No products in the cart.
Bonade, 2 mg+0.03 mg 21 pcs
€24.99 €20.82
EAN: 3582910090861
SKU: 231101
Categories: Contraceptive, Gynecology and Obstetrics, Hormonal, Medicine
Description
Bonade is a low-dose monophasic oral combined estrogen-gestogen contraceptive. The action of Bonade is based on the combined action of various factors, the most important of which is suppression of ovulation and increase of cervical secretion viscosity.
The gestagenic component of Bonade, dienogest, is a derivative of nortestosterone and has an anti-androgenic effect. Dienogest also has a favorable effect on the lipid profile, increasing HDL content.
In women taking combined oral contraceptives (CTCs), the cycle becomes more regular, painful menstruation is less often observed, the intensity and duration of bleeding decreases.
Pharmacokinetics
Dienogest
Intake
Dienogest is quickly and almost completely absorbed after oral administration. Cmax in plasma (51 ng/ml) is reached 2.4±1.4 hours after drug administration. Bioavailability in combination with ethinylestradiol is about 96%.
Dienogest is bound to serum albumin (90%) and does not bind to specific transport proteins – sex hormone-binding globulin (hsBG) and corticosteroid-binding globulin (CRB). Any effect on the processes of physiological transport of endogenous steroids is unlikely. Ethinylestradiol-induced increase in hGH concentration has no effect on dienogestin binding to serum proteins.
The pharmacokinetics of dienogest is not affected by the hGH concentration. After a daily dose, the plasma concentration of the drug increases approximately 1-5 times, and the Css is reached after about 4 days.
Metabolism
Dienogest is metabolized primarily by hydroxylation, but also by hydrogenation, conjugation, and aromatization to form inactive metabolites.
The total clearance after a single dose is 3.6 l/h.
The T1/2 of dienogest is 8.5-10.8 hours. A small amount of dienogest is excreted unchanged by the kidneys. Metabolites are excreted by the kidneys and in the bile at a ratio of 3:1. T1/2 of metabolites is 14.4 h.
Ethinylestradiol
Intake
Ethinylestradiol is quickly and completely absorbed after oral administration. Cmax in plasma (67 ng/ml) is reached within 1.5-4 hours. During absorption and “first passage” through the liver, ethinylestradiol is metabolized, resulting in an average bioavailability of 44% with oral administration.
Distribution
Ethinylestradiol is almost completely (98%), although non-specific, bound to albumin. Ethinylestradiol induces the synthesis of hGH. The recorded Vd of ethinylestradiol is 2.8-8.6 L/kg.
Css is reached during the second half of the treatment cycle, when serum drug levels become twice as high as an individual dose.
Metabolism
Ethinylestradiol undergoes presystemic conjugation both in the mucosa of the small intestine and in the liver. The main metabolic pathway is aromatic hydroxylation, followed by conjugation with glucuronic and/or sulfuric acids.
The metabolic clearance rate from plasma is 2.3-7 ml/min/kg. The plasma concentration of ethinylestradiol decreases, and the decrease has a biphasic character: the first phase is characterized by a T1/2 of about 1 h, the second – 10-20 h.
It is not excreted unchanged. Metabolites of ethinylestradiol are excreted by the kidneys and liver in a ratio of 4:6, with a T1/2 of about 24 h.
Indications
Indications
Contraception.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Composition
Composition
1 tablet contains:
acting substances:
Ethinylestradiol 30 mcg,
Dienogest 2 mg,
accompaniettes:
Lactose monohydrate – 57.17 mg,
corn starch – 12 mg,
povidone 30LP – 3 mg,
.
sodium starch glycolate – 5 mg,
magnesium stearate – 0.8 mg.
composition of the film coating:
acquapolish white 014.17 MS (hypromellose – 48%, hydroxypropylcellulose – 12%, talc – 20%, cotton seed oil hydrogenated – 5%, titanium dioxide – 15%) – 9 mg.
How to take, the dosage
How to take, the dosage
Bonade is taken orally one tablet a day, without chewing and with a little water, at the same time every day. Tablets are taken for 21 days without interruption under the scheme indicated on the blister. Each blister contains 21 tablets. Each tablet is marked with the day of the week on which it is to be taken. The pills are not taken for the next 7 days. During this period, menstrual bleeding (bleeding withdrawal) should begin. It usually begins 2-3 days after taking the last pill of Bonade.
After a 7-day break, on the 8th day, the pills from a new pack (if the pack contains 21 pills) or a blister (if the pack contains 63 pills) are started, even if bleeding has not yet stopped. This means that the woman will always start a new pack (blister) on the same day of the week and that each month the bleeding will stop around the same day of the month.
