No products in the cart.
Bisoprolol-Vertex, 10 mg 60 pcs
€8.58 €7.51
Out of stock
(E-mail when Stock is available)
Description
Bisoprolol is a selective beta1-adrenoblocker without sympathomimetic activity of its own; it has antihypertensive, antiarrhythmic and antianginal effects. By blocking in low doses beta1-adrenoreceptors of the heart, it reduces catecholamine-stimulated formation of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) from adenosine triphosphate (ATP), decreases intracellular calcium ions (Ca2+) flow, has negative chrono-, dromo-, batmo- and inotropic effects (decreases heart rate, inhibits conduction and excitability, decreases myocardial contractility).
With increasing dose has beta2-adrenoblocking effect.
Total peripheral vascular resistance at the beginning of administration of beta-adrenoblockers, in the first 24 hours, increases (as a result of reciprocal increase of activity of alpha-adrenoreceptors and elimination of stimulation of beta2-adrenoreceptors) which in 1-3 days returns to baseline, and with long-term prescription decreases.
The antihypertensive effect is connected with decrease of the minute blood volume, sympathetic stimulation of peripheral vessels, decrease of renin-angiotensin-aldosteron system activity (it is more important for patients with initial renin hypersecretion), restoration of aortic arch baroreceptors sensitivity (their activity in response to arterial pressure (AP) decrease is not increased) and the influence on the central nervous system. In case of arterial hypertension the effect comes in 2-5 days, stable effect – in 1-2 months.
Antianginal effect is caused by decrease of myocardial oxygen demand as the result of heart rate reduction and contractility decrease, prolongation of diastole, improvement of myocardial perfusion. By increasing left ventricular end-diastolic pressure and increasing ventricular muscle fiber stretch may increase myocardial oxygen demand, especially in patients with chronic heart failure (CHF).
. In contrast to non-selective beta-adrenoblockers when administered in medium therapeutic doses, it has less pronounced effect on the organs containing beta2-adrenoreceptors (pancreas, skeletal muscles, smooth muscle of peripheral arteries, bronchi and uterus) and on carbohydrate metabolism, does not cause delay of sodium ions (Na+) in the body. When used in high doses has a blocking effect on both subtypes of beta-adrenoreceptors.
Pharmacokinetics.
Bisoprolol is almost completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract (80-90%). Food intake does not affect the absorption of the drug. Maximum plasma concentration is reached after 2-3 hours. Binding with plasma proteins is approximately 35%. Hematoencephalic barrier and placental barrier permeability is low, secretion with breast milk is low.
Metabolized in the liver. Period of half-life (T1/2) is 9-12 hours; it is prolonged in patients with kidney function disorders (in creatinine clearance less than
40 ml/min – 3 times), in elderly age and in case of liver diseases (in cirrhosis it is prolonged up to 21.7 hours). Excreted by the kidneys – 50% unchanged, less than 2% through the intestine.
