No products in the cart.
Amphotericin B, lyophilizate 50 mg 10 ml
€1.00
Out of stock
(E-mail when Stock is available)
Description
Pharmacological action – antifungal.
Bonds with sterols (ergosterols) of the cell membrane of sensitive fungi. As a result membrane permeability is violated and intracellular components get into the extracellular space.
Pharmacodynamics
It has fungicidal or fungistatic action depending on the concentration in the biological fluids and the sensitivity of the pathogen. It is active against many pathogenic fungi including Candida spp., Histoplasma capsulatum, Cryptococcus neoformans, Aspergillus spp. or Leishmania.
Pharmacokinetics
In intravenous administration it is distributed in most organs and tissues of the body, it is not determined in the cerebrospinal fluid. It penetrates through the placenta. Binding with plasma proteins is 90%. Excreted by kidneys, very slowly, 2-5% in the active form. Can be detected in the urine for 7 weeks after withdrawal.
When used topically, it is practically not absorbed.
Indications
Indications
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Composition
Composition
1 vial contains:
The active ingredient:
Amphotericin B 50,000 IU;
sodium phosphate monosubstituted,
deoxycholic acid
How to take, the dosage
How to take, the dosage
Intravenously by drip for 2-4 h, the recommended concentration is 0.1 mg/ml. A test dose of 1 mg (base) is diluted in 20 ml of 5% dextrose solution and administered intravenously for at least 20-30 minutes under control of blood pressure, pulse, body temperature every 30 minutes for 2-4 hours.
When well tolerated, the recommended daily dose is 0.25-0.3 mg/kg, depending on the severity of the disease.
In case of hypersensitivity to the drug, cardiovascular system disorders, renal function insufficiency, treatment starts with a low dose of 5-10 mg and gradually increases by 5-10 mg/day until the recommended daily dose is 0.5-0.7 mg/kg.
The selection of therapeutic doses is carried out individually depending on the type and severity of the infection. When using the drug every other day the dose should not exceed 1.5 mg/kg (in order to avoid the development of cardiopulmonary insufficiency). The maximum daily dose is 1.5 mg/kg.
Sporotrichosis: course dose of 2.5 g, duration of therapy – 9 months.
Aspergillosis: course dose – 3.6 g, duration of treatment – 11 months.
Rhinocerebral phycomycosis: course dose – 3-4 g.
If therapy is interrupted for more than 7 days, it should be resumed from the lowest dose (0.25 mg/kg), gradually increasing to the desired level.
In children: intravenously, initially 0.25 mg/kg (base) daily in 5% dextrose solution for 6 h; with tolerance, the dose is gradually increased (usually by 0.125 to 0.25 mg/kg each day or every other day) to a maximum dose of 1 mg/kg or 30 mg per 1 m2. In children, it is administered in the lowest effective doses.
The solution for intravenous administration is prepared using a solution with an initial concentration of 5 mg/ml. For this purpose, using sterile syringe (needle not less than #20), 10 ml of sterile water for injection without bacteriostatic additives is put directly into the vial with the drug. The contents of the bottle is shaken until a clear colloidal solution is formed. To obtain solution with 0.1 mg/ml concentration it is diluted with 5% dextrose solution with pH not lower than 4.2 in 1:50 ratio. The pH of the dextrose solution is usually greater than 4.2, otherwise 1 -2 ml of buffer should be added before dilution.
The following buffer solution is recommended: sodium hydrophosphate (anhydrous) -1.59 g, sodium dihydrophosphate (anhydrous) 0.96 g, water for injection up to 100 ml.
Before adding to dextrose solution the buffer solution is sterilized by filtering through a bacterial ceramic or membrane filter, or by autoclaving for 30 minutes at 1 atm and 121 °С.
Interaction
Interaction
Pharmaceutically incompatible with heparin, 0.9% sodium chloride solution and other solutions containing electrolytes.
The presence of bacteriostatic additives (including benzyl alcohol) may cause precipitation of the drug.
Synergism is with nitrofurans.
Increases the effect and toxicity of anticoagulants, theophylline and sulfonylurea drugs, flucytosine (prolongs the elimination half-life); reduces the effect of ethinylestradiol – risk of breakthrough bleeding.
Hepatic microsomal enzyme inhibitors (including cimetidine, non-narcotic analgesics, antidepressants) slow the rate of metabolism, increase serum concentrations (increased toxicity).
Hepatic microsomal enzyme inducers (including phenytoin, rifampicin, barbiturates, carbamazepine) accelerate metabolism in the liver (reduced effect).
It enhances the toxic effect of cardiac glycosides (especially against the background of initial potassium deficiency in the body) and curare-like myorelaxants.
Glucocorticosteroids, carbohydrate inhibitors, adrenocorticotropic hormones increase the risk of hypokalemia.
