No products in the cart.
Betoftan, eye drops 0.5% 5 ml
€12.42 €10.35
Description
Betoftan is an anti-glaucoma drug. Betaxolol is a selective beta1-adrenoblocker without intrinsic sympathomimetic activity. It has no membrane stabilizing (local anesthetic) effect.
When used topically, betaxolol reduces both elevated and normal intraocular pressure by reducing intraocular fluid production. The onset of hypotensive effect is usually observed 30 min after using the drug, and the maximum decrease in ophthalmotonus occurs after about 2 h. After a single instillation the effect on ophthalmotonus lasts for 12 hours.
Betaxolol does not cause decreased blood flow in the optic nerve, miosis, accommodation spasm and hemeralopia (unlike other beta-adrenoblockers).
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Betaxolol is highly lipophilic, as a result of which it penetrates well through the cornea into the anterior chamber of the eye, Cmax in the anterior chamber is determined 20 min after instillation. When applied topically, systemic absorption is low and plasma concentrations are below the threshold (2 ng/ml) of detection.
Distribution and excretion
Binding to plasma proteins is 50%. T1/2 – 14-22 hours. Excreted by the kidneys (15% unchanged). The barrier penetrability is low, secretion with breast milk is insignificant.
Indications
Indications
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Composition
Composition
1 ml of eye drops contains:
acting substance:
betaxolol (in hydrochloride form) 5 mg;
auxiliary substances:
Sodium hydrophosphate dodecahydrate,
Sodium dihydrophosphate monohydrate,
Sodium chloride,
disodium edetate dihydrate,
benzalkonium chloride,
purified water
How to take, the dosage
How to take, the dosage
Instillation into the conjunctival sac 1 drop 2 times a day (for the first month under control of intraocular pressure).
Interaction
Interaction
When concomitant use of Betoftan and adrenaline solution for ophthalmic use, mydriasis may develop in some cases.
When Betoftan is used in combination with catecholamine depleting drugs (such as reserpine), an increase in such effects as BP decrease and bradycardia may be observed.
Concomitant use of Betoftan and oral beta-adrenoblockers may increase the risk of adverse effects (both local and systemic) due to additive effects.
Caution should be exercised when concomitant use of Betoftan and adrenergic psychotropic drugs due to possible potentiation of their effects.
When co-administration of muscle relaxants and hypoglycemic agents there may be increase in their action.
Additional co-administration with sympathomimetics will increase their vasoconstrictor effect.
If necessary, it can be used in combination with other topical ophthalmic drugs. In this case the interval between their application should be at least 10 minutes.
Special Instructions
Special Instructions
The treatment is carried out with regular medical supervision. It can mask the manifestations of thyrotoxicosis and hypoglycemia (in patients with diabetes mellitus receiving antidiabetic drugs). Reduces compensatory cardiovascular reactions in response to the use of general anesthetics and iodine-containing contrast agents. Before surgical intervention using general anesthesia, the drug should be withdrawn or the anesthetic with the least negative inotropic effect should be selected.
In elderly patients there is an increased risk of hypothermia, psychiatric disorders, cardiovascular side effects. In patients with hepatic and renal dysfunction, clinical observation in the first 4 days is recommended. Against the background of a severe allergological history, the severity of hypersensitivity reactions may increase and the lack of therapeutic effect from the usual doses of adrenaline. It is recommended to exclude alcoholic beverages during treatment. Treatment should be discontinued gradually over a period of about 2 weeks. Use with caution when driving motor vehicles and people whose profession requires high concentration of attention.
Betoftan contains the preservative benzalkonium chloride, which may be adsorbed by soft contact lenses and have a damaging effect on eye tissue. Therefore, patients wearing soft contact lenses should remove them before using the drops and put them back on no earlier than 20 minutes after the application.
To avoid contaminating the dropper, do not touch the eye during the application.
Beta-adrenoblockers should be prescribed with caution in patients who are prone to hypoglycemia because these drugs may mask the symptoms of acute hypoglycemia.
