No products in the cart.
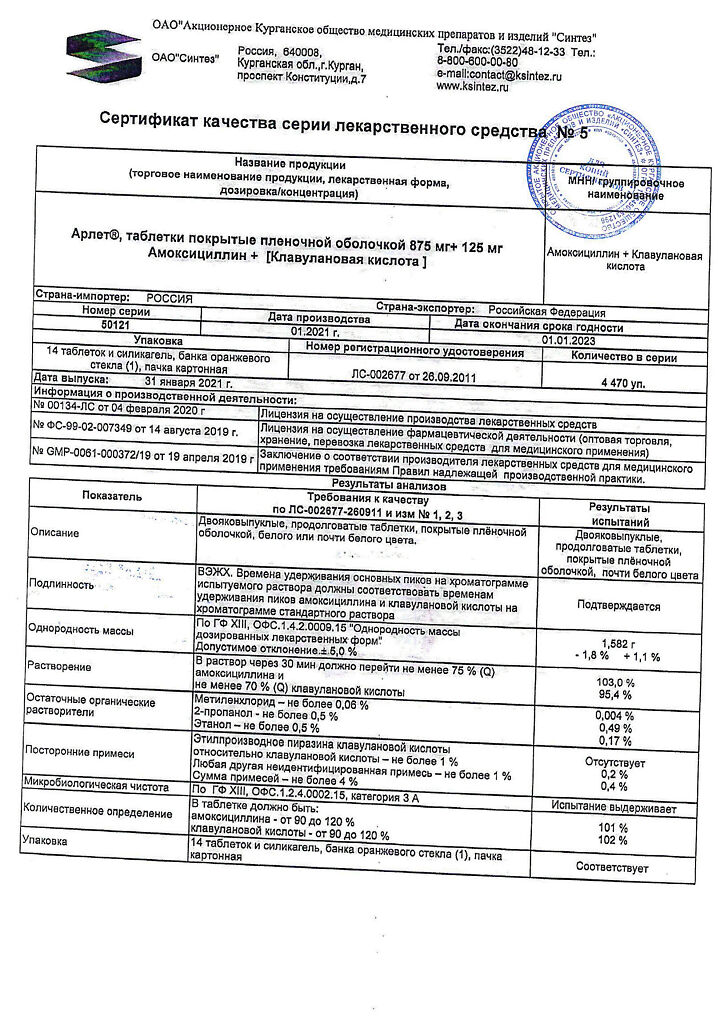
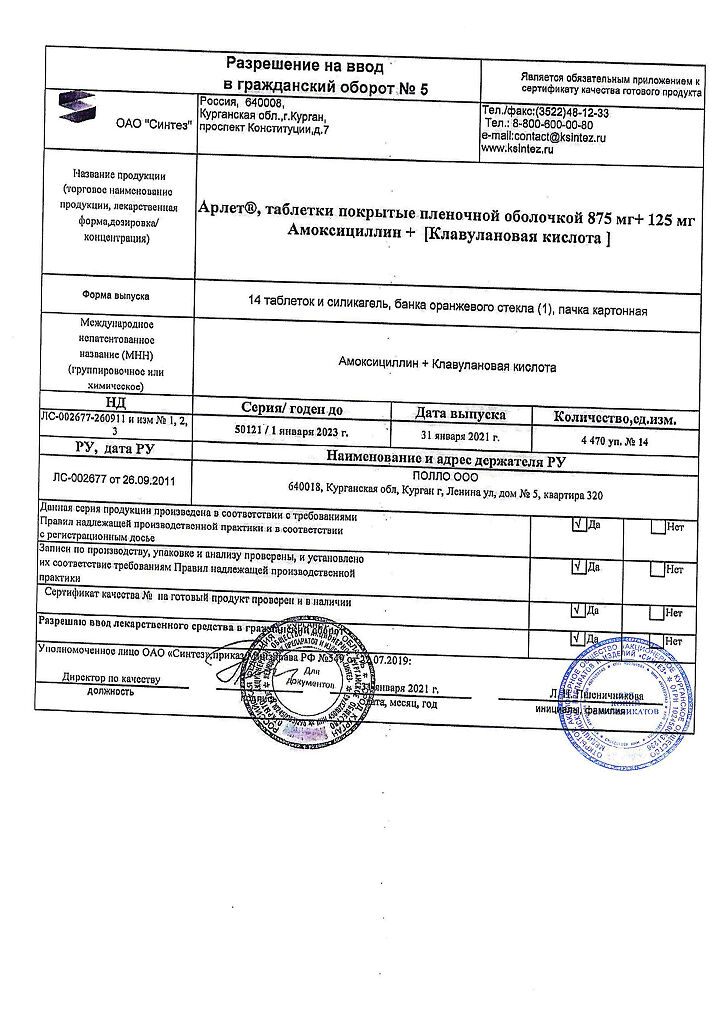
Arlet, 875 mg+125 mg 14 pcs
€1.00
Out of stock
(E-mail when Stock is available)
Description
Pharmacotherapeutic group
Penicillin semisynthetic antibiotic + beta-lactamase inhibitor
ATX code: J01CR02
Pharmacodynamics:
A broad spectrum antibiotic from the group of penicillin inhibitor-resistant β-lactamase enzymes produced by many pathogenic microorganisms to protect (resist) the action of β-lactam antibiotics (penicillins cephalosporins carbapenems). Bacterial β-lactamases destroy (hydrolyze) the antibiotic into inactive fragments (substances). Bacteria that produce β-lactamases are resistant (resistant) to penicillins and cephalosporins.
The drug Arlet® contains two active substances: amoxicillin (semi-synthetic penicillin with a broad spectrum of antibacterial activity) and clavulanic acid (irreversible inhibitor of β-lactamases).
Amoxicillin is a broad spectrum semi-synthetic antibiotic active against many Gram-positive and Gram-negative microorganisms. Amoxicillin is degraded by β-lactamases; therefore the spectrum of its antibacterial activity does not include microorganisms producing β-lactamases.
Clavulanic acid is a β-lactam compound with the ability to inactivate a wide range of β-lactamases by forming a stable inactivated complex with them, which prevents enzymatic destruction of amoxicillin.
Clavulanic acid is similar in structure to β-lactam antibiotics but has almost no antibacterial activity of its own. Clavulanic acid inhibits β-lactamases of types II III IV and V (according to the Richmond-Sykes classification) but is inactive against β-lactamases of type I produced by Enterobacter spp. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Serratia spp. Acinetobacter spp.