Prevent concomitant administration with nephrotoxic drugs (aminoglycosides, cyclosporine, pentamidine, etc.) – the risk of renal dysfunction increases.
The anticancer drugs, radiation therapy and medications that inhibit medullar hematopoiesis increase the risk of anemia and other hematologic disorders.
The anticancer drugs increase nephrotoxicity, bronchospasm, and decreased blood pressure.
Glucocorticosteroids and corticotropin increase hypokalemia, which may lead to arrhythmias. If simultaneous administration of these drugs is necessary, blood electrolyte composition and ECG should be monitored.
Amphotericin B may increase the toxicity of cardiac glycosides (due to hypokalemia).
Concomitant administration with imidazoles (including fluconazole, itraconazole, ketoconazole, miconazole, clotrimazole) may lead to the development of resistance to amphotericin B. Combined treatment with imidazoles with amphotericin B should be prescribed with caution.
The simultaneous use of nephrotoxic drugs (aminoglycosides, cyclosporine, pentamidine and others) should be avoided – there is an increased risk of renal dysfunction.
Longens the myorelaxant effect of depolarizing myorelaxants.
The leukocyte mass should be administered at a significant interval after administration of amphotericin B (risk of respiratory system complications).
Special Instructions
Special Instructions
Amphotericin B should be used primarily for the treatment of advanced and life-threatening fungal infections. It should not be used to treat non-invasive (superficial) mycoses such as oral, vaginal or esophageal candidiasis in patients with normal blood neutrophils.
The likelihood of toxic effects increases with long-term treatment.
At the time of treatment check weighing of patients, general blood and urine tests, control of potassium concentration in blood, determine the functional state of kidneys, liver, ECG. Patients who are taking potassium supplements should regularly monitor the concentration of potassium and magnesium in the plasma.
Injection of the drug in patients on hemodialysis is possible only after completion of dialysis procedure.
All procedures with the solution should be performed with strict adherence to asepsis because the product itself and all dilution solutions do not contain preservatives or bacteriostatic agents.
If intravenous systems previously installed for other purposes are used, the system should be flushed with 5% dextrose solution for injection.
In case of anemia, the drug should be discontinued.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to amphotericin B and other components of the drug, marked liver and kidney function abnormalities, diseases of the hematopoietic system, diabetes mellitus.
For the ointment – hypersensitivity to amphotericin B.
Side effects
Side effects
The digestive system: often – decreased appetite, dyspepsia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, gastralgia, hepatotoxicity (increased activity of “liver” enzymes, hyperbilirubinemia); rarely – acute liver failure, hepatitis, jaundice, hemorrhagic gastroenteritis, melena.
Nervous system disorders: frequently – headache, infrequently – convulsions, transient vertigo, peripheral neuropathy, encephalopathy.
Sense organs: infrequent – visual impairment, diplopia; hearing loss, tinnitus.
Hematopoietic organs: frequently – normochromic normocytic anemia; infrequent – agranulocytosis, blood clotting disorders, leukopenia, hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, eosinophilia, leukocytosis.
Cardiovascular system disorders: often – decreased arterial blood pressure; infrequent – arrhythmia, including ventricular fibrillation, ECG changes, increased arterial pressure, shock, cardiac arrest, heart failure.
Respiratory system disorders: frequently – tachypnoea; infrequently – dyspnea, allergic pneumonitis, pulmonary edema.
Recreational system disorders: common – renal dysfunction, including azotemia, hypokalemia, hypostenuria, renal tubular acidosis, nephrocalcinosis; infrequent – acute renal failure, oliguria, anuria, nephrogenic non-sugar diabetes. Prior administration of 0.9% sodium chloride solution reduces the risk of nephrotoxicity; sodium bicarbonate administration reduces the risk of renal tubular necrosis.
Allergic reactions: frequently – anaphylactoid reactions, bronchospasm, sneezing; infrequently – rash, especially maculopapular, itching, exfoliative dermatitis, toxic epidermal necrolysis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome.
Local reactions: thrombophlebitis at the injection site, chemical burns.
Others: often fever, weight loss, myalgia, arthralgia, general weakness.
Laboratory measures: hypokalemia, hyperkalemia, hypomagnesemia, hypocalcemia, hypercreatininemia.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: cardiac and respiratory arrest.
Treatment: symptomatic. It is necessary to monitor cardiac and respiratory activity, liver and kidney function, peripheral blood count and electrolyte content and prescribe supportive therapy. It is not eliminated by hemodialysis.
The patient must be stabilized before resuming treatment.
