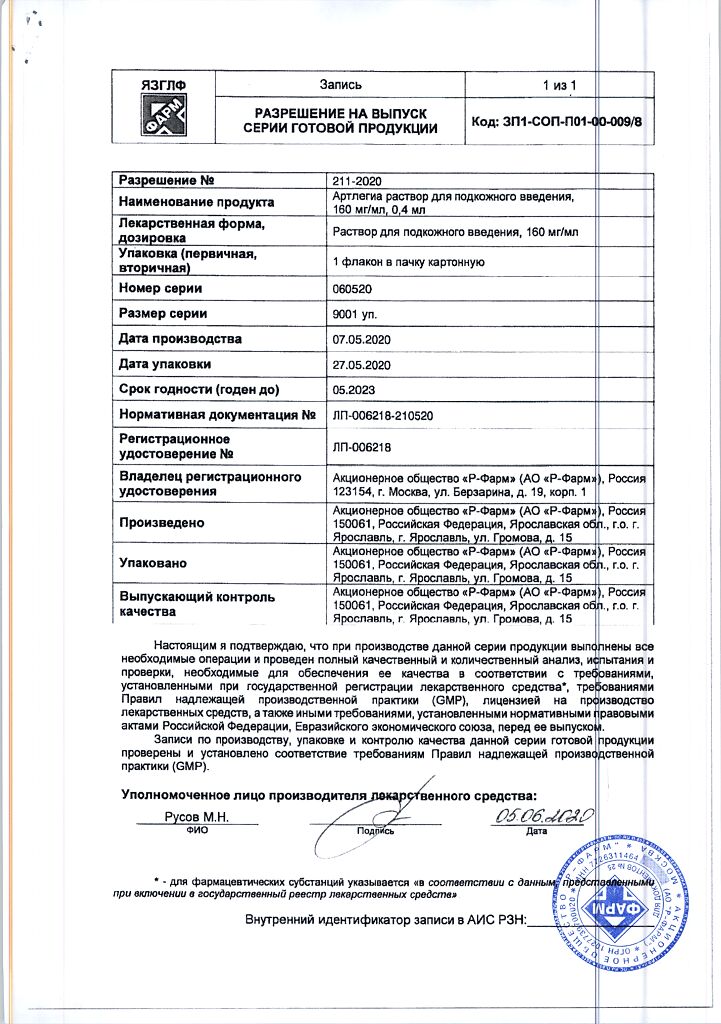
No products in the cart.
Description
Pharmacotherapeutic group: monoclonal antibodies
ATX code: L04AC
Pharmacological properties:
Olokizumab is a humanized (with an attached hypervariable site) monoclonal antibody belonging to immunoglobulin isotype (immunoglobulin, Ig) G4/kappa. Olokizumab selectively binds to human IL-6 and effectively neutralizes the effects of IL-6 in vivo and in vitro. The data indicate that olokizumab does not bind significantly to other molecules of the IL-6 family and does not affect their function, nor does it activate the IL-6 signaling pathway.
Pharmacodynamics:
. In double-blind, randomized phase 2 clinical trials, subcutaneous administration of olokizumab at doses ranging from 60 to 480 mg/month in patients with moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis caused a marked reduction in plasma levels of C-reactive protein (CRP) within 7 days of treatment start, persisting for at least 10 weeks after a single administration, and throughout the therapy with multiple administrations of the drug.
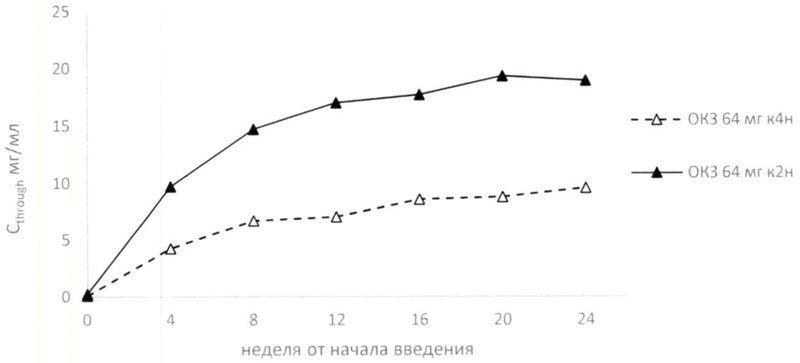
In patients with moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis insufficiently controlled by methotrexate therapy, subcutaneous administration of olokizumab at a dose of 64 mg every 2 weeks (k2n) or 64 mg every 4 weeks (k4n) caused a dramatic decrease in mean plasma CRP levels by week 2 of treatment. Low CRP levels persisted for 24 weeks throughout the treatment period.
