No products in the cart.
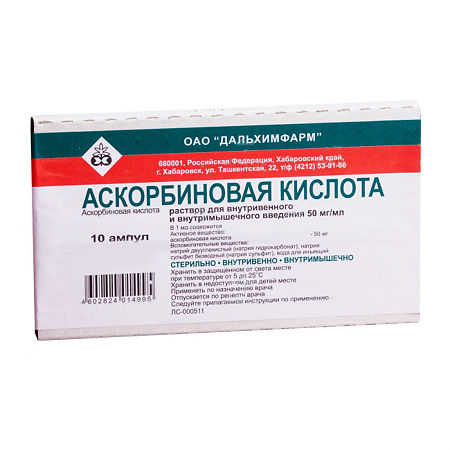
Ascorbic acid, 50 mg/ml 1 ml 10 pcs
€1.00
Out of stock
(E-mail when Stock is available)
Description
Ascorbic acid has pronounced restorative properties and is involved in the regulation of carbohydrate metabolism, redox processes, blood coagulation, normalization of capillary permeability, tissue regeneration, synthesis of steroid hormones, collagen, procollagen.
Form of release
Form of release
Injection solution.
Additional information
| Conditions of storage | In a place protected from light at a temperature no higher than 15 ° C |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Dalkhimpharm, Russia |
| Medication form | solution |
| Brand | Dalkhimpharm |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Ascorbic acid, 50 mg/ml 1 ml 10 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.