Start Bonade
If you have not taken any hormonal contraceptives in the previous month, start Bonade on day 1 of your natural menstrual cycle (that is, day 1 of your menstrual bleeding). Take the pill marked with the corresponding day of the week. For example, if menstruation begins on Friday, take the pill marked with the letters indicating Friday. Then, you should continue taking the pills on the following days in the prescribed order. It is also acceptable to start using from days 2-5 of the cycle, but in this case it is recommended to use an additional barrier method of contraception (condom) during the first 7 days of using the pills from the first package (blister).
If you are switching from other PDAs, a contraceptive vaginal ring, or a contraceptive patch, you can start taking Bonade the day after taking the last pill from the previous PDA package (i.e. without interruption). If the previous pack also contained inactive pills (without the active ingredient), you can start Bonade the day after the last active pill. It is also possible to start using later, but in no case later than the next day, after the usual break in use (a break of 7 days for products containing 21 tablets) or after taking the last inactive tablet (for products containing 28 tablets in a pack).
If a contraceptive patch or contraceptive vaginal ring is used, Bonade should be started on the day it is removed, but no later than the day the new ring or patch is to be inserted.
If you are switching from a progestagen-only oral contraceptive (mini-pills), you can stop the mini-pill any day and start Bonade the next day, at the same time. During the first 7 days of using the pills, it is also necessary to use an additional barrier method of contraception.
If you are switching from a gestagen-releasing injectable contraceptive, implant, or intrauterine device (IUD), you should start Bonade on the day the next injection is due or on the day the implant or IUD is removed. During the first 7 days of using the pills, it is also necessary to use an additional barrier method of contraception.
In the immediate postpartum period, your doctor may recommend waiting until after your first normal menstrual cycle before starting Bonade. Sometimes, with a doctor’s recommendation, you can start using the medication earlier.
After a spontaneous miscarriage or abortion in the first trimester of pregnancy, a doctor should be consulted. It is usually recommended that the drug be started immediately.
Missed pills
If the delay in taking the next pill is less than 12 hours, the contraceptive effect of Bonade is maintained. The patient should take the pill as soon as she remembers it. The next pill should be taken at the usual time.
If pills are missed for more than 12 hours, contraceptive protection may be reduced. The more consecutive pills you miss, and the closer that miss is to the beginning or end of the pill, the greater the risk of pregnancy.
The following rules can guide you in this regard:
– if more than 1 tablet from the package (blister) is missed, a physician should be consulted;
– if 1 tablet is missed in the first week of the drug, the missed tablet should be taken as soon as the patient remembers (even if this means taking two pills at once). The next pill should be taken at the usual time. An additional barrier method of contraception should be used for the next 7 days. If sexual intercourse occurred during the week before skipping the pill, it is necessary to consider the possibility of pregnancy. A physician should be consulted immediately;
If 1 tablet is missed in the second week of taking the drug, the missed tablet should be taken as soon as possible as soon as the patient remembers (even if this means taking 2 pills at the same time). The next pill should be taken at the usual time. If the woman has taken the pills correctly in the 7 days preceding the first missed pill, the contraceptive effect of Bonade is maintained and the woman does not need to use additional contraceptive measures. Otherwise, and if 2 or more pills are missed, additional barrier methods of contraception must be used for 7 days;
If 1 pill is missed in the third week of the drug, but all pills were taken correctly in the 7 days preceding the first missed pill, no additional contraceptive methods are needed if the woman sticks to either of the following two options:
1. The missed pill should be taken as soon as possible as soon as the patient remembers (even if this means taking 2 pills at once). The next tablet should be taken at the usual time. The next package (blister) should be started as soon as the pills from the current package (blister) are finished, so that there is no break between packages (blisters). Bleeding cancellation is unlikely until the pills from the second package (blister) are finished, but there may be mucous discharge or breakthrough uterine bleeding during the days of taking the drug.
2. The pills in the current package (blister) should be discontinued, paused for 7 days or less (including the day you missed the pill), and then the pills in the new package (blister) should be started.
The absence of expected menstrual bleeding after a break in the pills may mean that the woman is pregnant. In this case, the woman should consult her doctor before starting the pills from a new package (blister).
With this regimen, a woman can always start the pills in the next package (blister) on the day of the week that she usually does.
In situations where discontinuation of Bonade is recommended, or where its reliability may be compromised, abstain from sexual intercourse or use a non-hormonal contraceptive method (such as a condom or other barrier method). Rhythmic or temperature methods should not be used. These methods can be unreliable because taking PDAs causes changes in basal temperature and cervical mucus.