Clinical Efficacy:
The efficacy of subcutaneous administration of olokizumab at a dose of 64 mg every 2 weeks (k2n) and every 4 weeks (k4n) has been studied in patients with moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis inadequately controlled by methotrexate therapy in the CREDO1 clinical trial.
Olokizumab in both doses was significantly more effective than placebo in reducing rheumatoid arthritis activity regardless of gender, body mass index, disease activity, rheumatoid factor and/or cyclic cytrirole peptide antibody levels. The length of time from diagnosis to treatment initiation and the duration of prior methotrexate therapy also had no effect on the clinical efficacy of the drug. In addition, the proportion of patients who achieved low disease activity and remission was significantly higher among those who received olokizumab compared to placebo. Patients who received olokizumab were also more likely to have better quality of life, less pain, and fewer painful and swollen joints. The effects of olokizumab were noticeable as early as 4 weeks of treatment, with a pronounced effect developing after approximately 12 weeks of initiation of the drug and lasting for at least 24 weeks.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
The bioavailability of olokizumab was assessed using data from 173 patients with mild to moderate rheumatoid arthritis who received different doses of olokizumab for 12 weeks, combined with data from 40 patients with mild to moderate rheumatoid arthritis after a single administration of different doses of olokizumab and data from 41 healthy volunteers after a single administration of different doses of olokizumab. When administered subcutaneously, the bioavailability is 63% (relative standard error rate (RER) = 4.9%).
After a single subcutaneous injection of olokizumab in patients with mild to moderate rheumatoid arthritis at doses ranging from 0.3 to 6 mg/kg, the maximum blood concentration of the drug (Cmax) increased dose-dependently. The time to reach Cmax ranged from 4 to 12 days, with detectable levels of olokizumab persisting up to approximately 16 weeks.
After a single subcutaneous injection of 64 mg of olokizumab in patients with moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis insufficiently controlled on methotrexate treatment, Cmax was reached after an average of 7 to 10 days (Table 1).
When repeatedly administered, steady-state blood concentrations of olokizumab increased during the initial period of therapy and reached equilibrium after 16 (64 mg k4n) and 14 (64 mg k2n) weeks from treatment initiation (Table 1, Figure 1).
Table 1. Pharmacokinetic parameters of olokizumab after subcutaneous administration to patients with moderate to severe RA
The following table shows the pharmacokinetic parameters of olokizumab after subcutaneous administration to patients with moderate to severe RA
figure>
| FC parameter | Baseline values | Week 20 | |||
| OKZ 64 mg k4n N = 18 | OKZ 64 mg k2n N = 18 | OKZ 64 mg k4n N = 18 | OKZ 64 mg k2n N = 18 | ||
| Cmax (µg/mL) | 6.18 | 6.22 | 17.00 | 21.55 | |
| % CV | 50.0 | 39.2 | 55.7 | 25.0 | |
| AUC0-t* (µg*h/ml) | 2886 | 1556 | 8411 | 5485 | |
| % CV | 45.3 | 38.9 | 29.9 | 31.8 | |
| tmax (h) | 190.2 | 234.4 | 244.5 | 127.8 | |
| Median | 166.5 | 236.7 | 167.6 | 96.7 | |
| Min. – max. | 92.8-402.3 | 95.8-359.2 | 95.4-670.7 | 0.0-334.7 | |
RA, rheumatoid arthritis; OKZ, olokizumab; k2n, every 2 weeks; k4n, every 4 weeks; Cmax, maximum blood concentration of drug; AUC0-t, area under the concentration-time curve; tmax, time to reach maximum drug concentration; *AUC for k4n administration was calculated over a period of 672 hours (28 days) and for k2n administration over a period of 336 hours (14 days)

Biotransformation/p>
In an in vitro study on cryopreserved human hepatocytes, olokizumab reversed the inhibitory effect of IL-6 on CYP1A1/2, 2B6, 2C9, 3A4/5 and 2C19 activity as well as on NTCP activity.
