No products in the cart.
Anti-Flu Kids, 5 pcs.
€8.00 €7.18
Out of stock
(E-mail when Stock is available)
Description
Pharmacotherapeutic group
The remedy for acute respiratory infections and “cold” symptoms (analgesic non-narcotic + H1-histamine receptor blocker + vitamin).
ATC code: N02BE51
Pharmacological properties
The combined medicine with vitamin C and raspberry flavor. Paracetamol (acetami-nophen) has analgesic and antipyretic effect.
Ascorbic acid (vitamin C) increases resistance to infections and improves the tolerance of paracetamol.
Chlorpheniramine maleate has anti-allergic effect, eliminates runny nose, lacrimation, itching in the eyes and nose. Quickly relieves fever, headache and 2 muscle pain, sore throat, runny nose.
Indications
Indications
Symptomatic treatment of ARVI, including influenza and “colds” in children from 2 to 12 years of age, accompanied by high fever, chills, body aches, headache and muscle pain, sore throat, runny nose, nasal congestion, watery eyes, sneezing.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacotherapeutic group
Acute respiratory infections and “cold” symptoms are eliminated (non-narcotic analgesic + H1-histamine receptor blocker + vitamin).
ATX code: N02BE51
Pharmacological properties
Combined preparation with vitamin C and raspberry flavor. Paracetamol (acetaminophen) has an analgesic and antipyretic effect.
Ascorbic acid (vitamin C) increases the body’s resistance to infections and improves the tolerance of paracetamol.
Chlorpheniramine maleate has an antiallergic effect, eliminates runny nose, lacrimation, itching in the eyes and nose. Quickly relieves fever, headache and muscle pain, sore throat, runny nose.
Special instructions
Special instructions
Given the drug’s ability to cause drowsiness, children should be freed from activities that require increased concentration for 4 hours after taking the drug.
Contains natural sugar. Each sachet contains 1 XE.
Very rare cases of serious skin reactions have been reported. If your skin turns red, rashes, blisters or peels, you should stop using paracetamol and consult a doctor immediately.
Paracetamol and ascorbic acid can distort laboratory test results (quantitative determination of glucose and uric acid in plasma, bilirubin, liver transaminase activity, LDH).
For hyperthermia lasting more than 3 days and pain for more than 5 days, a doctor’s consultation is required.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
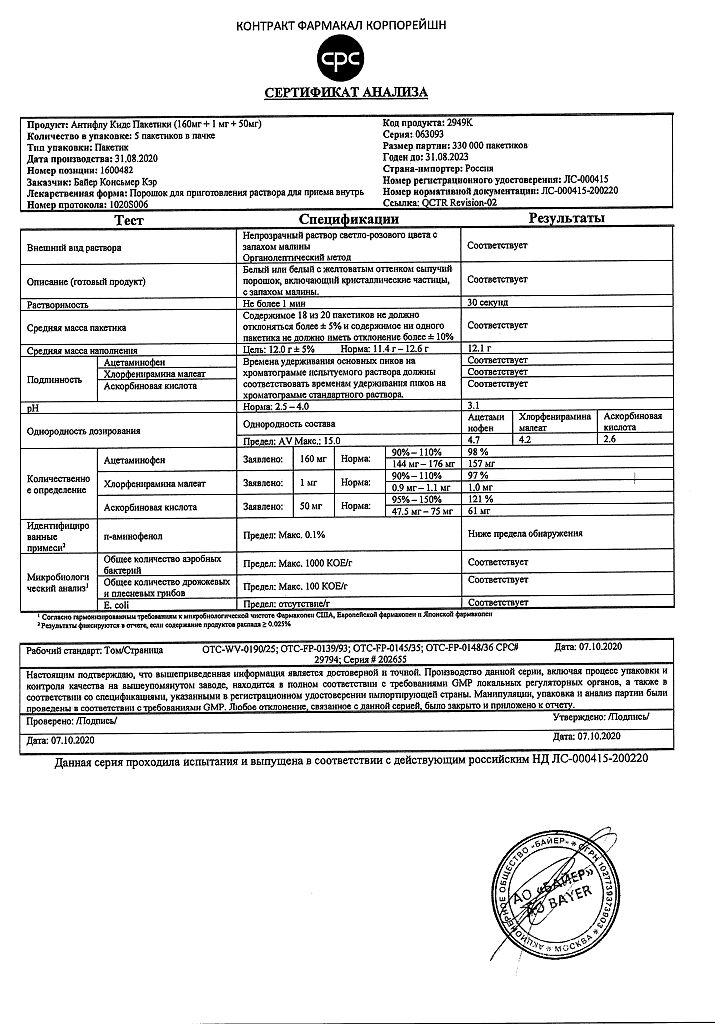
Paracetamol, Chlorphenamine, [Ascorbic Acid]
Composition
Composition
Powder for the preparation of solution for oral administration.
