No products in the cart.
Betaloc Zoc, 50 mg 30 pcs
€8.52 €7.46
Description
Pharmacotherapeutic group: beta1-adrenoblocker selective
ATX code: C07AB02
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
Metoprolol is a b1-adrenoblocker that blocks b1-receptors at doses significantly lower than those required to block b2-receptors.
Metoprolol has little membrane-stabilizing effect and does not exhibit partial agonist activity.
Metoprolol reduces or inhibits the agonist effect that catecholamines, released during nervous and physical stress, have on cardiac activity. This means that metoprolol has the ability to inhibit the increase in heart rate (HR), minute volume and increased
heart contractility, as well as increased blood pressure (BP) caused by the sudden release of catecholamines.
Unlike common tablet forms of selective b1-adrenoblockers (including metoprolol tartrate), during Betaloc® ZOC use constant concentration of the drug in plasma is observed and stable clinical effect (b1-blockade) is provided for more than 24 hours.
Due to the absence of obvious peak plasma concentrations, clinically Betaloc® ZOC is characterized by better b1-selectivity compared to conventional tablet forms of b1-adreno-blockers. In addition, the potential risk of side effects observed at peak plasma concentrations of the drug, such as bradycardia and weakness in the legs when walking, is significantly reduced.
Patients with symptoms of obstructive lung disease may be prescribed Betalok® ZOK in combination with b2-adrenomimetics if necessary. When used in combination with b2-adrenomimetics, Betaloc® ZOC in therapeutic doses has less effect on bronchodilation induced by b2-adrenomimetics than non-selective b-adrenoblockers. Metoprolol affects insulin production and carbohydrate metabolism to a lesser extent than non-selective b-adrenoblockers. Compared with non-selective b-adrenoblockers, the drug effect on cardiovascular system response in hypoglycemic conditions is significantly less pronounced.
Administration of Betaloc® ZOC in arterial hypertension leads to a significant reduction of blood pressure for more than 24 hours both when lying and standing and under load. At the beginning of metoprolol therapy, an increase in vascular resistance is noted. However, with long-term therapy BP may decrease due to decreased vascular resistance with unchanged cardiac output.
In MERIT-HF study (survival in chronic heart failure (NYHA class II-IV) and reduced cardiac output fraction (≤ 0.40), including 3991 patients) Betaloc® ZOC showed increased survival and decreased hospitalization rate. With long-term treatment, patients achieved an overall improvement in symptoms (according to NYHA grades). Also therapy with Betaloc® ZOC showed increased left ventricular ejection fraction, decreased left ventricular end systolic and end diastolic volumes.
Quality of life during treatment with Betaloc® ZOC did not deteriorate or improve. Improved quality of life during treatment with Betaloc® ZOC was observed in patients after myocardial infarction.
Pharmacokinetics
Tablets disintegrate rapidly on contact with liquid, with dispersion of the active substance in the gastrointestinal tract. The rate of release of the active substance depends on the acidity of the environment. The duration of therapeutic effect after using Betaloc® ZOC (sustained release tablets) is more than 24 hours, while a constant rate of active substance release is achieved over 20 hours. The elimination half-life is on average 3.5 hours.
Betaloc® ZOC is completely absorbed after oral administration. Systemic bioavailability after a single oral dose is approximately 30-40%.
Metoprolol undergoes oxidative metabolism in the liver. The three major metabolites of metoprolol showed no clinically significant b-blocking effect. About 5% of the oral dose of the drug is excreted unchanged in the urine, the rest of the drug is excreted as metabolites. Binding to blood plasma proteins is low, approximately 5-10%.
Indications
Indications
The drug Betaloc ZOK is indicated for use in adults aged 18 years and older.
• Arterial hypertension.
• Angina pectoris.
• Stable symptomatic chronic heart failure with impaired left ventricular systolic function (as an adjuvant therapy to the main treatment of chronic heart failure).
• Reduced mortality and recurrent infarction after the acute phase of myocardial infarction.
• Heart rhythm disturbances, including supraventricular tachycardia, decreased ventricular contraction frequency with atrial fibrillation and ventricular extrasystoles.
• Functional disorders of cardiac activity, accompanied by tachycardia.
