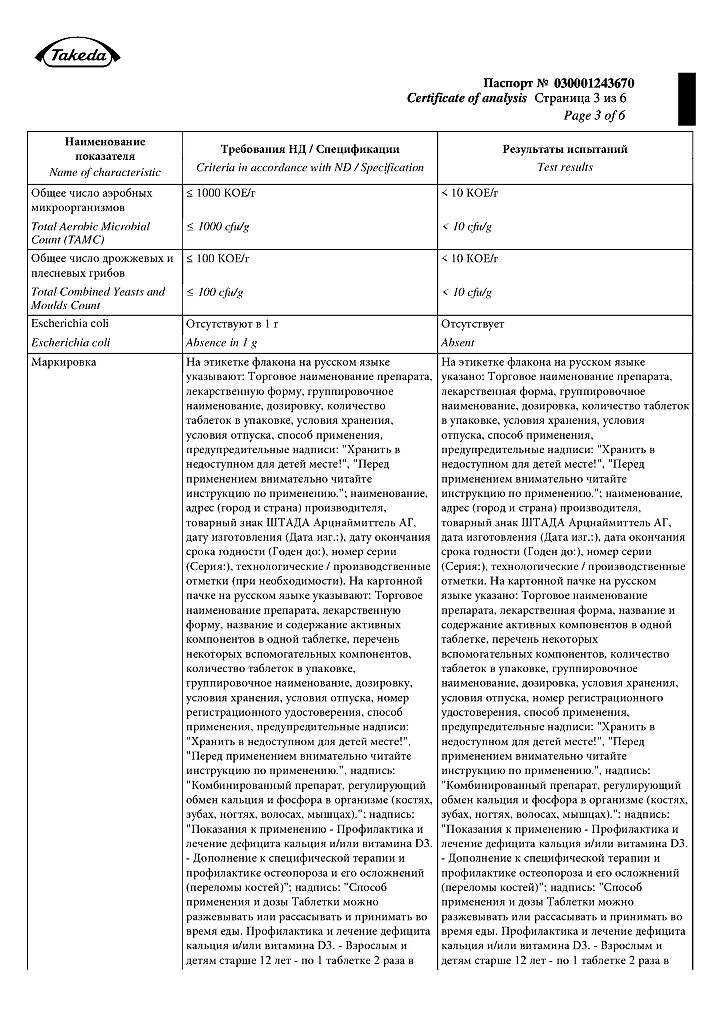
Uncommon: hypercalcemia and hypercalciuria.
Very rare: Milk-alkali syndrome (Burnett’s syndrome). Usually noted only in case of overdose (see section “Overdose”).
Gastrointestinal disorders:
Rarely: constipation, flatulence, nausea, abdominal pain, diarrhea, dyspepsia.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders:
Very rare: itching, rash, urticaria.
Immune system disorders:
Not known: hypersensitivity reactions such as angioedema or laryngeal edema.
Interaction
Interaction
Hypercalcemia can potentiate the toxic effects of cardiac glycosides when used simultaneously with calcium and vitamin D preparations. Monitoring of ECG and serum calcium levels is necessary.
Calcium supplements may reduce the absorption of tetracyclines from the gastrointestinal tract. Therefore, tetracycline drugs should be taken at least 2 hours before or 4-6 hours after taking Calcium-D3 Nycomed.
To prevent decreased absorption of bisphosphonate drugs, it is recommended to take them at least an hour before taking Calcium-D3 Nycomed.
Glucocorticosteroids reduce the absorption of calcium, so treatment with glucocorticosteroids may require an increase in the dose of Calcium-D3 Nycomed.
With simultaneous use of thiazide diuretics, the risk of hypercalcemia increases, because they increase tubular reabsorption of calcium. When thiazide diuretics are used concomitantly, serum calcium levels should be regularly monitored.
Calcium reduces the effectiveness of levothyroxine by reducing its absorption. The period of time between doses of levothyroxine and Calcium-D3 Nycomed should be at least 4 hours.
The absorption of quinolone antibiotics is reduced when used simultaneously with calcium supplements. Therefore, quinolone antibiotics should be taken 2 hours before or 6 hours after taking Calcium-D3 Nycomed.
Calcium salts may reduce the absorption of iron, zinc and strontium ranelate. Therefore, preparations of iron, zinc or strontium ranelate should be taken at least two hours before or two hours after taking Calcium – D3 Nycomed.
Treatment with orlistat may potentially interfere with the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (eg vitamin D3).
Overdose
Overdose
Overdose can lead to hypercalcemia and hypervitaminosis D.
Symptoms of overdose (hypercalcemia): anorexia, thirst, polyuria, muscle weakness, nausea, vomiting, constipation, abdominal pain, fatigue, bone pain, mental disorders, polydipsia, nephrocalcinosis, urolithiasis and, in severe cases, cardiac arrhythmias. With long-term use of excessive doses (over 2500 mg of calcium) – kidney damage, soft tissue calcification.
Milk-alkali syndrome (Burnett’s syndrome) can occur in patients who ingest large amounts of calcium and well-absorbed alkaline solutions.
If signs of overdose are detected, you should stop taking calcium and vitamin D3, as well as thiazide diuretics and cardiac glycosides, and consult a doctor.
Treatment: gastric lavage, replacement of fluid loss, use of loop diuretics (for example, furosemide), glucocorticosteroids, calcitonin, bisphosphonates.
It is necessary to monitor the content of electrolytes in the blood plasma, renal function and diuresis.
In severe cases, it is necessary to measure central venous pressure (CVP) and monitor the electrocardiogram (ECG).
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Takeda Pharmaceuticals LLC, Russia
Additional information
| Manufacturer | Takeda Pharmaceuticals LLC, Russia |
|---|---|
| Medication form | chewable tablets |
| Brand | Takeda Pharmaceuticals LLC |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Calcium-D3 Nicomed Strawberry-Amelon, 60 pcs. with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.