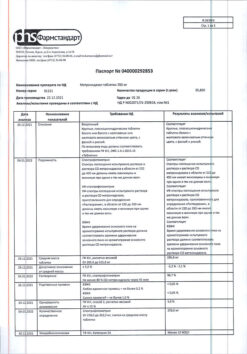
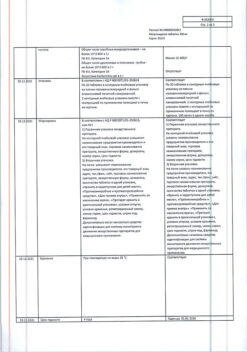
No products in the cart.
Biseptol, 480 mg tablets 28 pcs
€1.00
Out of stock
(E-mail when Stock is available)
Description
A combined antibacterial drug, contains sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim.
Sulfamethoxazole, similar in structure to PABA, disrupts the synthesis of dihydrofolic acid in bacterial cells, preventing the inclusion of PABA in its molecule.
Trimethoprim enhances the effect of sulfamethoxazole by disrupting the reduction of dihydrofolic acid to tetrahydrofolic acid, the active form of folic acid responsible for protein metabolism and microbial cell division.
It is a broad spectrum bactericidal drug.
It is active against Gram-positive aerobic bacteria: Streptococcus spp. including Streptococcus pneumoniae (hemolytic strains are more sensitive to penicillin), Staphylococcus spp., Bacillus anthracis, Listeria spp, Nocardia asteroides, Enterococcus faecalis, Mycobacterium spp. (including Mycobacterium leprae, excluding Mycobacterium tuberculosis); Gram-negative aerobic bacteria: Neisseria meningitidis, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Escherichia coli (including enterotoxigenic strains), Salmonella spp. (including Salmonella typhi and Salmonella paratyphi); Vibrio cholerae, Haemophilus influenzae (including ampicillin-resistant strains), Bordetella pertussis, Klebsiella spp, Proteus spp., Pasteurella spp., Francisella tularensis, Brucella spp., Citrobacter spp., Enterobacter spp., Legionella pneumopbila, Providencia, some Pseudomonas species (except Pseudomonas aeruginosa), Serratia marcescens, Shigella spp, Yersinia spp., Morganella spp. as well as against Chlamydia spp. (including Chlamydia trachomatis, Chlamydia psittaci); against Gram-positive anaerobes: Actinomyces israelii; against protozoa: Plasmodium spp., Toxoplasma gondii; against pathogenic fungi: Coccidioides immitis, Histoplasma capsulatum, Pneumocystis carinii, Leishmania spp.
The drug is resistant to: Corynebacterium spp., Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Treponema spp., Leptospira spp., viruses.
Depresses the activity of E. coli, which leads to a decrease in the synthesis of thiamine, riboflavin, nicotinic acid and other B vitamins in the intestine.
The duration of therapeutic action is 7 hours.
Pharmacokinetics
Assimilation
./p>
After oral administration, the active ingredients are completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Cmax in plasma is reached within 1-4 hours after oral administration.
Pdistribution
.
Trimethoprim penetrates well into body tissues and biological media: lungs, kidneys, prostate, bile, saliva, sputum, cerebrospinal fluid. Binding of trimethoprim with plasma proteins is 50%; sulfamethoxazole – 66%.
Elimation
T1/2 of trimethoprim is 8.6-17 h, of sulfamethoxazole – 9-11 h. The main route of excretion is the kidneys; trimethoprim is excreted unchanged up to 50%; sulfamethoxazole – 15-30% in the active form.
Indications
Indications
Treatment of infectious and inflammatory diseases caused by microorganisms sensitive to the drug:
– respiratory tract infections (including bronchitis, pneumonia, lung abscess, pleural empyema);
– otitis media, sinusitis;
– infections of the genitourinary system (including pyelonephritis, urethritis, salpingitis, prostatitis);
– gonorrhea;
— gastrointestinal infections (including typhoid fever, paratyphoid fever, bacterial dysentery, cholera, diarrhea);
– infections of the skin and soft tissues (including furunculosis, pyoderma).
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Combined antibacterial drug containing sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim.
Sulfamethoxazole, similar in structure to PABA, disrupts the synthesis of dihydrofolic acid in bacterial cells, preventing the inclusion of PABA in its molecule.
Trimethoprim enhances the effect of sulfamethoxazole by interfering with the reduction of dihydrofolic acid into tetrahydrofolic acid, the active form of folic acid responsible for protein metabolism and microbial cell division.
It is a broad-spectrum bactericidal drug.