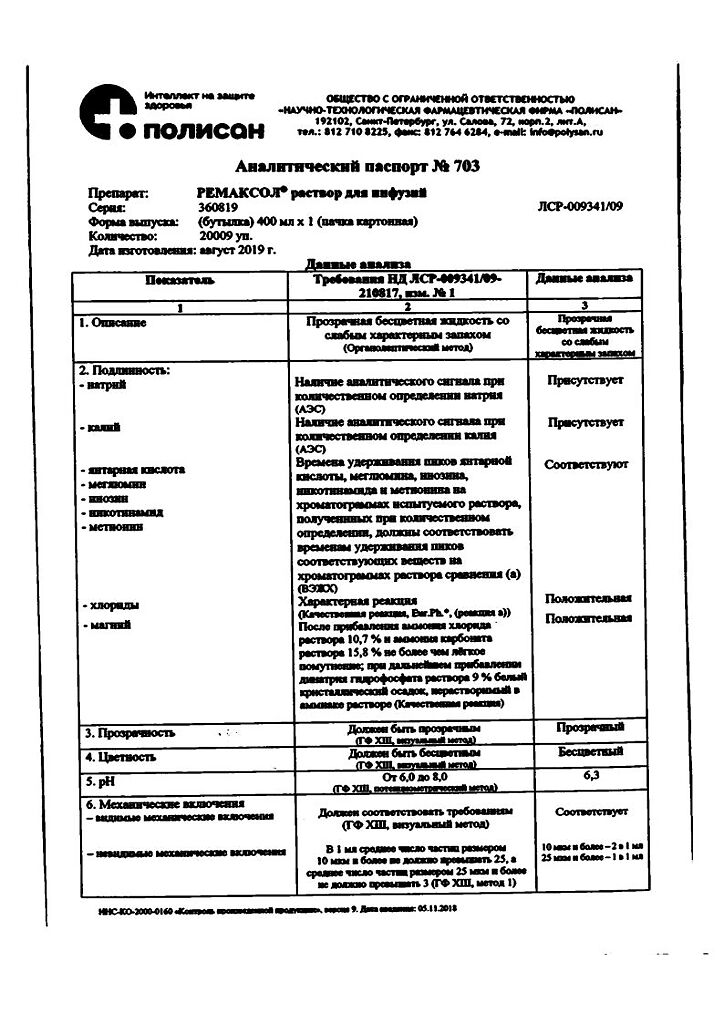
Indications
Indications
Arterial hypertension,
prevention of angina attacks,
chronic heart failure.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Bisoprolol is a selective beta1-blocker without its own sympathomimetic activity; has antihypertensive, antiarrhythmic and antianginal effects. By blocking beta1-adrenergic receptors of the heart in low doses, it reduces the catecholamine-stimulated formation of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) from adenosine triphosphate (ATP), reduces the intracellular current of calcium ions (Ca2+), has a negative chrono-, dromo-, bathmo- and inotropic effect (reduces heart rate, inhibits conductivity and excitability, reduces myocardial contractility).
With increasing dose, it has a beta2-adrenergic blocking effect.
The total peripheral vascular resistance at the beginning of the use of beta-blockers, in the first 24 hours, increases (as a result of a reciprocal increase in the activity of alpha-adrenergic receptors and the elimination of stimulation of beta2-adrenergic receptors), which returns to its original level after 1-3 days, and decreases with long-term administration.
The antihypertensive effect is associated with a decrease in minute blood volume, sympathetic stimulation of peripheral vessels, a decrease in the activity of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (of greater importance for patients with initial hypersecretion of renin), restoration of the sensitivity of the baroreceptors of the aortic arch (there is no increase in their activity in response to a decrease in blood pressure (BP)) and an effect on the central nervous system. In case of arterial hypertension, the effect occurs after 2-5 days, stable effect – after 1-2 months.
The antianginal effect is due to a decrease in myocardial oxygen demand as a result of a decrease in heart rate and decreased contractility, prolongation of diastole, and improved myocardial perfusion. By increasing end-diastolic pressure in the left ventricle and increasing the stretch of ventricular muscle fibers, it can increase myocardial oxygen demand, especially in patients with chronic heart failure (CHF).
In contrast to non-selective beta-blockers, when prescribed in average therapeutic doses, it has a less pronounced effect on organs containing beta2-adrenergic receptors (pancreas, skeletal muscles, smooth muscles of peripheral arteries, bronchi and uterus) and on carbohydrate metabolism, and does not cause retention of sodium ions (Na+) in the body. When used in large doses, it has a blocking effect on both subtypes of beta-adrenergic receptors.
Pharmacokinetics.
Bisoprolol is almost completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract (80-90%). Eating does not affect the absorption of the drug. The maximum concentration in blood plasma is achieved after 2-3 hours. Bonding with plasma proteins is approximately 35%. Permeability through the blood-brain barrier and placental barrier is low, secretion into breast milk is low.
Metabolized in the liver. The half-life (T1/2) is 9-12 hours, lengthens if renal function is impaired (with creatinine clearance less than
40 ml/min – 3 times), in old age, with liver diseases (with cirrhosis it increases to 21.7 hours). Excreted by the kidneys – 50% unchanged, less than 2% through the intestines.