Elimination
Olokizumab clearance estimates in patients with mild to moderate rheumatoid arthritis were 0.17 L/d (relative standard error ratio [% RER] = 4.9%) with low to medium individual variability.
Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic relationship
The level of CRP reduction in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis receiving olokizumab was independent of the drug dose. In addition, patients with mild to moderate rheumatoid arthritis showed a positive correlation of plasma concentration of olokizumab with neutropenia and elevated plasma levels of ACT, ALT and triglycerides, although the effect size was small. There was also a persistent reduction in VEGF and amyloid serum protein A levels in all treatment groups by day 14 after administration of olokizumab, without dose dependence.
Indications
Indications
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
How to take, the dosage
How to take, the dosage
The drug Artlegia is injected subcutaneously, into the thigh or anterior abdominal wall, 0.4 ml of a solution with a concentration of 160 mg/ml at a time. The solution should be heated to room temperature before injection. The storage time of the drug at >8 ° C should not exceed 4 hours.
The first administration of the drug should be carried out under the supervision of a qualified medical officer. The patient should be observed for 30 minutes after the first injection. After training in hypodermic injection techniques under the supervision of a healthcare professional, the patient (or their caregiver) can administer the product independently. A physician experienced in the diagnosis and treatment of rheumatoid arthritis decides whether the patient can inject Artlegia independently.
Only single-use syringes should be used for the administration of Artlegia.
Dose skipping
If another injection of the medication was missed, the missed dose should be given as soon as possible and the interval between any two injections should be at least half the interval of the chosen dosing regimen (see Table 2).
Table 2. Actions to take if an injection is missed
OKZ – olokizumab; k2n – every 2 weeks; k4n – every 4 weeks
Stopping the drug
Therapy with Artlegia should be stopped if the patient has
Elevated biochemical measures of liver function consistent with the following conditions:
The patient has any of the following laboratory abnormalities:
Confirmed pregnancy during use of Artlegia (see “Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding”).
Gastrointestinal perforation (see section “Special Precautions”).
Severe or life-threatening infection (see section “Special Precautions”).
The use in children
The safety and efficacy of Artlegia in children and adolescents under 18 years of age has not been established at this time. There are no data on its use.
Dosing regimen:
The recommended dose is 64 mg once every 4 weeks or once every 2 weeks subcutaneously.
Patient special groups
Elderly patients (>65 years): No dose adjustment is necessary.
Patients with renal impairment: The safety and efficacy of Artlegia in patients with renal impairment have not been studied. There are no data on its use.
Patients with hepatic impairment: The safety and effectiveness of Artlegia in patients with hepatic impairment has not been studied. There are no data on its use.
Interaction
Interaction
Simultaneous use with methotrexate had no effect on the exposure of olokizumab. No effect of olokizumab on methotrexate exposure is also expected when used concomitantly, no clinical data are available. In all clinical trials in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, olokizumab was used together with methotrexate.
There have been no specific clinical studies of drug interactions of olokizumab. The CREDO1 clinical trial reported no cases of clinically significant drug interactions of olokizumab with other drugs.
In an in vitro study on cryopreserved human hepatocytes, olokizumab reversed the inhibitory effect of IL-6 on CYP1A1/2, 2B6, 2C9, 3A4/5 and 2C19 activity as well as on NTCP activity. Thus, it should be taken into consideration that in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis the doses of drugs metabolized by these CYP isoforms may require adjustment after initiation of the drug Artlegia.
The concentrations of the following drugs may decrease when co-administered with Artlegia (the list is not exhaustive): Statins (simvastatin, lovastatin, atorvastatin); oral contraceptives; calcium channel blockers; glucocorticoids (dexamethasone, methylprednisolone); warfarin; quinidine; theophylline; tizanidine; phenytoin; pimozide; cyclosporine; sirolimus; tacrolimus; benzodiazepines (e.g., diazepam, alprazolam, triazolam, midazolam, bromazepam).
Directions for use
Directions for use
Remove the vial of Artlegia from the refrigerator in advance: wait about 30 minutes before injecting to allow the product to warm up to room temperature. Do not warm the product.
Prepare for the injection
Step 1
Wash your hands with warm water and soap, choose a flat, clean surface, inspect the vial of product carefully, and do not use it if:
Special Instructions
Special Instructions
The treatment with Arthlegia may be prescribed and monitored by physicians experienced in the diagnosis and treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.