For one sachet:
Active ingredients:
paracetamol (acetaminophen) 160 mg,
ascorbic acid 50 mg,
chlorpheniramine maleate 1 mg.
Excipients:
citric acid 50 mg,
dye Red charming 0.05 mg,
raspberry flavor 100 mg,
silicon dioxide (syloid) 4 mg,
silicon dioxide 20 mg,
sodium citrate dihydrate 2 mg,
corn starch 1 mg,
powdered sugar 2794.95 mg,
sucrose 8800 mg,
titanium dioxide 1 mg,
calcium phosphate 1 mg.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
Not recommended for use during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to individual components of the drug, severe liver and kidney dysfunction, angle-closure glaucoma, prostate hypertrophy, sucrase/isomaltase deficiency, fructose intolerance, glucose-galactose malabsorption, children under 2 years of age.
Use with caution for: arterial hypertension, severe cardiovascular diseases, diabetes mellitus, bronchial asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, thyrotoxicosis, pheochromocytoma, difficulty urinating with prostate adenoma, blood diseases, congenital hyperbilirubinemia (Gilbert, Dubin-Johnson and Rother syndromes), progressive malignant diseases, viral hepatitis, hyperoxalaturia, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency.
Side Effects
Side Effects
Allergic reactions: skin rash, itching, urticaria, toxic epidermal necrolysis (Lyell’s syndrome), polymorphobullous erythema (Stevens-Johnson syndrome), acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis, angioedema (Quincke’s edema), anaphylactic shock.
From the central nervous system: dizziness, sleep disturbance (drowsiness), headache, excitability, decreased speed of psychomotor reactions, feeling of fatigue.
From the hematopoietic system: anemia, thrombocytopenia, thrombocytopenic purpura, leukopenia, pancytopenia, agranulocytosis, hemolytic anemia, methemoglobinemia.
From the digestive system: nausea, vomiting, stomach discomfort, abdominal pain, diarrhea.
Disorders of the liver and biliary tract: liver damage (increased activity of liver enzymes), hepatitis, as well as dose-dependent liver failure, liver necrosis. Long-term unjustified use can lead to liver fibrosis and liver cirrhosis.
From the urinary system: urinary retention, with long-term use of high doses nephrotoxic effect.
Respiratory disorders: bronchospasm or exacerbation of bronchial asthma, including in patients sensitive to acetylsalicylic acid or other NSAIDs.
Other: mydriasis, accommodation paresis, increased intraocular pressure.
Interaction
Interaction
It is not recommended to take simultaneously with sleeping pills, sedatives and drugs containing alcohol.
Increases the concentration of benzylpenicillin and tetracyclines in the blood. Improves the absorption of iron preparations in the intestines (converts ferric iron to divalent iron); may increase iron excretion when used concomitantly with deferoxamine. Increases the risk of developing crystalluria during treatment with salicylates and short-acting sulfonamides, slows down the excretion of acids by the kidneys, increases the excretion of drugs that have an alkaline reaction (including alkaloids), and reduces the concentration of oral contraceptives in the blood. Increases overall ethanol clearance. When used simultaneously, it reduces the chronotropic effect of isoprenaline. Reduces the therapeutic effect of antipsychotic drugs (neuroleptics) – phenothiazine derivatives, tubular resorption of amphetamine and tricyclic antidepressants. Reduces the effectiveness of uricosuric drugs.