Special instructions
Special instructions
From the nervous system: weakness, fatigue, dizziness, headache, sleep disorders, mental disorders (depression, rarely hallucinations), feeling of cold and paresthesia in the extremities.
From the cardiovascular system: orthostatic hypotension, bradycardia, impaired AV conduction, the appearance of symptoms of heart failure, worsening intermittent claudication and the main clinical symptoms of Raynaud’s syndrome.
From the organ of vision: decreased secretion of tear fluid, conjunctivitis.
From the digestive system: diarrhea, constipation, nausea, abdominal pain.
From the musculoskeletal system: muscle weakness, muscle cramps.
From the skin and subcutaneous tissues: skin itching; in some cases – increased manifestations of psoriasis, the appearance of psoriasis-like rashes.
From the respiratory system: in predisposed patients, symptoms of bronchial obstruction may appear.
Other: sweating, hot flashes, impaired potency, decreased glucose tolerance in patients with diabetes, allergic reactions.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Bisoprolol
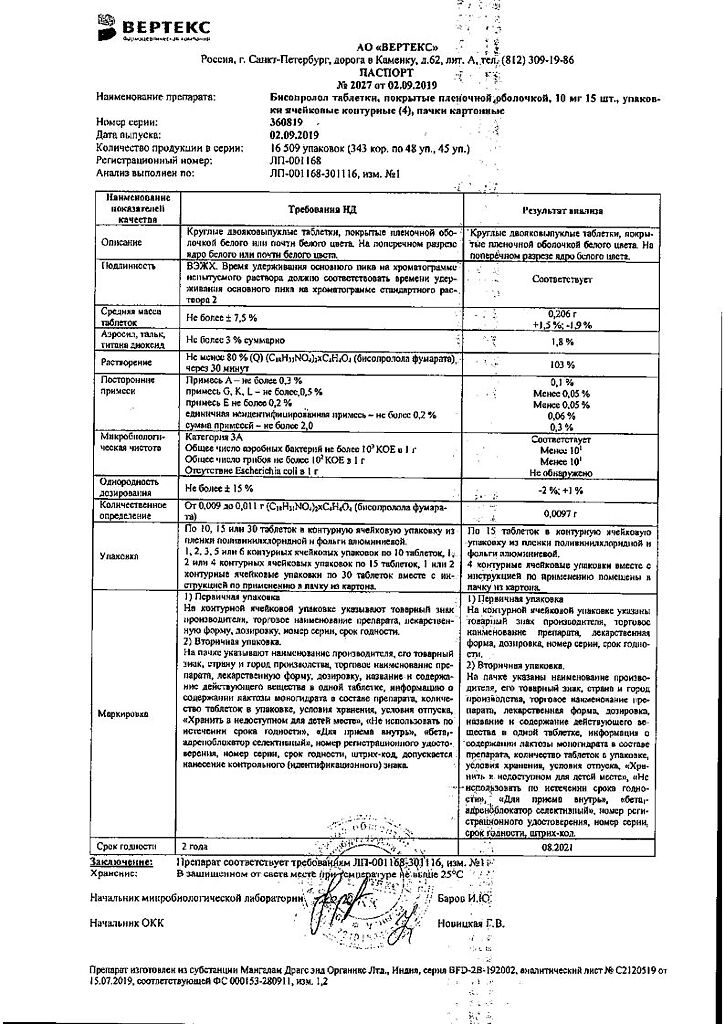
Composition
Composition
1 tablet contains:
Active substance:
bisoprolol fumarate 10 mg.
Excipients:
lactose monohydrate,
microcrystalline cellulose,
colloidal silicon dioxide,
crospovidone,
magnesium stearate.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Acute heart failure,
chronic heart failure in the stage of decompensation,
cardiogenic shock,
collapse,
AV block II and III degrees (without pacemaker),
SSSU;
sinoatrial blockade,
severe bradycardia (HR
Prinzmetal’s angina,
pronounced decrease in blood pressure (systolic blood pressure
history of severe forms of bronchial asthma and COPD,
late stages of peripheral circulatory disorders,
Raynaud’s disease,
pheochromocytoma (without simultaneous use of alpha-blockers),
metabolic acidosis,
simultaneous use of MAO inhibitors (except for MAO type B inhibitors),
children and adolescents up to 18 years of age,
hypersensitivity to bisoprolol and other beta-blockers.
