No products in the cart.
Amlodipine-Teva, tablets 5 mg 30 pcs
€1.00
Out of stock
(E-mail when Stock is available)
Description
Dihydropyridine derivative is a second generation BMCC with antianginal and hypotensive effects. Binding to S6 segment of III and IV domains of L-type calcium channel alpha1-subunit, it blocks calcium channels, reduces transmembrane Ca2+ transfer into cell (more in vascular smooth muscle cells than in cardiomyocytes). It has hypotensive and antianginal effect.
The mechanism of hypotensive action of amlodipine is due to a direct relaxing effect on vascular smooth muscle.
Myocardial ischemia is decreased due to dilation of coronary and peripheral arteries and arterioles in unchanged and in ischemic areas of myocardium, decrease of RPO, decrease of myocardial oxygen demand.
Lengthens the flow of oxygen to the myocardium in patients with vasospastic angina (Prinzmetal’s angina); prevents the development of coronary spasm caused by smoking. In patients with angina a single daily dose increases exercise time, delays the development of another angina attack and S-T segment depression (by 1 mm) on exercise, reduces the frequency of angina attacks and nitroglycerin consumption.
It has a long-term dose-dependent hypotensive effect. The hypotensive effect is due to the direct vasodilating effect on the vascular smooth muscles. In arterial hypertension a single daily dose gives clinically significant lowering of BP during 24 hours (in “lying” and “standing” positions).
. In patients with CCC diseases (including coronary atherosclerosis with lesion of one vessel and up to stenosis of 3 or more arteries, atherosclerosis of carotid arteries), patients who have undergone MI, percutaneous transluminal angioplasty of coronary arteries or patients with angina pectoris, use of amlodipine prevents carotid intima-media thickening, reduces mortality from MI, stroke, transluminal angioplasty, coronary artery bypass grafting; leads to fewer hospitalizations for unstable angina and progression of CHF; reduces the frequency of interventions to restore coronary blood flow.
The risk of death or complications and lethal outcomes in patients with CHF (class III-IV according to NYHA) during therapy with digoxin, diuretics and ACE inhibitors is not increased. In patients with CHF (III-IV class according to NYHA) of non-ischemic etiology when using amlodipine there is a possibility of pulmonary edema.
It does not cause sharp decrease of BP, decrease of exercise tolerance, LV ejection fraction. It reduces the degree of LV myocardial hypertrophy.
It does not influence myocardial contractility and conduction, does not cause reflex elevation of HR, inhibits platelet aggregation, increases glomerular filtration rate, has weak natriuretic action.
In diabetic nephropathy it does not increase severity of microalbuminuria. It does not have adverse effects on metabolism and plasma lipids.
The time of onset of effect is 2-4 hours; duration – 24 hours.
Indications
Indications
Arterial hypertension (monotherapy or in combination with other hypotensive drugs),
stable angina pectoris and vasospastic angina pectoris (monotherapy or in combination with other antianginal drugs).
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Composition
Composition
1 tablet contains:
The active ingredient:
amlodipine besylate (in terms of amlodipine 10 mg) – 13.888 mg.
Auxiliary substances:
microcrystalline cellulose,
calcium hydrophosphate (anhydrous),
sodium carboxymethyl starch (type A),
magnesium stearate.
How to take, the dosage
How to take, the dosage
Ingestion, once a day. The initial dose for arterial hypertension and angina pectoris is 5 mg/day, which is increased to a maximum of 10 mg/day, if necessary.
Patients with low body weight or short stature or with significant hepatic impairment may require lower doses.
Interaction
Interaction
Microsomal oxidation inhibitors may increase plasma concentrations of amlodipine, increasing the risk of side effects, and microsomal liver enzyme inducers may decrease.
In contrast to other DMARDs no clinically significant interaction with NSAIDs, especially indomethacin, has been noted.
Thiazide and “loop” diuretics, beta-adrenoblockers, verapamil, ACE inhibitors and nitrates increase antianginal or hypotensive effects.
There is no effect on the pharmacokinetic parameters of digoxin and warfarin.
Cimetidine does not affect the pharmacokinetics of amlodipine.
Ca2+ preparations may reduce the effect of BMCCs.
Antiviral agents (ritonavir) increase plasma concentrations of BMCCs, including amlodipine.
Neuroleptics and isoflurane – increase the hypotensive effect of dihydropyridine derivatives.
Special Instructions
Special Instructions
During treatment it is necessary to control body weight and see a dentist (to prevent soreness, bleeding and gum hyperplasia).
Amlodipine has no effect on plasma concentrations of K+, glucose, TG, total cholesterol, LDL, uric acid, creatinine and urea nitrogen.
Abrupt withdrawal of the drug should be avoided because of the risk of worsening the course of angina pectoris.
Amlodipine tablets are not recommended in hypertensive crisis.
Women of childbearing age should use reliable methods of contraception during treatment.
At the time of treatment, caution should be exercised when driving vehicles and engaging in potentially hazardous activities requiring increased concentration and rapid psychomotor reactions.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity (including to other dihydropyridines),
pronounced arterial hypotension (BP less than 90 mm Hg),
pregnancy, lactation.
With caution. Arterial hypotension, aortic stenosis, CHD of non-ischemic etiology (class III-IV according to NYHA),
hepatic insufficiency,
acute myocardial infarction (and during 1 month after), GOCMP, CCSU,
age less than 18 years, elderly.