The presence of clavulanic acid in the drug protects amoxicillin from destruction by β-lactamases and expands the spectrum of its antibacterial activity to include microorganisms usually resistant (resistant) to it and to other penicillins and cephalosporins.
The drug has a wide spectrum of bactericidal antibacterial activity. It is active against the following microorganisms:
– Gram-positive aerobes: Streptococcus pneumoniae Streptococcus pyogenes Streptococcus viridans Streptococcus agalactiae. Streptococcus bovis; Staphylococcus aureus (except methicillin-resistant strains) Staphylococcus epidermidis (except methicillin-resistant strains) Staphylococcus saprophyticus and other coagulase-negative staphylococci Ente- roccocus spp. (including Enterococcus faecalis) Bacillis anthracis Corynebacterium spp. Listeria monocytogenes Nocardia asteroides;
– Gram-negative aerobes: Escherichia coli Haemophilus influenzae Klebsiella spp. Moraxella catarrhalis Bordetella petrussis Brucella spp. Campylobacter jejuni Eikenella corro- dens Enterobacter spp. Gardnerella vaginalis Haemophilus ducreyi Neisseria gonorrhoeae Neisseria meningitidis Pasteurella multocida Proteus spp. Salmonella spp. Shigella spp. Vibrio cholerae Yersinia enterocolitica;
– Gram-positive and gram-negative anaerobes: Actinomyces israelii Bacteroides spp. (including Bacteroides fragihs) Clostridium spp. (except Clostridium difficile) Fusobacterium spp. Peptococcus spp. Peptostreptococcus spp. Prevotella spp.;
– other microorganisms: Borrelia burgdorferi Chlamydia spp. Helicobacter pylori Leptospira icterohaemorrhagiae Treponema pallidum.