• Prevention of migraine attacks.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacotherapeutic group: beta-blockers; selective beta blockers
ATX code: С07АВ02
Mechanism of action
Metoprolol is a selective beta1-blocker, i.e. it acts on beta1 receptors of the heart in lower doses than required to act on beta2 adrenergic receptors localized in the peripheral vessels and bronchi.
Metoprolol does not have intrinsic sympathomimetic activity and has a slight membrane-stabilizing effect. Beta-blockers have negative inotropic and chronotropic effects.
Metoprolol weakens the effect of catecholamines released during physical and nervous stress and helps reduce heart rate, cardiac output and blood pressure. In a state of stress with increased secretion of adrenaline by the adrenal glands, metoprolol does not interfere with normal physiological vasodilation.
Pharmacodynamic effects
The selectivity of Betaloc ZOK is dose dependent, however, since the peak plasma concentration with this dosage form is significantly lower compared to that with conventional tablet forms, a higher degree of beta1 selectivity is achieved with the use of the ZOK dosage form (extended release tablets).
In therapeutic doses, metoprolol has a lesser effect on the bronchial muscles than non-selective beta-blockers, which makes it possible to prescribe metoprolol to patients with bronchial asthma or other severe obstructive pulmonary diseases in combination with beta2-adrenergic agonists.
Metoprolol, to a lesser extent than non-selective beta-blockers, affects insulin secretion and carbohydrate metabolism, and therefore can be prescribed to patients with diabetes. Metoprolol has less effect on cardiovascular reactions during hypoglycemia, such as tachycardia, and plasma glucose concentrations are restored to normal values more quickly than with non-selective beta-blockers.
Clinical efficacy and safety
For arterial hypertension, the drug Betaloc ZOK significantly reduces blood pressure for more than 24 hours, both in the supine and standing positions, as well as during physical activity. At the beginning of metoprolol therapy, an increase in total peripheral vascular resistance is observed. However, with long-term treatment, a decrease in blood pressure is observed due to a decrease in total peripheral vascular resistance with unchanged cardiac output.
Metoprolol reduces the risk of death from cardiovascular causes in patients with moderate to severe hypertension.
No changes in water and electrolyte balance were noted.
Effect in chronic heart failure: in the MERIT-HF survival study, which included 3991 patients with heart failure (NYHA functional class II–IV) and reduced ejection fraction (≤ 0.40), Betaloc ZOK was shown to improve survival and reduce the number of hospitalizations. With long-term treatment, patients experience an overall improvement in heart failure symptoms (according to NYHA classes and Overall Treatment Evaluation score).
It has also been shown that therapy with Betaloc ZOK increases left ventricular ejection fraction and reduces end-systolic and end-diastolic volumes of the left ventricle.
With tachyarrhythmia, the effect of increased sympatholytic activity is blocked, which leads to a decrease in heart rate, primarily due to a decrease in automation in pacemaker cells, as well as due to an increase in supraventricular conduction time. Metoprolol reduces the risk of recurrent heart attack and cardiac death, especially sudden death after myocardial infarction.
Pharmacokinetic properties
Absorption
Upon contact with liquid, the tablets quickly disintegrate, and the active substance is dispersed in the gastrointestinal tract. The rate of release of the active substance depends on the acidity of the medium. The duration of the therapeutic effect after taking the drug Betaloc ZOK (extended-release tablets) is more than 24 hours, while a constant rate of release of the active substance is achieved for 20 hours. The half-life averages 3.5 hours.
The drug Betaloc ZOK is completely absorbed after oral administration. Systemic bioavailability after oral administration of a single dose is approximately 30–40%.
Distribution
Plasma protein binding is low, approximately 5–10%. Biotransformation
Metoprolol undergoes oxidative metabolism in the liver. The three main metabolites of metoprolol did not exhibit a clinically significant beta-blocking effect.
Elimination
About 5% of the oral dose of the drug is excreted unchanged in the urine, the rest of the drug is excreted in the form of metabolites.
Special instructions
Special instructions
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery
When driving vehicles and engaging in potentially hazardous activities that require increased concentration and speed of psychomotor reactions, it should be taken into account that when using the drug Betaloc ZOK, dizziness and fatigue may occur.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Metoprolol
Composition
Composition
Active ingredient: metoprolol.