Active against gram-positive aerobic bacteria: Streptococcus spp., including Streptococcus pneumoniae (hemolytic strains are more sensitive to penicillin), Staphylococcus spp., Bacillus anthracis, Listeria spp., Nocardia asteroides, Enterococcus faecalis, Mycobacterium spp. (including Mycobacterium leprae, excluding Mycobacterium tuberculosis); gram-negative aerobic bacteria: Neisseria meningitidis, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Escherichia coli (including enterotoxogenic strains), Salmonella spp. (including Salmonella typhi and Salmonella paratyphi); Vibrio cholerae, Haemophilus influenzae (including ampicillin-resistant strains), Bordetella pertussis, Klebsiella spp., Proteus spp., Pasteurella spp., Francisella tularensis, Brucella spp., Citrobacter spp., Enterobacter spp., Legionella pneumopbila, Providencia, some Pseudomonas species (except Pseudomonas aeruginosa), Serratia marcescens, Shigella spp., Yersinia spp., Morganella spp., as well as Chlamydia spp. (including Chlamydia trachomatis, Chlamydia psittaci); for gram-positive anaerobes: Actinomyces israelii; for protozoa: Plasmodium spp., Toxoplasma gondii; pathogenic fungi: Coccidioides immitis, Histoplasma capsulatum, Pneumocystis carinii, Leishmania spp.
The following are resistant to the drug: Corynebacterium spp., Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Treponema spp., Leptospira spp., viruses.
Inhibits the vital activity of E. coli, which leads to a decrease in the synthesis of thiamine, riboflavin, nicotinic acid and other B vitamins in the intestines.
The duration of therapeutic action is 7 hours.
Pharmacokinetics
Suction
After taking the drug orally, the active substances are completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Cmax in blood plasma is achieved within 1-4 hours after oral administration.
Distribution
Trimethoprim penetrates well into the tissues and biological environments of the body: lungs, kidneys, prostate, bile, saliva, sputum, cerebrospinal fluid. The binding of trimethoprim to plasma proteins is 50%; sulfamethoxazole – 66%.
Removal
T1/2 of trimethoprim – 8.6-17 hours, sulfamethoxazole – 9-11 hours. The main route of elimination is the kidneys; in this case, trimethoprim is excreted unchanged up to 50%; sulfamethoxazole – 15-30% in active form.
Special instructions
Special instructions
Biseptol should be prescribed with caution if there is a significant allergy history.
With long-term (more than a month) courses of treatment, regular blood tests are necessary, since there is a possibility of hematological changes (most often asymptomatic). These changes can be reversible with the administration of folic acid (3-6 mg/day), which does not significantly impair the antimicrobial activity of the drug. Particular caution is required when treating elderly patients or patients with suspected underlying folate deficiency. The administration of folic acid is also advisable for long-term treatment with the drug in high doses.
To prevent crystalluria, it is recommended to maintain a sufficient volume of urine excreted. The likelihood of toxic and allergic complications of sulfonamides increases significantly with a decrease in the filtration function of the kidneys.
During treatment, it is also inadvisable to consume foods containing large amounts of PABA – green parts of plants (cauliflower, spinach, legumes), carrots, tomatoes.
Excessive sun and UV exposure should be avoided.
The risk of side effects is significantly higher in patients with AIDS.
It is not recommended to use the drug Biseptol for tonsillitis and pharyngitis caused by group A β-hemolytic streptococcus, due to the widespread resistance of strains.
Trimethoprim may change the results of determining serum methotrexate levels using the enzymatic method, but does not affect the result when choosing a radioimmunoassay method.
Co-trimoxazole can increase the results of the Jaffe reaction with picric acid for the quantitative determination of creatinine by 10%.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Co-trimoxazole [Sulfamethoxazole, Trimethoprim]
Composition
Composition
1 tablet contains:
Active ingredients: sulfamethoxazole – 400 mg, trimethoprim – 80 mg.
Excipients: potato starch, talc, magnesium stearate, polyvinyl alcohol, methyl parahydroxybenzoate, propyl parahydroxybenzoate, propylene glycol.
Contraindications
Contraindications
— established damage to the liver parenchyma;
– severe renal dysfunction in the absence of the ability to control the concentration of the drug in the blood plasma;
— severe renal failure (creatinine clearance less than 15 ml/min);
– severe blood diseases (aplastic anemia, B12-deficiency anemia, agranulocytosis, leukopenia, megaloblastic anemia, anemia associated with folic acid deficiency);
– hyperbilirubinemia in children;
— deficiency of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (risk of hemolysis);
– pregnancy;
– lactation;
– children under 3 years of age (for this dosage form);
– hypersensitivity to the components of the drug;
– hypersensitivity to sulfonamides.
The drug is prescribed with caution in cases of folic acid deficiency in the body, bronchial asthma, and thyroid diseases.
Side Effects
Side Effects
The drug is generally well tolerated.
From the nervous system: headache, dizziness; in some cases – aseptic meningitis, depression, apathy, tremor, peripheral neuritis.