Beta-adrenoblockers may mask some symptoms of hyperthyroidism (e.g., tachycardia). In patients with suspected thyrotoxicosis, beta-adrenoblockers should not be abruptly withdrawn, as this may cause worsening of symptoms.
Beta-adrenoblockers may cause myasthenia-like symptoms (e.g., diplopia, ptosis, and general weakness).
Beta-adrenoblockers should be gradually (not overnight) withdrawn 48 hours before general anesthesia prior to elective surgery, because they can decrease myocardial sensitivity to sympathetic stimulation necessary for cardiac function during general anesthesia.
Perhaps caution should be exercised when prescribing beta-adrenoblockers in patients with severely reduced respiratory function. Although clinical studies have shown no effect of betaxolol on respiratory function, hypersensitivity should not be excluded.
Patients taking beta-adrenoblockers may have a history of atopy or anaphylactic reactions. In cases of recurrent reactions, these patients may not be sensitive to the usual doses of adrenaline necessary to control anaphylaxis.
The drug may enter the systemic bloodstream during instillation. Thus, the same side effects as with IV and parenteral administration of beta-adrenoblockers may occur.
Betoftan has minimal effect on BP and HR. However, caution should be exercised when prescribing it to patients with AV-blockade of degree I or cardiac insufficiency. The treatment should be stopped when the first signs of cardiovascular decompensation appear.
Impact on driving and operating ability
Patients whose vision is temporarily reduced after instillation of the drug are not recommended to engage in activities requiring increased attention and reaction until it is restored.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Limitations to use
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, unstable angina pectoris, bradycardia tendency, 1st degree AV blockade, peripheral circulation disorder, decompensated diabetes mellitus, hypoglycemia, pheochromocytoma, liver and kidney function disorders, hyperthyroidism, muscle weakness, elderly age, children (safety and efficacy are not defined).
Side effects
Side effects
Local reactions: transient eye discomfort after injection, lacrimation; in some cases – decreased corneal sensitivity, red eye, keratitis, photophobia, anisocoria, blurred vision, itching, dry eye, allergic reactions.
Systemic side effects have been rarely reported.
CNS side effects: dizziness, nausea, somnolence, insomnia, headache, depression, increased symptoms of myasthenia gravis.
Cardiovascular system: bradycardia, impaired cardiac conduction and heart failure.
Respiratory system: dyspnea, bronchospasm, bronchial asthma, respiratory failure.
Overdose
Overdose
In case of contact with the eyes with an excessive amount of the drug, the eyes should be rinsed with warm water.
Symptoms: arterial hypotension, bradycardia, acute heart failure are possible.
Treatment: symptomatic.
Pregnancy use
Pregnancy use
Possible if the expected effect of therapy is greater than the potential risk to the fetus.
The FDA fetal category is C.
Breastfeeding should be stopped during treatment.
It is contraindicated in children under 18 years of age.
Similarities
Similarities
Additional information
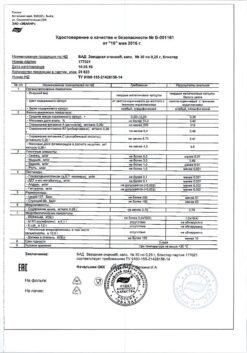
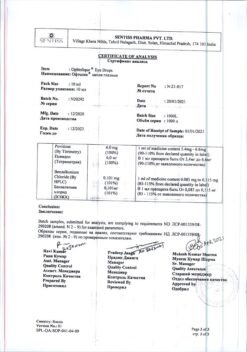
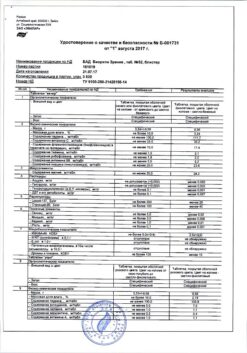
| Shelf life | 3 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | In a dry, light-protected place at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C |
| Manufacturer | C.O.Rompharm Company S.R.L., Romania |
| Medication form | eye drops |
| Brand | C.O.Rompharm Company S.R.L. |
Related products
Buy Betoftan, eye drops 0.5% 5 ml with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.