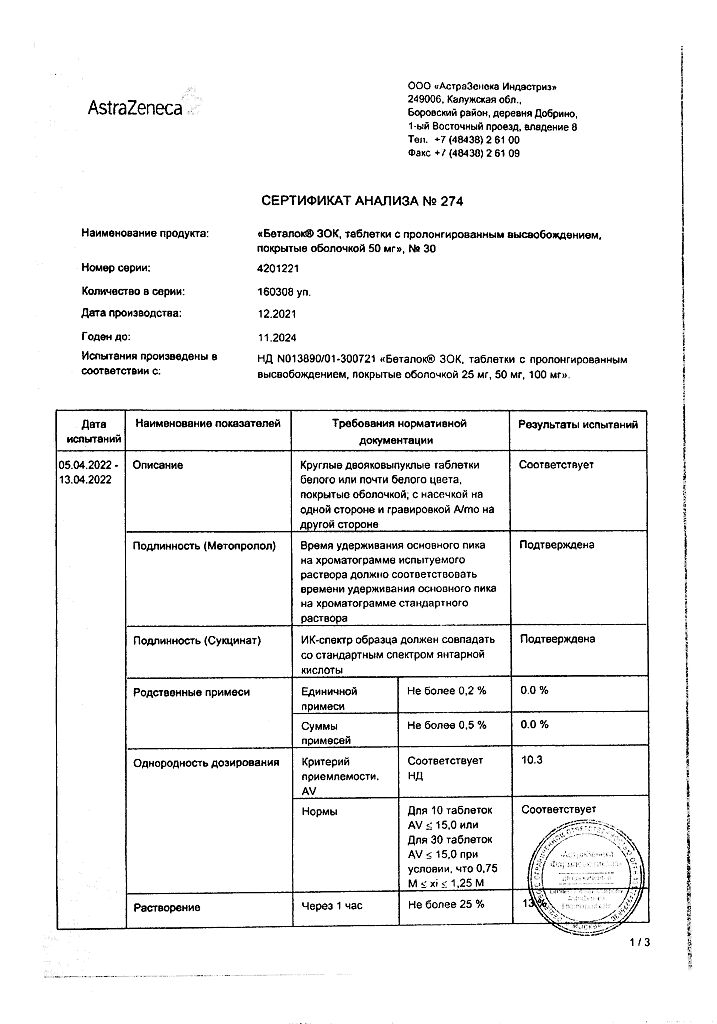
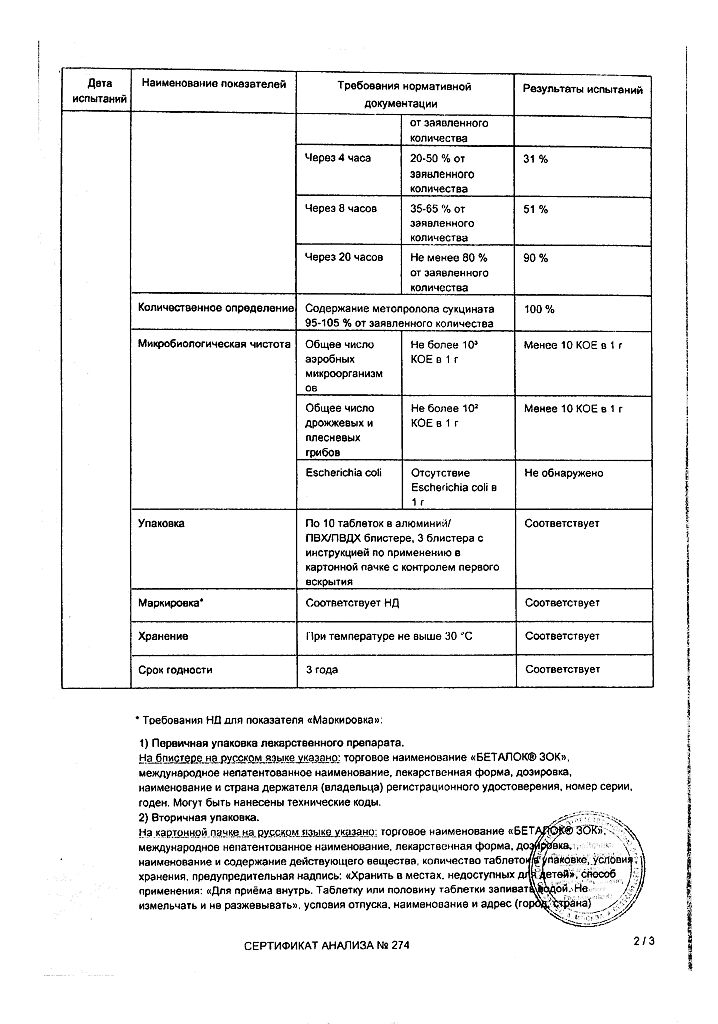
Betaloc ZOK 25 mg extended-release film-coated tablets Each extended-release film-coated tablet contains 23.75 mg metoprolol succinate, corresponding to 19.5 mg metoprolol and 25 mg metoprolol tartrate.