It can either increase or decrease the effect of anticoagulant drugs. Paracetamol (or its metabolites) interacts with enzymes involved in vitamin K-dependent clotting factor synthesis. Interactions between paracetamol and warfarin or coumarin derivatives may result in an increase in the international normalized ratio (INR) and an increased risk of bleeding. Patients taking oral anticoagulants should not take paracetamol for long periods of time without medical supervision.
Ethanol enhances the sedative effect of chlorphenamine. Antidepressants, antiparkinsonian and phenothiazine antipsychotic drugs increase the risk of side effects (urinary retention, dry mouth, constipation). Glucocorticosteroids increase the risk of developing glaucoma.
Inducers of microsomal oxidation in the liver (phenytoin, ethanol, barbiturates, rifampicin, phenylbutazone, tricyclic antidepressants) increase the production of hydroxylated active metabolites of paracetamol, which makes it possible to develop severe hepatotoxic reactions even with a small overdose. Inhibitors of microsomal oxidation (including cimetidine) reduce the risk of hepatotoxic action of paracetamol. Diflunisal increases the plasma concentration of paracetamol by 50% and increases hepatotoxicity. Ethanol reduces the concentration of ascorbic acid in the body and also contributes to the development of acute pancreatitis. The use of barbiturates reduces the effectiveness of paracetamol and increases the excretion of ascorbic acid in the urine. Strengthens the effect of sleeping pills.
When used simultaneously with chloramphenicol, it is possible to increase its half-life from blood plasma and increase the toxic effect.
Medicines that cause delayed gastric emptying, such as propantheline, may result in delayed absorption of paracetamol and thus delay the onset of action.
Medicines that cause gastric emptying faster, such as metoclopramide, may cause paracetamol to be absorbed more quickly and thus hasten its onset of action.
Antagonists of tropisetron and granisetron, 5-hydroxytryptamine type 3, can completely inhibit the analgesic effect of paracetamol through a pharmacodynamic interaction.
Paracetamol should not be taken together with zidovudine unless advised by a physician due to the increased tendency for the white blood cell count to decrease (neutropenia).
Continuous combination therapy with more than one analgesic should be avoided; due to possible additive side effects.
Overdose
Overdose
In case of overdose, you should immediately seek medical help.
Paracetamol
Symptoms: diarrhea, loss of appetite, nausea and vomiting, abdominal discomfort and/or abdominal pain, increased sweating. The clinical picture of an acute overdose of paracetamol develops within 6-14 hours after taking paracetamol. Symptoms of chronic overdose appear 2-4 days after increasing the dose of the drug. In cases of severe poisoning, severe liver failure may occur, including hepatic encephalopathy, coma and death. Hypokalemia and metabolic acidosis (including lactic acidosis) can also develop in conditions of acute and/or chronic overdose. Frequent clinical manifestations after 3-5 days are jaundice, fever, hepatic breath, hemorrhagic diathesis, hypoglycemia, and liver failure. Acute renal failure with acute tubular necrosis, which is diagnosed by severe pain in the lumbar region, hematuria and proteinuria, can develop without severe impairment of liver function.
Treatment: gastric lavage, activated carbon in the first 6 hours, administration of SH-group donors and precursors for the synthesis of glutathione – methionine 8-9 hours after an overdose and N-acetylcysteine after 12 hours.
Chlorpheniramine
Symptoms: dizziness, agitation, sleep disturbances, depression, seizures and coma.
Treatment: symptomatic.
Ascorbic acid
High doses of ascorbic acid (more than 3000 mg) can cause temporary osmotic diarrhea and gastrointestinal disturbances, such as nausea and stomach discomfort.
Treatment: symptomatic, forced diuresis.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
At 15–30 °C
Shelf life
Shelf life
3 years
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Contract Pharmacal Corporation, USA
Additional information
| Shelf life | 3 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | At 15-30 °C |
| Manufacturer | Bayer Bitterfeld GmbH, Germany |
| Medication form | Powder for preparation of solution for oral administration |
| Brand | Bayer Bitterfeld GmbH |
Related products
Buy Anti-Flu Kids, 5 pcs. with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.