No products in the cart.
Biosulin R, 100 me/ml 10 ml
€14.40 €12.48
Description
Biosulin P, a short-acting insulin, is human insulin produced using recombinant DNA technology.
It interacts with specific receptor of outer cytoplasmic cell membrane and forms insulin-receptor complex, stimulating intracellular processes, including synthesis of several key enzymes (hexokinase, pyruvate kinase, glycogen synthetase).
The decrease of glucose in blood is caused by the increase of its intracellular transport, increased absorption and assimilation by tissues, stimulation of lipogenesis and glycogenogenesis and decreased rate of glucose production by liver.
The duration of action of Biosulin P is mainly due to the rate of absorption, which depends on several factors (e.g., dose, route and site of administration), so the action profile of insulin is subject to significant fluctuations, both in different people and in the same person. After subcutaneous administration, the onset of action of Biosulin P is observed after approximately 30 minutes, with maximum effect between 2 and 4 hours, and duration of action of 6-8 hours.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
The completeness of absorption and onset of effect of insulin depends on the route of administration (i.e., injection or injection) and the site of administration (abdomen, thigh, buttocks), the dose (amount of insulin administered), and the concentration of insulin in the drug.
Distribution
Distribution in tissues is uneven. It does not penetrate the placental barrier and is not excreted with the breast milk.
Metabolism
It is broken down by insulinase mainly in the liver and kidneys.
Elimination
The T1/2 is a few minutes. Excreted with the urine is 30-80%.
Indications
Indications
diabetes mellitus type 1 (insulin dependent);
diabetes mellitus type 2 (non-insulin-dependent): stage of resistance to oral hypoglycemic agents, partial resistance to these drugs (during combination therapy), intercurrent diseases;
emergency conditions in patients with diabetes mellitus, accompanied by decompensation of carbohydrate metabolism.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Biosulin R – short-acting insulin, is a human insulin obtained using recombinant DNA technology.
Interacts with a specific receptor on the outer cytoplasmic membrane of cells and forms an insulin-receptor complex that stimulates intracellular processes, incl. synthesis of a number of key enzymes (hexokinase, pyruvate kinase, glycogen synthetase).
The decrease in blood glucose levels is due to an increase in its intracellular transport, increased absorption and assimilation by tissues, stimulation of lipogenesis, glycogenogenesis, and a decrease in the rate of glucose production by the liver.
The duration of action of Biosulin R is mainly determined by the rate of absorption, which depends on several factors (for example, on the dose, route and site of administration), and therefore the action profile of insulin is subject to significant fluctuations, both in different people and in the same person. After subcutaneous administration, the onset of action of Biosulin R is observed after approximately 30 minutes, the maximum effect is between 2 and 4 hours, the duration of action is 6-8 hours.
Pharmacokinetics
Suction
The completeness of absorption and the onset of the effect of insulin depends on the method of administration (s.c. or i.m.) and the site of administration (abdomen, thigh, buttocks), dose (volume of insulin administered), and insulin concentration in the drug.
Distribution
Distributed unevenly in tissues. Does not penetrate the placental barrier and is not excreted in breast milk.
Metabolism
It is destroyed by insulinase mainly in the liver and kidneys.
Removal
T1/2 – several minutes. Excreted in urine – 30–80%.
Special instructions
Special instructions
Do not use Biosulin R if the solution has become cloudy, colored, or if solid particles are visible.
During insulin therapy, it is necessary to constantly monitor blood glucose levels.
The causes of hypoglycemia, in addition to insulin overdose, can be: drug replacement, skipping meals, vomiting, diarrhea, increased physical activity, diseases that reduce the need for insulin (impaired liver and kidney function, hypofunction of the adrenal cortex, pituitary gland or thyroid gland), change of injection site, as well as interaction with other drugs.
Incorrect dosing regimen or interruptions in insulin administration, especially in patients with type 1 diabetes, can lead to hyperglycemia. Usually, the first symptoms of hyperglycemia develop gradually, over several hours or days (thirst, increased urination, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, redness and dryness of the skin, dry mouth, loss of appetite, the smell of acetone in the exhaled air). If left untreated, hyperglycemia in type 1 diabetes can lead to life-threatening diabetic ketoacidosis.