Excipients, the presence of which must be taken into account in the composition of the medicinal product: sodium stearyl fumarate – 0.241 mg (see section Special instructions and precautions for use).
Betaloc ZOK 50 mg extended-release film-coated tablets Each extended-release film-coated tablet contains 47.5 mg metoprolol succinate, corresponding to 39 mg metoprolol and 50 mg metoprolol tartrate.
Excipients, the presence of which must be taken into account in the composition of the medicinal product: sodium stearyl fumarate – 0.3 mg (see section Special instructions and precautions for use).
Betaloc ZOK 100 mg extended-release film-coated tablets Each extended-release film-coated tablet contains: 95 mg metoprolol succinate, corresponding to 78 mg metoprolol and 100 mg metoprolol tartrate.
Excipients, the presence of which must be taken into account in the composition of the medicinal product: sodium stearyl fumarate – 0.5 mg (see section Special instructions and precautions for use).
Full list of excipients:
Ethylcellulose Hyprolose
Microcrystalline cellulose Silicon dioxide
Sodium stearyl fumarate
Tablet shell
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
Like most drugs, Betaloc ZOK should not be prescribed during pregnancy and breastfeeding, unless the expected benefit to the mother outweighs the potential risk to the fetus and/or child. Like other antihypertensive agents, beta blockers may cause side effects such as bradycardia in the fetus, neonates, or breast-fed children.
Lactation
The amount of metoprolol excreted in breast milk and the beta-blocking effect in a breastfed baby (when the mother takes metoprolol in therapeutic doses) are negligible.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to metoprolol, to other beta-blockers or to any of the excipients.
Atrioventricular block II and III degrees. Heart failure in the stage of decompensation.
Continuous or intermittent therapy with inotropic drugs acting on beta-adrenergic receptors.
Clinically significant sinus bradycardia.
Sick sinus syndrome (in patients without a functioning permanent pacemaker).
Cardiogenic shock.
Severe peripheral circulatory disorders, including the threat of gangrene. Arterial hypotension (systolic blood pressure (BP) less than 100 mm Hg).
Betaloc ZOK is contraindicated in patients with suspected acute myocardial infarction with a heart rate (HR) less than 45 beats per minute, a PQ interval of more than 0.24 seconds, or a systolic blood pressure of less than 100 mmHg. Art.
In patients receiving beta-blockers, intravenous administration of slow calcium channel blockers such as verapamil is contraindicated.
Pheochromocytoma (without simultaneous use of alpha-blockers). Breastfeeding period.
Special instructions and precautions for use
With caution: first degree atrioventricular block, Prinzmetal angina, bronchial asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, diabetes mellitus, severe renal failure, severe liver failure, metabolic acidosis, simultaneous use with cardiac glycosides, pheochromocytoma (with simultaneous use of alpha-blockers), pregnancy, thyrotoxicosis, psoriasis, elderly age, depression (including a history), obliterating diseases of the peripheral arteries (intermittent claudication), Raynaud’s syndrome.
Patients taking beta-blockers should not receive intravenous calcium channel blockers such as verapamil.
Patients with bronchial asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease should be prescribed concomitant therapy with a beta2-agonist. It is necessary to prescribe the minimum effective dose of Betaloc ZOK, and an increase in the dose of the beta2-adrenergic agonist may be required.