Anaphylactic or anaphylactoid reactions: administration of preparations containing proteins may be associated with immunological/allergic or non-immunological hypersensitivity reactions to the drug, which may be severe. These reactions may occur in the form of an acute infusion reaction, an allergic reaction or a delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction. Thus, the first administration of Artlegia should be performed in a medical facility where drugs and equipment for anaphylactic and anaphylactoid reactions are available. In clinical trials, there has been a case of a serious anaphylactic reaction to the administration of Artlegia.
Infections: an increased incidence of infections is typical for patients receiving immunosuppressive drugs, including blockers of IL-6 signaling pathway. The use of Artlegia is associated with increased risk of development or activation of infections. The therapy with Artlegia should not be started in patients with infections in active phase. Treatment with Artlegia should be used with caution in patients with risk factors for infections. In case of serious infections the therapy with Artlegia should be discontinued. Patients should be advised about possible signs and symptoms of infection which require immediate medical attention.
Tuberculosis infection: Before initiating therapy with Artlegia it is necessary to examine the patient for the presence of latent tuberculosis infection. Patients with latent form of tuberculosis infection should undergo a standard course of anti-tuberculosis therapy before the start of therapy with Artlegia.
Artlegia should be used with caution in patients in close contact (living together or being in other confined spaces such as the workplace, social gatherings or in a building for long periods during the day) with a person with active tuberculosis. Before using Artlegia in these patients, the risk-benefit ratio of the drug should be carefully evaluated.
Risk of gastrointestinal perforation: cases of gastrointestinal perforation, mainly with diverticulitis, are known with the use of inhibitors of IL-6 signaling pathway. Caution should be exercised when using Artlegia in patients with a history of diverticulitis or intestinal perforation and other risk factors for intestinal perforation. If gastrointestinal symptoms, such as abdominal pain, occur during treatment with Artlegia, the patient should be evaluated immediately.
Renal impairment: Patients with renal impairment have not been included in the clinical study of Artlegia. Due to lack of data caution should be exercised when using Artlegia in patients with impaired renal function.
Hepatic disorders: the use of Artlegia, as well as other IL-6 inhibitors, is associated with increased levels of ALT, ACT and gamma-glutamyltransferase (see section “Increased liver transaminases”). Patients with ALT or ACT levels â¥1.5ÃVGN were not included in the clinical study. Caution should be exercised when using Artlegia in patients with liver dysfunction and hepatic impairment.
Monitoring of laboratory blood parameters: in clinical trials a decrease in absolute numbers of neutrophils and leukocytes during treatment with Artlegia and other IL-6 inhibitors has been registered. According to data on use of other IL-6 inhibitors, neutropenia against the background of treatment did not lead to increased incidence of infections. Patients with a white blood cell count < 3.5Ã109/l, neutrophil count < 2000Ã106/l (< 2000/mm³) were not included in the clinical trial.
Vaccination: The safety of immunization with live vaccines against a background of IL-6 inhibitors, including olokizumab, has not been established. Patients with the need for live vaccines were not included in the clinical trial.
Malignant neoplasms: There are no data on the safety of using olokizumab in patients with malignant neoplasms; the risk of malignancy on therapy with Artlegia is not known.
Studies to study the effect of the drug on the ability to drive vehicles and mechanisms have not been conducted. Although no adverse reactions related to dizziness have been reported with olokizumab therapy to date, dizziness has often been observed with therapy with other IL-6 inhibitors. Patients who experience dizziness during therapy with Artlegia should be advised not to drive vehicles or operate machinery until the dizziness subsides.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to olokizumab, any drug component in history.
Active infectious diseases (including tuberculosis).
Children under 18 years of age.
Hereditary intolerance of fructose (the drug contains sorbitol).
Pregnancy.
The period of breastfeeding.