Pharmacokinetics:
The main pharmacokinetic parameters of amoxicillin and clavulanic acid are similar. In combination, amoxicillin and clavulanic acid do not affect the pharmacokinetics of each other.
The two components are quickly and completely absorbed after oral intake Food intake has little effect on the degree of absorption; however, clavulanic acid is better absorbed when a tablet of the drug is taken at the beginning of a meal.
The maximum plasma concentrations are reached about 1 hour after ingestion. Values of maximum concentration for amoxicillin (depending on the dose) are 3-12 mcg/ml for clavulanic acid – about 2 mcg/ml.
Both components are characterized by a large volume of distribution. Therapeutic concentrations of both active substances are determined in various organs, tissues and body fluids: in lungs sputum abdominal organs pelvic organs (uterus ovaries prostate) in the middle ear in the skin liver palatine tonsils sinuses sinuses gall bladder; in fatty bone and muscle tissues; in pleural synovial and peritoneal fluid; in bile urine saliva bronchial secretion in purulent discharge in interstitial fluid.
Amoxicillin and clavulanic acid do not penetrate the blood-brain barrier in non-inflamed cerebral membranes.
The binding to plasma proteins is moderate: 25% for clavulanic acid and 18% for amoxicillin.
Amoxicillin and clavulanic acid penetrate the placental barrier (no adverse effect on the fetus was found) and in trace concentrations are excreted with the breast milk.
Amoxicillin is partially metabolized in the liver (10% of the administered dose) to inactive metabolites clavulanic acid is extensively metabolized in the liver (50-70% of the administered dose).
Amoxicillin is excreted from the body mainly by the kidneys through tubular secretion and glomerular filtration (52±15% of the dose in unchanged form within 7 hours) and a small amount – in the bile. About 10-25% of the initial dose of amoxicillin is excreted by the kidneys as inactive penicillic acid. Clavulanic acid is excreted by the kidneys through glomerular filtration (40-65%) partially as metabolites and by the intestine.
The half-life (T1/2) of amoxicillin and clavulanic acid is 1-15 hours. In patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance 10-30 ml/min) the half-life increases to 75 hours for amoxicillin and 45 hours for clavulanic acid. In anuria, the T1/2 of both active substances varies between 10 and 15 hours.
The two components are eliminated by hemodialysis and minor amounts by peritoneal dialysis.
Indications
Indications
Infections caused by sensitive strains of microorganisms:
– infections of the upper respiratory tract and ENT organs (acute and chronic sinusitis, acute and chronic middle otitis, tonsillitis, pharyngitis);
– lower respiratory tract infections (acute bronchitis with bacterial superinfection, chronic bronchitis, pneumonia);
– urinary tract infections;
– infections in gynecology;
– skin and soft tissue infections;
– bone and connective tissue infections;
– biliary tract infections (cholecystitis, cholangitis);
– odontogenic infections.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Composition
Composition
1 tablet contains
amoxicillin trihydrate 825 mg,
clavulanic acid 125 mg;
excipients:
polyvinylpyrrolidone (povidone),
talc (magnesium disilicate),
Starch 1500,
calcium stearate (calcium stearate),
aerosil (colloidal silicon dioxide),
microcrystalline cellulose.
coating composition:
Hypromellose (oxypropyl methylcellulose), propylene glycol, titanium dioxide, polyethylene oxide 4000 (macrogol 4000).