Side Effects
Side Effects
From the nervous system: weakness, fatigue, dizziness, headache, sleep disorders, mental disorders (depression, rarely hallucinations), feeling of cold and paresthesia in the extremities.
From the cardiovascular system: orthostatic hypotension, bradycardia, impaired AV conduction, the appearance of symptoms of heart failure, worsening intermittent claudication and the main clinical symptoms of Raynaud’s syndrome.
From the organ of vision: decreased secretion of tear fluid, conjunctivitis.
From the digestive system: diarrhea, constipation, nausea, abdominal pain.
From the musculoskeletal system: muscle weakness, muscle cramps.
From the skin and subcutaneous tissues: skin itching; in some cases – increased manifestations of psoriasis, the appearance of psoriasis-like rashes.
From the respiratory system: in predisposed patients, symptoms of bronchial obstruction may appear.
Other: sweating, hot flashes, impaired potency, decreased glucose tolerance in patients with diabetes, allergic reactions.
Interaction
Interaction
With the simultaneous use of antacids and antidiarrheals, the absorption of beta-blockers may be reduced.
With the simultaneous use of antiarrhythmic drugs, a sharp decrease in blood pressure, a decrease in heart rate, and the development of arrhythmia and/or heart failure are possible.
With the simultaneous use of antihypertensive drugs, the antihypertensive effect may be enhanced.
With the simultaneous use of cardiac glycosides, conduction disturbances are possible.
With the simultaneous use of sympathomimetics (including those included in cough suppressants, nasal drops, eye drops), the effectiveness of bisoprolol decreases.
With the simultaneous use of verapamil and diltiazem, a sharp decrease in blood pressure, a decrease in heart rate, and the development of arrhythmia and/or heart failure are possible.
With simultaneous use of guanfacine, severe bradycardia and conduction disturbances are possible.
With the simultaneous use of insulin and hypoglycemic agents for oral administration, the effect of insulin or other hypoglycemic agents is enhanced (regular monitoring of plasma glucose levels is necessary).
With simultaneous use of clonidine, severe bradycardia, arterial hypotension, and conduction disturbances are possible.
In case of sudden withdrawal of clonidine in patients receiving bisoprolol, a sharp increase in blood pressure is possible.
With the simultaneous use of nifedipine, other calcium channel blockers, dihydropyridine derivatives, the antihypertensive effect of bisoprolol is enhanced.
With the simultaneous use of reserpine and alpha-methyldopa, severe bradycardia is possible.
With simultaneous use of rifampicin, a slight decrease in T1/2 of bisoprolol is possible.
With the simultaneous use of ergotamine derivatives (including drugs for the treatment of migraines containing ergotamine), symptoms of peripheral circulatory disorders increase.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms:
arrhythmia, ventricular extrasystole, severe bradycardia, AV block, marked decrease in blood pressure, chronic heart failure, cyanosis of fingernails or palms, difficulty breathing, bronchospasm, dizziness, fainting, convulsions.
Treatment: gastric lavage and administration of adsorbent drugs;
Symptomatic therapy:
in case of developed AV block – intravenous administration of 1-2 mg of atropine, epinephrine or placement of a temporary pacemaker; for ventricular extrasystole – lidocaine (class IA drugs are not used); when blood pressure decreases, the patient should be in the Trendelenburg position; if there are no signs of pulmonary edema, intravenous plasma-substituting solutions; if ineffective, administration of epinephrine, dopamine, dobutamine (to maintain chronotropic and inotropic effects and eliminate a pronounced decrease in blood pressure); for heart failure – cardiac glycosides, diuretics, glucagon; for convulsions – intravenous diazepam; for bronchospasm – beta2-adrenergic agonists by inhalation
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Vertex, Russia
Additional information
| Manufacturer | Vertex, Russia |
|---|---|
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Vertex |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Bisoprolol-Vertex, 10 mg 60 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.