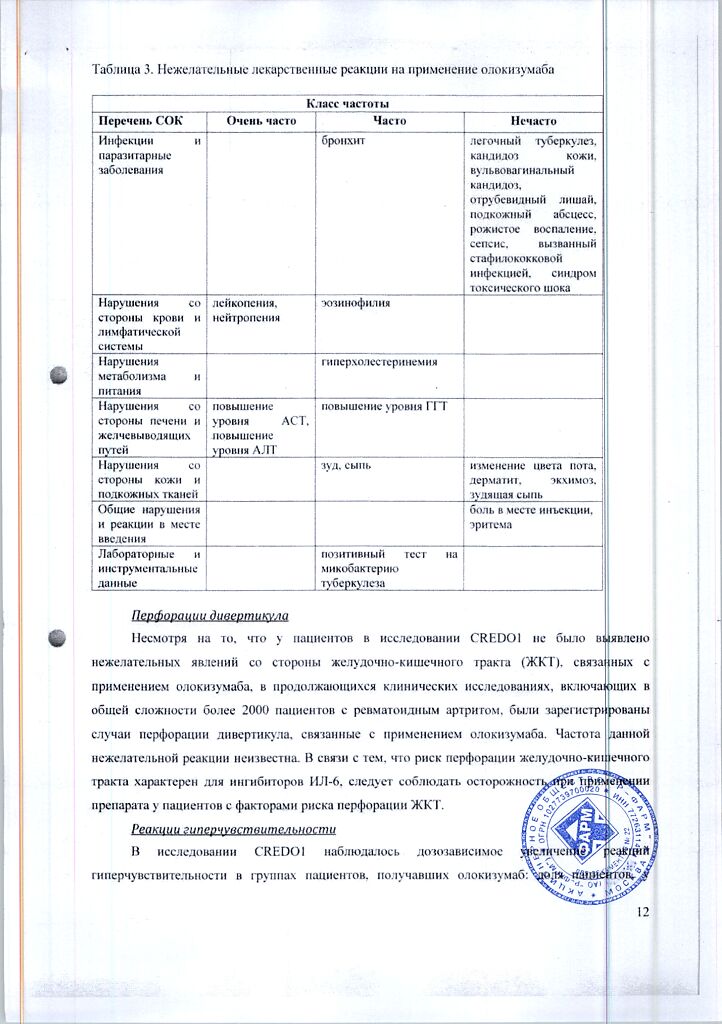
Side effects
Side effects
The safety of Artlegia was evaluated in a double-blind, randomized clinical trial, CREDO1. A total of 428 patients with moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis with insufficient control on methotrexate therapy participated in the study. 142 patients received olokizumab 64 mg once every 2 weeks (k2n), 143 patients received olokizumab 64 mg once every 4 weeks (k4n), and 143 patients received placebo. All patients were on background therapy with methotrexate.
The most common adverse reactions were leukopenia, neutropenia, and elevated liver transaminases.
The list of adverse reactions is listed according to MedDRA systemic organ classes (SOC). Within each class, adverse reactions are categorized by frequency of occurrence: very common (â¥1/10), common (â¥1/100 to < 1/10), infrequent (â¥1/1000 to < 1/100), rare (â¥1/10 000 to < 1/1000), very rare (< 1/10 000) and frequency unknown.
Table 3. Adverse drug reactions to the use of olokizumab
Diverticular perforations
Although there were no gastrointestinal (GI) adverse events associated with the use of olokizumab in patients in the CREDO1 study, there have been cases of diverticular perforation associated with olokizumab in ongoing clinical trials involving a total of over 2,000 patients with rheumatoid arthritis. The frequency of this adverse reaction is unknown. Because the risk of gastrointestinal perforation is common with IL-6 inhibitors, caution should be exercised when using the drug in patients with risk factors for gastrointestinal perforation.
Hypersensitivity reactions
The CREDO1 study observed a dose-dependent increase in hypersensitivity reactions in patient groups treated with olokizumab: The proportion of patients who experienced at least one adverse event related to hypersensitivity reactions during treatment, including: itching, rash, allergic dermatitis, and increased blood eosinophil levels, was 4.2% in the group receiving olokizumab k4n, 7.0% in the group receiving olokizumab k2n, and 2.1% in the placebo group.
In ongoing clinical trials, a case of anaphylactic reaction to olokizumab administration has been reported (frequency unknown).
Infections
In the CREDO1 study, infections occurred at approximately the same rate in all treatment groups: 14.1% in the group receiving olokizumab 64 mg k4n, 15.4% in the group receiving olokizumab 64 mg k2n and 16.2% in the placebo group.
The patient group receiving olokizumab 64 mg k2n was more likely to develop serious infection-related adverse events (2.8%) compared to the patient group receiving olokizumab 64 mg k4n (0%) and placebo (1.4%).
The patient groups receiving olokizumab had the following serious infections not seen in the placebo group: subcutaneous abscess (2), pulmonary tuberculosis (1), sepsis due to staphylococcal infection (1), and toxic shock syndrome (1).