Cessation of the drug
You can stop taking Bonade at any time. If discontinuing because you want to get pregnant, it is usually recommended that you wait until your first normal menstrual period and then try to get pregnant. With this method, it is easier to establish the date of delivery.
Recommendations in case of gastrointestinal disorders
If vomiting or diarrhea occurs, the active ingredients in Bonade may not be fully absorbed. If vomiting continues for 3-4 hours after taking the contraceptive pill, the result may be the same as skipping the pill. You should proceed as recommended for skipping the pill. Consult your doctor if you have severe diarrhea.
Delaying the onset of menstrual bleeding
You can delay the onset of menstrual bleeding by starting the pills in the next pack (if the pack contains 21 pills) or blister (if the pack contains 63 pills) immediately after you finish your current pack (blister). You can take the tablets as long as necessary, or as long as the tablets in the package (blister) run out. If it is necessary for a bleeding discontinuation to start, you should stop taking the tablets. During the use of Bonade tablets from a new pack (blister), you may get copious or smeared bloody discharge. The pills in the next package (blister) should be started after the usual 7-day interval.
Changing the day menstrual bleeding starts
If a woman takes the pill exactly as recommended, menstrual bleeding occurs on about the same days every 4 weeks. If it is necessary to change these days, you should shorten (but by no means prolong) the next interval without taking the pill. For example, if your bleeding starts on Fridays and you want it to start on Tuesdays (3 days earlier), then you should start the pills from the new package (blister) 3 days earlier than usual. If the interval without taking the pills is too short, you may not bleed at all during this interval. However, heavy or smeared bleeding may occur during the use of the pills from the new package (blister).
Particular groups of patients
Bonade is only indicated for children and adolescents after menarche.
Bonadé is not indicated after the onset of menopause.
The drug is contraindicated in women with severe liver disease until liver function returns to normal.
Bonade has not been specifically studied in women with impaired renal function. The available data do not suggest a change in dosing regimen in these patients.
Interaction
Interaction
The drug Bonade can affect the metabolism of other drugs, resulting in an increase (e.g., cyclosporine) or decrease (e.g., lamotrigine) in their plasma and tissue concentrations.
Drugs that can decrease the effectiveness of Bonade
These include medications used to treat:
– Epilepsy (e.g., primidone, phenytoin, barbiturates, carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, topiramate, felbamate) – the use of barrier methods of contraception throughout the therapy cycle and another 28 days after therapy ends is required;
Tuberculosis (e.g., rifampicin, rifabutin) and HIV infection (e.g., ritonavir, nevirapine) – require use of barrier methods of contraception throughout the therapy cycle and for another 28 days after therapy ends;
– Antibiotics for the treatment of some other infectious diseases (e.g., penicillin, tetracyclines, griseofulvin) – the use of barrier methods of contraception for the entire cycle of therapy and for another 7 days after its completion;
– St. John’s wort-based drugs (used to treat depressed conditions) – the use of barrier methods of contraception for the entire cycle of therapy and for another 28 days after its completion.
Drugs that may affect the metabolism of the active ingredients of Bonade
These include:
– antifungal drugs (e.g., ketoconazole);
– histamine H2-receptor blockers for the treatment of gastric and duodenal ulcers (e.g., cimetidine);
– certain drugs to treat arterial hypertension (e.g., verapamil, diltiazem);
– antibiotics to treat bacterial infections (macrolides, such as erythromycin);
– antidepressants;
grapefruit juice.
A woman should tell her doctor what medications (including herbal medicines) she is taking or has recently taken. Any doctor (including a dentist) who prescribes other medications, as well as the pharmacist, should be told that the woman is taking Bonade.
In some cases, the doctor may recommend the additional use of a barrier method of contraception (condom).
Special Instructions
Special Instructions
If any of the following conditions or risk factors are present, the potential risks and expected benefits of therapy should be carefully evaluated and discussed with the woman before she decides to start taking the drug. If there is an increase in symptoms of an existing disease, an exacerbation of the disease, or if there are early signs of these conditions or risk factors with this medication, a consultation with a physician should be conducted who can decide if the medication should be discontinued.
Thrombosis
The risk of deep vein thrombosis in women taking PDAs is higher than in those not taking them, but not as high as during pregnancy.
The results of epidemiological studies suggest an association between PDA use and an increased risk of thrombosis and thromboembolic diseases such as myocardial infarction, stroke, deep vein thrombosis, and pulmonary embolism when taking PDA. These complications are rare.
The risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE) is highest in the first year of use of these drugs, mostly during the first 3 months. An increased risk exists with initial use of a PDA or with renewed use of the same or different PDAs (after a break of 4 weeks or more between doses).