How to take, the dosage
How to take, the dosage
Arlette is taken orally.
Adults and children over 12 years of age (or with body weight of >40 kg) in mild or moderate course of infection take 1 tablet of Arlet 500/125 mg every 12 hours, in case of severe course of infection and respiratory tract infections – 1 tablet 500/125 mg every 8 hours.
Interaction
Interaction
Simultaneous use with methotrexate increases the toxicity of methotrexate. Administration together with allopurinol increases the frequency of exanthema. Antacids, glucosamine, laxatives, aminoglycosides – slow down and reduce absorption; ascorbic acid increases absorption. Bactericidal antibiotics (including aminoglycosides, cephalosporins, cycloserine, vancomycin, rifampicin) have a synergistic effect; bacteriostatic drugs (macrolides, chloramphenicol, lincosamides, tetracyclines, sulfonamides) – antagonistic.
It increases the effectiveness of indirect anticoagulants (by inhibiting intestinal microflora, reduces the synthesis of vitamin K and prothrombin index). When concomitant use of anticoagulants, it is necessary to monitor blood clotting indices.
Reduces the effectiveness of oral contraceptives, drugs, in the metabolism of which para-aminobenzoic acid is formed, ethinyl estradiol – the risk of bleeding “breakthrough”. Diuretics, allopurinol, phenylbutazone, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and other drugs that block tubular secretion increase the concentration of amoxicillin (clavulanic acid is eliminated mainly by glomerular filtration).
Special Instructions
Special Instructions
During the course of treatment it is necessary to monitor the hematopoietic, hepatic and renal function.
In patients with severe renal dysfunction an adequate dose adjustment or increased dosing intervals are required.
In order to reduce the risk of gastrointestinal side effects, the drug should be taken with meals.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity (including to cephalosporins and other beta-lactam antibiotics), infectious mononucleosis (including the appearance of a rash), children under 3 years of age (for this formulation).
With caution – pregnancy, lactation, severe hepatic insufficiency, gastrointestinal diseases (including colitis in anamnesis associated with the use of penicillins), chronic renal failure.
Side effects
Side effects
Digestive system: loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea; rarely – liver function disorders, increased alanine aminotransferase (ALT) or asparagine aminotransferase (ACT) activity; in single cases – cholestatic jaundice, hepatitis, pseudomembranous colitis.
Allergic reactions: itching, urticaria, erythematous rash; rarely – erythema multiforme, angioedema, anaphylactic shock; in single cases – exfoliative dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome.
Hematopoietic system: reversible increase of prothrombin time, leukopenia, reversible agranulocytosis and hemolytic anemia.
Central nervous system: dizziness, headache, reversible hyperactivity and seizures.
Renal and urinary tract: interstitial nephritis, crystalluria.
Others: candidiasis and other types of superinfections.
Overdose
Overdose
In most cases the symptoms of overdose include gastrointestinal disorders (abdominal pain, diarrhea, vomiting), anxiety, insomnia, dizziness are also possible, in single cases – seizures.
In case of overdose the patient should be under medical supervision; treatment is symptomatic.
In case of recent ingestion (less than 4 hours) it is necessary to conduct gastric lavage and prescribe activated charcoal to reduce absorption. Amoxicillin/clavulanate potassium is removed by hemodialysis.
Pregnancy use
Pregnancy use
Arlette may be administered – during pregnancy only in cases when the estimated benefit to the mother exceeds the potential risk to the fetus.
Amoxicillin and clavulanic acid penetrate into breast milk in small amounts, therefore if it is necessary to use the drug during lactation the issue of stopping breastfeeding should be considered.
Similarities
Similarities
Additional information
| Shelf life | 2 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | In a dry, light-protected place at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C |
| Manufacturer | Sintez OAO, Russia |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Sintez OAO |
Related products
Buy Arlet, 875 mg+125 mg 14 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.