Elevated liver transaminases
In the CREDO1 study, the incidence of elevated ALT, considered by investigators to be an adverse event, was 23.2% in the group receiving olokizumab 64 mg k4n. 17.5% in the group receiving olokizumab 64 mg k2n and 17.7% in the placebo group. The incidence of ACT elevation, considered by the investigators as an adverse event, was 15.5% in the group that received olokizumab k4n, 11.2% in the group that received olokizumab k2n, and 7.0% in the placebo group.
In general, there were fluctuations in individual ALT levels during the therapy period. In total, elevation of ALT levels above the upper limit of normal (1ÃVHN) was noted at least once during the treatment period (24 weeks) in approximately 50% of patients receiving olokizumab and 27% of patients receiving placebo (Table 4). None of the patients had a simultaneous increase in ALT and ACT >3ÃVGN with an increase in bilirubin >2ÃVGN.
Table 4 ALT elevations in patients in the CREDO1 study
*the highest ALT value in each patient over the 24-week treatment period was counted
VGN – upper limit of normal; OKZ – olokizumab
Hyperlipidemia
. In the CREDO1 study, elevated blood lipid levels during treatment, considered an adverse event by researchers, were observed in 8.5% of patients in the group receiving olokizumab 64 mg k4n, 8.4% of patients in the group receiving olokizumab 64 mg k2n and 2.8% of patients in the placebo group.
On average, total cholesterol, LDL, and HDL levels increased in the patient groups receiving olokizumab during the first 4 weeks of therapy. Then, in the group receiving olokizumab 64 mg k2n, average lipid levels decreased and returned to values in the placebo group by the end of the treatment period, whereas in patients receiving olokizumab 64 mg k4n, high average blood lipid levels persisted until the end of the treatment period.
Neutropenia
In the CREDO1 study, mean absolute neutrophil counts decreased after 12 weeks of therapy in the groups receiving olokizumab compared to placebo and then remained stable until the end of the treatment period (Table 5).
Table 5. Dynamics of mean absolute neutrophil count over 24 weeks of therapy
Accordingly, the proportion of patients who had an adverse event such as neutropenia at least once during treatment was 11.2% of patients in the group receiving olokizumab 64 mg k4n, 7.7% of patients in the group receiving olokizumab 64 mg k2n and 3.5% of patients in the placebo group.
Overdose
Overdose
There have been no cases of overdose in clinical trials. However, additional clinical data show that the overall safety profile of olokizumab in patients receiving 240 mg k2n (480 mg per month) for 12 weeks is comparable to the overall safety profile in patients receiving the drug at the recommended dose.
Children
There are no data on overdose in children.
Pregnancy use
Pregnancy use
A pregnancy test should be performed before prescribing Artlegia to women of childbearing age. The attending physician should explain in detail the risks of using Artlegia during pregnancy and instruct the fertile patient to use highly effective contraception methods and perform regular pregnancy tests during treatment and for at least 6 months after the last dose of Artlegia. If a patient receiving Artlegia becomes pregnant, she should stop using the drug immediately and see her physician.
Pregnancy
The use of the drug Artlegia in pregnant women has not been systematically studied. Due to the fact that the drug Artlegia is indicated for use in combination with methotrexate, which has well known teratogenic effects, the use of Artlegia in pregnancy is not recommended.
Reproductive toxicity has been found in animal studies. It is assumed that IL-6 plays an important role in the opening of the cervix and possibly in the birth of the placenta. Thus, the use of Artlegia may interfere with labor.
Lactation
The penetration of olokizumab into breast milk has not been studied. There are no clinical data on the risk to the breastfed child. Since the drug Artlegia is indicated for use in combination with methotrexate, which is secreted into the breast milk, it is recommended to stop breastfeeding when the drug is prescribed.
Fertility
There are no clinical data on the effect of olokizumab on fertility in humans.
In animal studies, no adverse effects of olokizumab on the fertility of male and female Javanese macaques were found.
Additional information
| Shelf life | 3 years. Do not use after the expiration date printed on the package. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | In a light-protected place at a temperature of 2 to 8 ° C. Store out of the reach of children. Do not freeze. |
| Manufacturer | R-Pharm AO, Russia |
| Medication form | solution |
| Brand | R-Pharm AO |
Related products
Buy Artlegia, 160 mg/ml 0.4 ml with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.