The overall risk of VTE in patients taking low-dose PDAs (
In very rare cases, venous or arterial thromboembolism can be fatal.
VTE, manifesting as deep vein thrombosis and/or pulmonary embolism, can occur with any PDA.
It is extremely rare for thrombosis in other blood vessels, such as the veins and arteries of the liver, mesentery, kidneys, brain, or retina, to occur with PDA use.
The symptoms of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) include unilateral swelling of the lower extremity or along a vein in the lower extremity, pain or discomfort in the lower extremity only when upright or walking, localized temperature rise in the affected lower extremity, redness or discoloration of the skin on the lower extremity.
Symptoms of pulmonary embolism (TELA): difficulty or rapid breathing; sudden cough, including with hemoptysis; sharp chest pain, which may increase with deep breaths; anxiety; severe dizziness; rapid or irregular heartbeat. Some of these symptoms (e.g., shortness of breath, coughing) are nonspecific and may be misinterpreted as signs of other more or less severe events (e.g., respiratory tract infection).
If women taking PDA have any of the symptoms listed above, you should consult your doctor immediately.
The risk of thrombosis (venous and/or arterial) and thromboembolism increases:
– with increasing age;
– in smokers (with more cigarettes or increasing age, the risk increases, especially in women over 35). Smoking should be discontinued when using Bonade, especially if the woman is over 35 years of age;
– If there is a family history of venous or arterial thromboembolism ever in a close relative or parent at a relatively young age. If there is an inherited or acquired predisposition, the woman should be evaluated by an appropriate specialist to decide whether Bonade can be taken;
– in overweight (body mass index more than 30 kg/m2);
– in dyslipoproteinemia;
– in arterial hypertension;
– in migraine;
– in heart valve disease;
– in atrial fibrillation;
– in systemic lupus erythematosus;
– in diabetes;
Contraindications
Contraindications
Bonade should not be used in the presence of any of the conditions/diseases listed below. If any of these conditions develop for the first time during its use, the drug should be stopped immediately.
Side effects
Side effects
Bonade may cause irregular bleeding (spotting or breakthrough uterine bleeding), especially during the first months of use.
There may be other adverse effects of Bonade, although not necessarily in all patients.
The following adverse reactions have been reported in women taking PDAs, but the reactions described may not have been caused by the pills. The adverse reactions listed below usually occur during the first months of contraceptive pill use and tend to subside over time.
The side effects identified during the use of the active ingredients of Bonade are listed by frequency of occurrence and by organ system.
Infectious and parasitic diseases: infrequent – vaginitis, vulvovaginitis, vaginal candidiasis or other fungal vulvovaginal infections; rare – salpingoophoritis (adnexitis), urinary tract infections, cystitis, mastitis, cervicitis, fungal infections, herpes oral infection, influenza, bronchitis, sinusitis, upper respiratory infections, viral infection.
Benign, malignant and unspecified neoplasms (including cysts and polyps): infrequently – ovarian cysts; rarely – uterine appendage cysts, uterine myoma, breast lipoma, breast cysts, cystic fibrosis mastopathy.
Allergic reactions: rare – allergic dermatitis, atopic dermatitis, neurodermatitis, eczema; unspecified frequency – urticaria, erythema multiforme.
Hematopoietic system: rarely – anemia.
Endocrine system: rarely – virilism.
Mental disorders: rare – depression; very rare – mood changes; unspecified frequency – decreased mood, insomnia, sleep disturbances, aggression.
Nervous system disorders: frequent – headache; infrequent – dizziness, migraine; rare – ischemic stroke, cerebrovascular disorders, dystonia.
Arom the eyes: rare – dry eyes, irritation of the mucous membrane of the eyes, oscillopsia; unspecified frequency – intolerance of contact lenses (discomfort while wearing them).
Hearing organ and labyrinth disorders: rarely – sudden hearing loss, tinnitus, dizziness, hearing loss.
The cardiovascular system: rare – cardiovascular disorders, tachycardia, pulmonary artery thrombosis or thromboembolism, thrombophlebitis, increased diastolic BP, orthostatic circulatory dystonia, hot flashes, varicose veins, vein disease, pain along the veins; infrequent – increased, decreased BP.
Respiratory system disorders: rarely – bronchial asthma, hyperventilation.
The digestive system: infrequent – abdominal pain, including upper and lower abdominal pain, discomfort, bloating, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea; rarely – gastritis, enteritis, dyspepsia.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: infrequent – itching (including generalized itching), acne, alopecia, rash, including macular rash; rare – psoriasis, hyperhidrosis, chloasma, hyperpigmentation, seborrhea, dandruff, hirsutism, cellulitis, spider veins; unspecified frequency – erythema nodosa.