It is not recommended to prescribe non-selective beta-blockers to patients with Prinzmetal’s angina. Beta-selective blockers should be prescribed to this group of patients with caution.
When using beta1-blockers, the risk of their effect on carbohydrate metabolism or the possibility of masking the symptoms of hypoglycemia is significantly less than when using non-selective beta-blockers.
In patients with chronic heart failure in the stage of decompensation, it is necessary to achieve a stage of compensation both before and during treatment with the drug.
Very rarely, patients with impaired atrioventricular conduction may experience deterioration (a possible outcome is atrioventricular block). If bradycardia develops during treatment, the dose of the drug should be reduced or the drug should be gradually discontinued.
The drug Betaloc ZOK can aggravate the course of existing peripheral circulatory disorders, mainly due to a decrease in blood pressure.
Caution should be exercised when prescribing the drug to patients with severe renal failure, metabolic acidosis, and simultaneous use with cardiac glycosides.
In patients taking beta-blockers, anaphylactic shock occurs in a more severe form. The use of epinephrine (adrenaline) in therapeutic doses does not always lead to the achievement of the desired clinical effect while taking metoprolol. Patients with pheochromocytoma should be prescribed an alpha-blocker simultaneously with Betaloc ZOK.
Abrupt withdrawal of beta-blockers is dangerous, especially in high-risk patients, and should therefore be avoided. If it is necessary to discontinue the drug, it should be done gradually over at least 2 weeks, with a twofold reduction in the dose of the drug at each stage until a final dose of 12.5 mg (half a 25 mg tablet) is reached, which should be taken for at least 4 days until the drug is completely discontinued. If symptoms appear (eg, increased symptoms of angina, increased blood pressure), a slower withdrawal regimen is recommended. Abrupt withdrawal of a beta-blocker may worsen the course of chronic heart failure and increase the risk of myocardial infarction and sudden death.
In case of surgery, the anesthesiologist should be informed that the patient is taking Betaloc ZOK. In patients undergoing surgery, discontinuation of beta-blocker therapy is not recommended. Avoid prescribing high doses without prior titration of the drug in patients with cardiovascular risk factors undergoing non-cardiac surgery due to the increased risk of bradycardia, arterial hypotension and stroke, including death.
Clinical trial data on efficacy and safety in patients with severe stable symptomatic chronic heart failure (NYHA class IV) are limited. Such patients should be treated by physicians with specialized knowledge and experience.
Patients with symptomatic heart failure combined with acute myocardial infarction and unstable angina were excluded from studies based on which indications for use were determined. The effectiveness and safety of the drug for this group of patients have not been described. Use in unstable heart failure in the decompensation stage is contraindicated.
Excipients
This medicine contains less than 1 mmol (23 mg) of sodium per tablet, which means it is essentially sodium-free.
Side Effects
Side Effects
Security Profile Summary
The drug Betaloc ZOK is well tolerated by patients; adverse reactions are mostly mild and reversible.
Summary of Adverse Reactions
To assess the frequency of adverse reactions, the following criteria were used: very often (≥1/10), often (≥1/100, but <1/10), infrequently (≥1/1,000, but <1/100), rarely (≥1/10,000, but <1/1,000), very rarely (<1/10,000), frequency unknown (estimate based on available data impossible).
Heart disorders
often: bradycardia, orthostatic hypotension (very rarely accompanied by fainting), coldness of the extremities, palpitations;
uncommon: temporary increase in symptoms of heart failure, first degree atrioventricular block, cardiogenic shock in patients with acute myocardial infarction, edema, pain in the heart area;
rarely: other conduction disorders, arrhythmias;
very rare: gangrene in patients with previous severe peripheral circulatory disorders.
Nervous system disorders
very often: increased fatigue; often: dizziness, headache;
uncommon: paresthesia, convulsions, depression, decreased concentration, drowsiness or insomnia, nightmares;
rarely: increased nervous excitability, anxiety;
very rare: amnesia/memory impairment, depression, hallucinations.
Gastrointestinal disorders
often: nausea, abdominal pain, diarrhea, constipation; uncommon: vomiting;
rarely: dryness of the oral mucosa.