The dose of the drug must be adjusted in case of significant physical activity, infectious diseases, fever, thyroid dysfunction, Addison’s disease, hypopituitarism, liver and/or kidney dysfunction, diabetes mellitus in people over 65 years of age, increasing the intensity of physical activity or changing the usual diet.
Concomitant diseases (especially infectious) and conditions accompanied by fever increase the need for insulin.
The transition from one type of insulin to another should be carried out under the control of blood glucose levels.
The drug reduces tolerance to alcohol.
Due to the possibility of precipitation in some catheters, the use of the drug in insulin pumps is not recommended.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery
In connection with the primary prescription of insulin, a change in its type, or significant physical or mental stress on the body, the ability to drive a car or operate various mechanisms, as well as engage in other potentially hazardous activities that require increased attention and speed of psychomotor reactions, may be reduced.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Insulin soluble human genetically engineered
Composition
Composition
1 ml of injection solution contains:
active ingredient:
human isophane insulin 100 units;
excipients:
glycerol;
metacresol;
water for injections
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
Data on the use of the drug during pregnancy and breastfeeding are not provided.
Contraindications
Contraindications
increased individual sensitivity to insulin or other components of the drug; hypoglycemia.
Side Effects
Side Effects
Metabolism: hypoglycemic conditions (pallor of the skin, increased sweating, palpitations, tremor, hunger, agitation, paresthesia in the mouth, headache). Severe hypoglycemia can lead to the development of hypoglycemic coma.
Local reactions: hyperemia, swelling and itching at the injection site, with long-term use – lipodystrophy at the injection site.
Allergic reactions: rarely – skin rash, Quincke’s edema; in isolated cases – anaphylactic shock.
Other: edema, transient refractive errors (usually at the beginning of therapy).