Muscular system disorders: rare – back pain, muscle and skeletal discomfort, myalgia, pain in the extremities.
Gender and mammary system disorders: often – pain in the mammary glands, discomfort; infrequently – change of duration and volume of menstrual bleeding, including heavy menstrual bleeding, scanty menstrual bleeding and absence of menstrual bleeding, acyclic bleeding, including vaginal bleeding and metrorrhagia, increased breast size, mammary gland engorgement, mammary gland swelling, painful menstrual bleeding, vaginal discharge, pelvic pain; rarely – cervical dysplasia, dyspareunia, galactorrhea; unspecified frequency – discharge from breasts, decreased libido, increased libido.
General disorders and disorders: infrequent – increased appetite, fatigue, asthenia, malaise, body weight changes (weight gain, loss and fluctuations); rare – anorexia, chest pain, peripheral edema, flu-like phenomena, increased body temperature, irritability; unspecified frequency – fluid retention.
Laboratory measures: rarely hypertriglyceridemia, hypercholesterolemia.
In women with estrogen-dependent hereditary angioedema, symptoms of angioedema may be provoked or worsened. There is a slight increase in the detection rate of breast cancer in women who use PDA. Because breast cancer rarely occurs in women under the age of 40, given the overall risk of developing breast cancer, the additional incidence is very small. The association with PDA use is not known.
If unwanted effects occur that are not listed in the instructions, the woman should tell her doctor.
Overdose
Overdose
No serious side effects have been reported in overdose.
Symptoms: nausea, vomiting and small vaginal bleeding or oozing may occur.
Treatment: there is no specific antidote, symptomatic treatment should be given.
Similarities
Similarities
Additional information
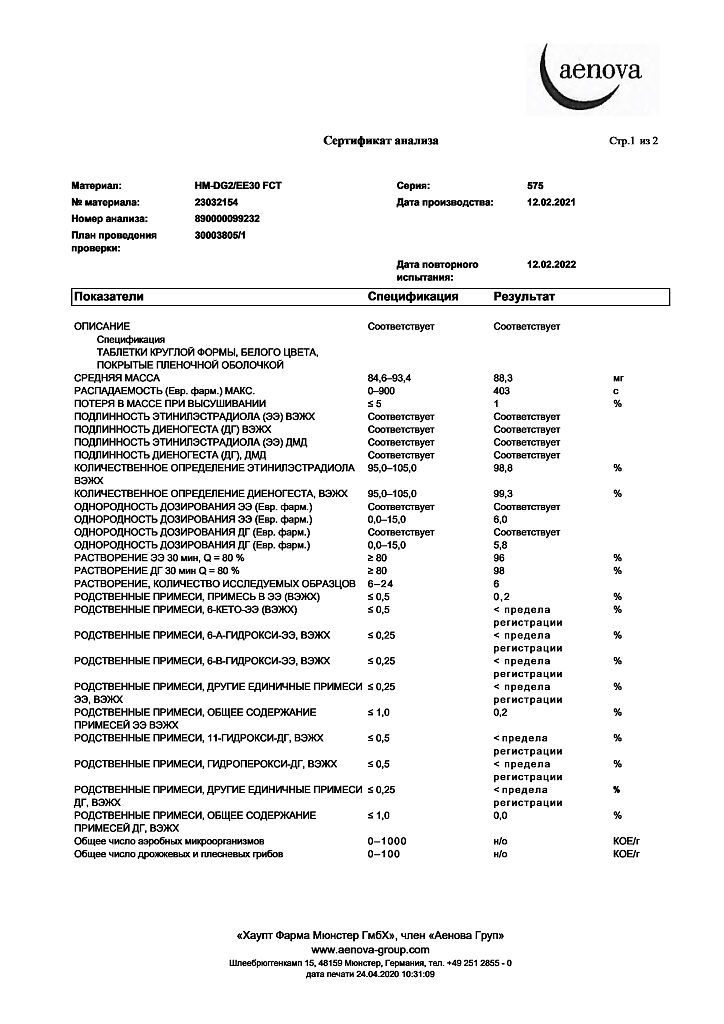
| Shelf life | 2 years. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | The drug should be kept out of reach of children at a temperature not exceeding 25 ° C. |
| Manufacturer | Haupt Pharma Münster GmbH, Germany |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Haupt Pharma Münster GmbH |
Related products
Gynecology and Obstetrics
Gynecology and Obstetrics
Buy Bonade, 2 mg+0.03 mg 21 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.