Disorders of the liver and biliary tract
rarely: liver dysfunction;
very rare: hepatitis.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
uncommon: skin rash (like psoriasis-like urticaria), increased sweating;
rarely: hair loss;
very rarely: photosensitivity, exacerbation of psoriasis.
Respiratory system disorders
often: shortness of breath on exertion;
uncommon: bronchospasm;
rarely: rhinitis.
Disorders of the sensory organs and labyrinth
rarely: visual disturbances, dryness and/or irritation of the eyes, conjunctivitis;
very rarely: ringing in the ears, taste disturbances.
Muscle, skeletal and connective tissue disorders
very rarely: arthralgia.
Metabolic and nutritional disorders
uncommon: weight gain.
Blood and lymphatic system disorders
very rarely: thrombocytopenia.
Disorders of the reproductive system and mammary glands
rare: impotence/sexual dysfunction.
Interaction
Interaction
Metoprolol is a CYP2D6 substrate, and therefore drugs that inhibit CYP2D6 (quinidine, terbinafine, paroxetine, fluoxetine, sertraline, celecoxib, propafenone and diphenhydramine) may affect the plasma concentrations of metoprolol.
The combined use of Betaloc ZOK with the following drugs should be avoided:
Barbituric acid derivatives
Barbiturates (study conducted with pentobarbital) increase the metabolism of metoprolol due to enzyme induction.
Propaphenone
When propafenone was prescribed to four patients treated with metoprolol, an increase in plasma concentrations of metoprolol was observed by 2-5 times, while two patients experienced side effects characteristic of metoprolol. This interaction was confirmed in a study on 8 volunteers. The interaction is likely due to the inhibition by propafenone, like quinidine, of the metabolism of metoprolol through the cytochrome P4502D6 system. Taking into account the fact that propafenone has beta-blocker properties, the co-administration of metoprolol and propafenone does not seem appropriate.
Verapamil
The combination of beta-blockers (atenolol, propranolol and pindolol) and verapamil can cause bradycardia and lead to a decrease in blood pressure. Verapamil and beta-blockers have a complementary inhibitory effect on atrioventricular conduction and sinus node function.
The combination of Betaloc ZOK with the following drugs may require dose adjustment:
Amiodarone
The combined use of amiodarone and metoprolol can lead to severe sinus bradycardia. Given the extremely long half-life of amiodarone (50 days), a possible interaction should be considered long after discontinuation of amiodarone.
Class I antiarrhythmic drugs
Class I antiarrhythmics and beta-blockers may result in additive negative inotropic effects, which can lead to serious hemodynamic side effects in patients with impaired left ventricular function. This combination should also be avoided in patients with sick sinus syndrome and atrioventricular conduction disorder. The interaction is described using disopyramide as an example.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
NSAIDs weaken the antihypertensive effect of beta-blockers. This interaction has been documented for indomethacin. It is likely that the described interaction will not be observed with sulindac. Negative interactions have been noted in studies with diclofenac.
Diphenhydramine
Diphenhydramine reduces the clearance of metoprolol to alpha-hydroxymetoprolol by 2.5 times. At the same time, an increase in the effect of metoprolol is observed.
Diltiazem
Diltiazem and beta-blockers mutually enhance the inhibitory effect on atrioventricular conduction and sinus node function. When metoprolol was combined with diltiazem, cases of severe bradycardia were observed.
Epinephrine (adrenaline)
Ten cases of severe hypertension and bradycardia have been reported in patients taking non-selective beta blockers (including pindolol and propranolol) and receiving epinephrine (adrenaline). The interaction was also observed in the group of healthy volunteers. It is assumed that similar reactions can be observed when epinephrine is used together with local anesthetics if it accidentally enters the vascular bed. It is assumed that this risk is much lower with the use of cardioselective beta-blockers.
Phenylpropanolamine
Phenylpropanolamine (norephedrine) in a single dose of 50 mg can cause an increase in diastolic blood pressure to pathological values in healthy volunteers. Propranolol mainly prevents the increase in blood pressure caused by phenylpropanolamine. However, beta-blockers may cause paradoxical hypertension reactions in patients receiving high doses of phenylpropanolamine. Several cases of hypertensive crisis have been reported while taking phenylpropanolamine.