From the respiratory system: bronchospasm, suffocation, cough, pulmonary infiltrates.
From the digestive system: nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, diarrhea, gastritis, abdominal pain, glossitis, stomatitis, cholestasis, increased activity of liver transaminases, hepatitis, sometimes with cholestatic jaundice, hepatonecrosis, pseudomembranous enterocolitis, pancreatitis.
From the hematopoietic system: leukopenia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, agranulocytosis, megaloblastic anemia, aplastic and hemolytic anemia, eosinophilia, hypoprothrombinemia, methemoglobinemia.
From the urinary system: polyuria, interstitial nephritis, impaired renal function, crystalluria, hematuria, increased urea concentration, hypercreatininemia, toxic nephropathy with oliguria and anuria.
From the musculoskeletal system: arthralgia, myalgia.
Allergic reactions: itching, photosensitivity, urticaria, drug fever, rash, exudative erythema multiforme (including Stevens-Johnson syndrome), toxic epidermal necrolysis (Lyell’s syndrome), exfoliative dermatitis, allergic myocarditis, fever, angioedema, scleral hyperemia.
Metabolic: hypoglycemia, hyperkalemia, hyponatremia.
Interaction
Interaction
When Biseptol is used simultaneously with thiazide diuretics, there is a risk of developing thrombocytopenia and bleeding (the combination is not recommended).
Co-trimoxazole increases the anticoagulant activity of indirect anticoagulants, as well as the effect of hypoglycemic drugs and methotrexate.
Co-trimoxazole reduces the intensity of hepatic metabolism of phenytoin (increases its T1/2 by 39%) and warfarin, enhancing their effect.
Rifampicin reduces T1/2 of trimethoprim.
When used concomitantly, pyrimethamine in doses exceeding 25 mg/week increases the risk of developing megaloblastic anemia.
When used concomitantly, diuretics (usually thiazides) increase the risk of thrombocytopenia.
Benzocaine, procaine, procainamide (as well as other drugs, as a result of hydrolysis of which PABA is formed) reduce the effectiveness of Biseptol.
Between diuretics (including thiazides, furosemide) and oral hypoglycemic agents (sulfonylurea derivatives), on the one hand, and antibacterial agents of the sulfonamide group, on the other hand, the development of a cross-allergic reaction is possible.
Phenytoin, barbiturates, PAS increase the manifestations of folic acid deficiency when used simultaneously with Biseptol.
Salicylic acid derivatives enhance the effect of Biseptol.
Ascorbic acid, hexamethylenetetramine (as well as other drugs that acidify urine) increase the risk of developing crystalluria during the use of Biseptol.
Cholestyramine reduces absorption when taken concomitantly with other drugs, so it should be taken 1 hour after or 4-6 hours before taking co-trimoxazole.
When used simultaneously with drugs that inhibit bone marrow hematopoiesis, the risk of developing myelosuppression increases.
In some cases, Biseptol® may increase the plasma concentration of digoxin in elderly patients.
Biseptol® may reduce the effectiveness of tricyclic antidepressants.
In patients after kidney transplantation, with the simultaneous use of co-trimoxazole and cyclosporine, there is a transient dysfunction of the transplanted kidney, manifested by an increase in serum creatinine concentrations, which is probably caused by the effect of trimethoprim.
Reduces the effectiveness of oral contraception (inhibits intestinal microflora and reduces the enterohepatic circulation of hormonal agents).
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: in case of sulfonamide overdose – lack of appetite, intestinal colic, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, headache, drowsiness, loss of consciousness, fever, hematuria, crystalluria are also possible. Bone marrow suppression and jaundice may develop later.
After acute trimethoprim poisoning, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, headache, depression, disturbance of consciousness, and suppression of bone marrow function are possible.
It is not known what dose of co-trimoxazole can be life-threatening.
Chronic poisoning: Use of co-trimoxazole in high doses over a long period can lead to suppression of bone marrow function, manifested by thrombocytopenia, leukopenia or megaloblastic anemia.
Treatment: discontinuation of the drug and taking measures aimed at removing it from the gastrointestinal tract (carry out gastric lavage no later than 2 hours after taking the drug or induce vomiting), drinking plenty of fluids if diuresis is insufficient and renal function is preserved. Administer calcium folinate (5-10 mg/day). Acidic urine accelerates the elimination of trimethoprim, but may also increase the risk of sulfonamide crystallization in the kidneys.
The blood picture, the composition of plasma electrolytes and other biochemical parameters should be monitored. Hemodialysis is moderately effective, but peritoneal dialysis is ineffective.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Polfa Warsaw Pharmaceutical Plant, Poland
Additional information
| Manufacturer | Polfa Warsaw Pharmaceutical Plant, Poland |
|---|---|
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Polfa Warsaw Pharmaceutical Plant |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Biseptol, 480 mg tablets 28 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.