Interaction
Interaction
There are a number of drugs that affect the need for insulin.
The hypoglycemic effect of insulin is enhanced by oral hypoglycemic drugs, MAO inhibitors, ACE inhibitors, carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, non-selective beta-blockers, bromocriptine, octreotide, sulfonamides, anabolic steroids, tetracyclines, clofibrate, ketoconazole, mebendazole, pyridoxine, cyclophosphamide, fenfluramine, lithium preparations; preparations containing ethanol.
The hypoglycemic effect of insulin is weakened by oral contraceptives, corticosteroids, thyroid hormones, thiazide diuretics, heparin, tricyclic antidepressants, sympathomimetics, danazol, clonidine, CCB, diazoxide, morphine, phenytoin, nicotine.
Under the influence of reserpine and salicylates, it is possible to both weaken and enhance the effect of the drug.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: hypoglycemia may develop.
Treatment: the patient can eliminate mild hypoglycemia himself by ingesting sugar or carbohydrate-rich foods. Therefore, diabetic patients are advised to carry sugar, sweet fruit juice or other sweets with them at all times.
In severe cases, when the patient loses consciousness, a 40% dextrose solution is administered intravenously; intramuscularly, subcutaneously, intravenously – glucagon. After regaining consciousness, the patient is advised to eat a meal rich in carbohydrates to prevent the recurrence of hypoglycemia.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
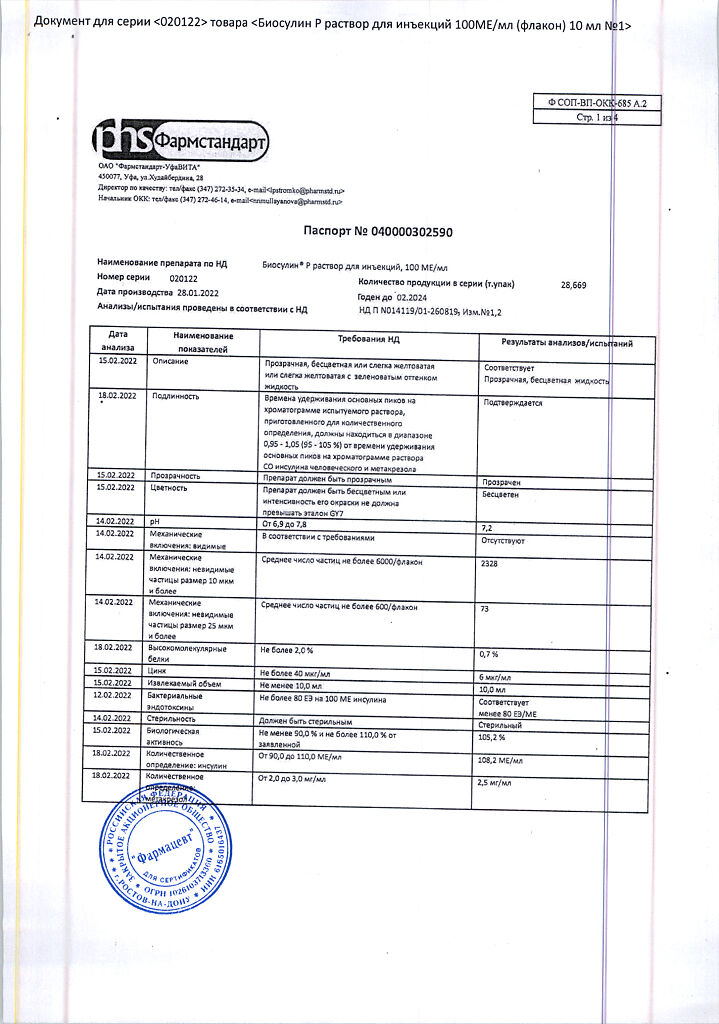
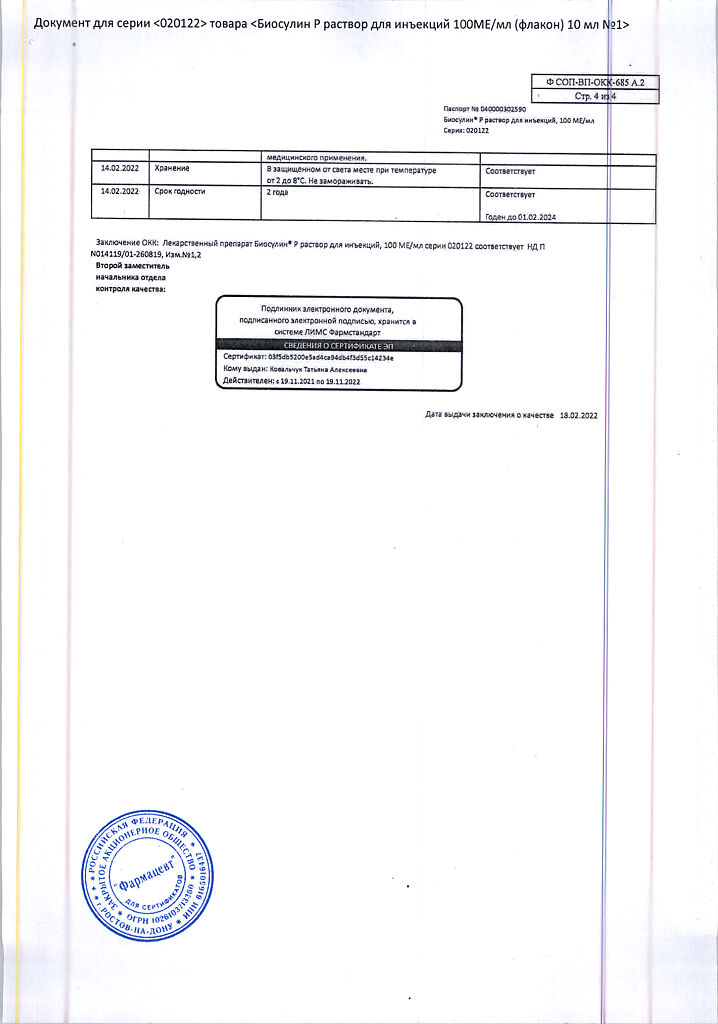
In a place protected from light, at a temperature of 2–8 °C (do not freeze)
Shelf life
Shelf life
2 years
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Pharmstandard-UfaVITA, Russia
Additional information
| Shelf life | 2 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | In the dark place at 2-8 °C (do not freeze) |
| Manufacturer | Pharmstandard-UfaVITA, Russia |
| Medication form | solution for injection |
| Brand | Pharmstandard-UfaVITA |
Related products
Buy Biosulin R, 100 me/ml 10 ml with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.