Quinidine
Quinidine inhibits the metabolism of metoprolol in a special group of patients with rapid hydroxylation (in Sweden, approximately 90% of the population), causing mainly a significant increase in plasma concentrations of metoprolol and increased beta-blockade. It is believed that a similar interaction is typical for other beta-blockers, the metabolism of which involves cytochrome P4502D6.
Clonidine
Hypertensive reactions during abrupt withdrawal of clonidine may be exacerbated by concomitant use of beta-blockers. When used together, if clonidine is discontinued, discontinuation of beta-blockers should begin several days before discontinuation of clonidine.
Rifampicin
Rifampicin may increase the metabolism of metoprolol, reducing plasma concentrations of metoprolol.
Patients concomitantly taking metoprolol and other beta-blockers (eye drops) or monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) should be closely monitored. While taking beta-blockers, inhalational anesthetics enhance the cardiodepressive effect. While taking beta-blockers, patients receiving oral hypoglycemic agents may require dose adjustment of the latter.
Plasma concentrations of metoprolol may increase when taking cimetidine or hydralazine.
Cardiac glycosides, when used together with beta-blockers, can increase atrioventricular conduction time and cause bradycardia.
Overdose
Overdose
Toxicity: metoprolol at a dose of 7.5 g in an adult caused intoxication with a fatal outcome. A 5-year-old child who took 100 mg of metoprolol showed no signs of intoxication after gastric lavage. Taking 450 mg of metoprolol by a 12-year-old teenager resulted in moderate intoxication. Administration of 1.4 g and 2.5 g of metoprolol to adults caused moderate and severe intoxication, respectively. Taking 7.5 g by adults resulted in extremely severe intoxication.
Symptoms
In case of an overdose of metoprolol, the most serious symptoms are from the cardiovascular system, but sometimes, especially in children and adolescents, symptoms from the central nervous system and suppression of pulmonary function, bradycardia, atrioventricular block of the I–III degree, asystole, a marked decrease in blood pressure, weak peripheral perfusion, heart failure, cardiogenic shock may predominate; depression of pulmonary function, apnea, as well as increased fatigue, impaired consciousness, loss of consciousness, tremor, convulsions, increased sweating, paresthesia, bronchospasm, nausea, vomiting, possible esophageal spasm, hypoglycemia (especially in children) or hyperglycemia, hyperkalemia; effects on the kidneys; transient myasthenic syndrome. Concomitant use of alcohol, antihypertensive drugs, quinidine or barbiturates may worsen the patient’s condition. The first signs of an overdose can be observed 20 minutes – 2 hours after taking the drug.
Treatment
Prescription of activated carbon and, if necessary, gastric lavage. IMPORTANT! Atropine (0.25–0.5 mg IV for adults, 10–20 mcg/kg for children) should be given before gastric lavage (due to the risk of vagal stimulation). If necessary, maintain airway patency (intubation) and adequate ventilation. Replenishment of circulating blood volume and glucose infusion. ECG monitoring. Atropine 1.0–2.0 mg intravenously, repeat if necessary (especially in case of vagal symptoms). In case of myocardial depression, infusion of dobutamine or dopamine is indicated. Glucagon 50–150 mcg/kg IV may also be given at 1-minute intervals. In some cases, adding epinephrine to therapy may be effective. For arrhythmia and a wide ventricular complex (QRS), sodium solutions (chloride or bicarbonate) are infused. It is possible to install a pacemaker. Cardiac arrest due to an overdose may require resuscitation for several hours. Terbutaline (injection or inhalation) can be used to relieve bronchospasm. Symptomatic treatment is carried out.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
At a temperature not exceeding 30 °C.
Shelf life
Shelf life
3 years. Do not use after expiration date.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
AstraZeneca Industries/AstraZeneca AB, Russia
Additional information
| Shelf life | 3 years. Do not use after the expiration date. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | Store at a temperature not exceeding 30°C. Keep out of reach of children. |
| Manufacturer | AstraZeneca Industries/AstraZeneca AB, Russia |
| Medication form | sustained release tablets |
| Brand | AstraZeneca Industries/AstraZeneca AB |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Betaloc Zoc, 50 mg 30 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.