Pregnancy use
Pregnancy use
Additional information
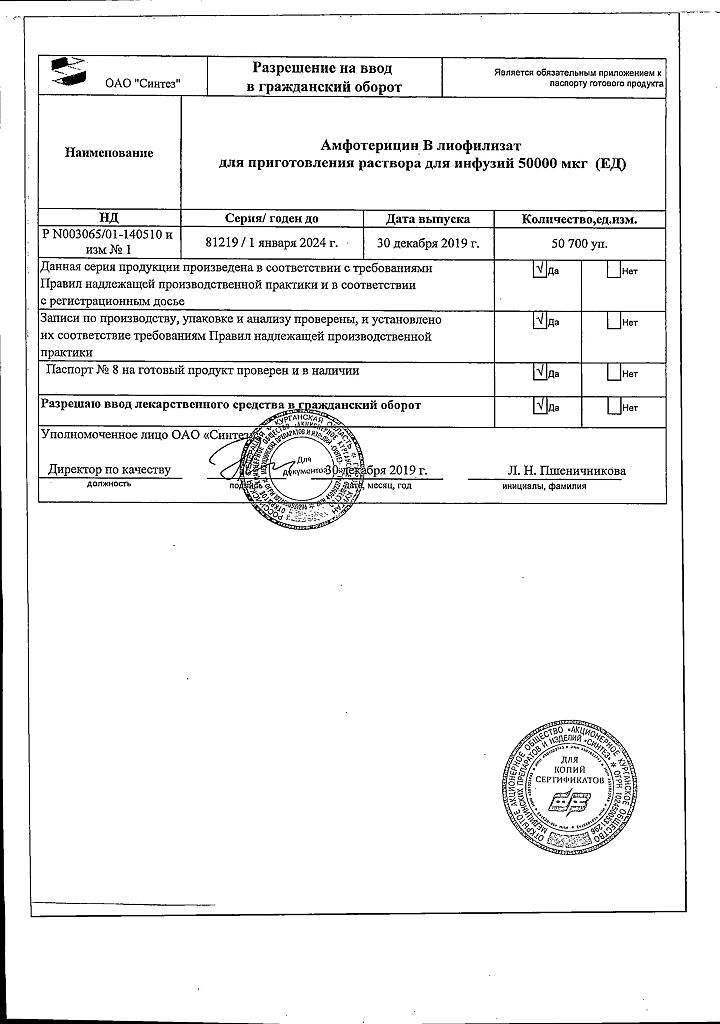
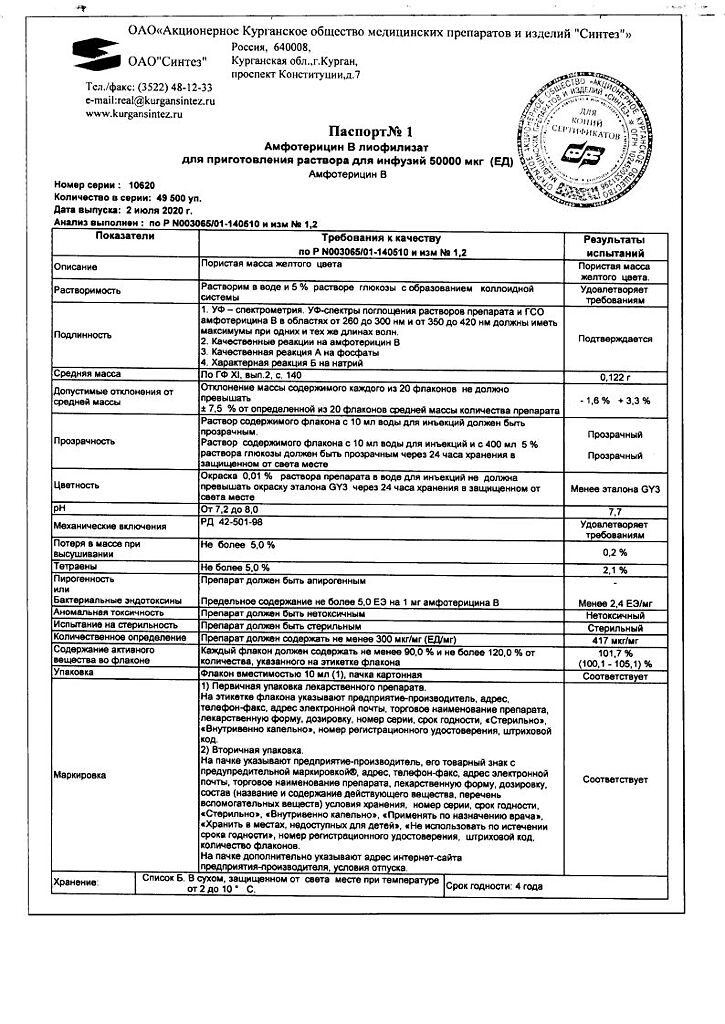
| Shelf life | 4 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | List B. Store in a dry, light-protected place at the temperature from 2 to 10°C. Keep out of reach of children. |
| Manufacturer | Sintez OAO, Russia |
| Medication form | lyophilizate |
| Brand | Sintez OAO |
Related products
Buy Amphotericin B, lyophilizate 50 mg 10 ml with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.