Side effects
Side effects
Asto: frequent – more than 1%, infrequent – less than 1%, rare – less than 0.1%, very rare – less than 0.01%.
System effects: common – peripheral edema (ankles and feet), palpitation; infrequent – excessive reduction of BP, orthostatic hypotension, vasculitis; rare – development or worsening of CH; very rare – arrhythmia (bradycardia, ventricular tachycardia, atrial fibrillation), myocardial infarction, pain in the chest, migraine.
Nervous system disorders: frequent – headache, dizziness, increased fatigue, somnolence; infrequent – malaise, fainting, asthenia, hypoesthesia, paresthesia, peripheral neuropathy, tremor, insomnia, emotional lability, unusual dreams, nervousness, depression, anxiety; rare – convulsions, apathy, agitation; very rare – ataxia, amnesia.
The digestive system: frequently – nausea, abdominal pain; infrequently – vomiting, altered bowel movements (including constipation, flatulence), dyspepsia, diarrhea, anorexia, dry mouth, thirst; rarely – gingival hyperplasia, increased appetite; very rarely – gastritis, pancreatitis, hyperbilirubinemia, jaundice (usually cholestatic), increased activity of liver transaminases, hepatitis.
Hematopoietic organs: very rarely – thrombocytopenic purpura, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia.
Urogenital system disorders: infrequent – pollakiuria, painful urge to urinate, nycturia, impotence; very rare – dysuria, polyuria.
Musculoskeletal system: infrequent – arthralgia, muscle cramps, myalgia, back pain, arthrosis; rarely – myasthenia.
Respiratory system: infrequent dyspnea and rhinitis; very rare – cough.
Allergic reactions: infrequent – skin itching, rash; very rare – angioedema, erythema multiforme, urticaria.
Others: infrequent – alopecia, tinnitus, gynecomastia, weight gain/decrease, visual disturbance, diplopia, accommodation disturbance, xerophthalmia, conjunctivitis, eye pain, perversion of taste, chills, nasal bleeding, increased sweating; rare – dermatitis;
very rare – cold sticky sweat, parosmia, skin pigmentation disorders, hyperglycemia.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: marked BP decrease with possible development of reflex tachycardia and excessive peripheral vasodilation (risk of severe and persistent arterial hypotension, including development of shock and death).
Treatment: gastric lavage, activated charcoal administration (especially during the first 2 hours after overdose), maintenance of cardiac function, cardiopulmonary function tests, elevated extremities, BCC and diuresis control, symptomatic and supportive therapy, intravenous calcium gluconate and dopamine administration.
Hemodialysis is ineffective.
Pregnancy use
Pregnancy use
Fetal Effects. C (Animal reproduction studies have found adverse effects on the fetus, and adequate and rigorously controlled studies in pregnant women have not been conducted, but the potential benefits associated with the use of the drug in pregnant women may justify its use despite the possible risks).
Similarities
Similarities
Additional information
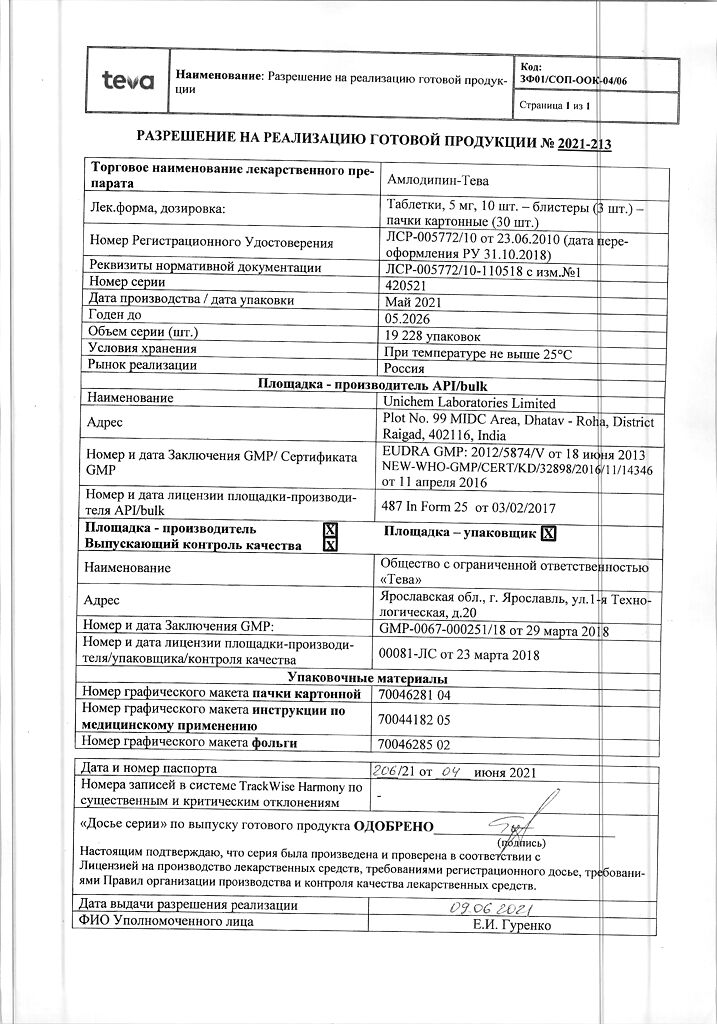
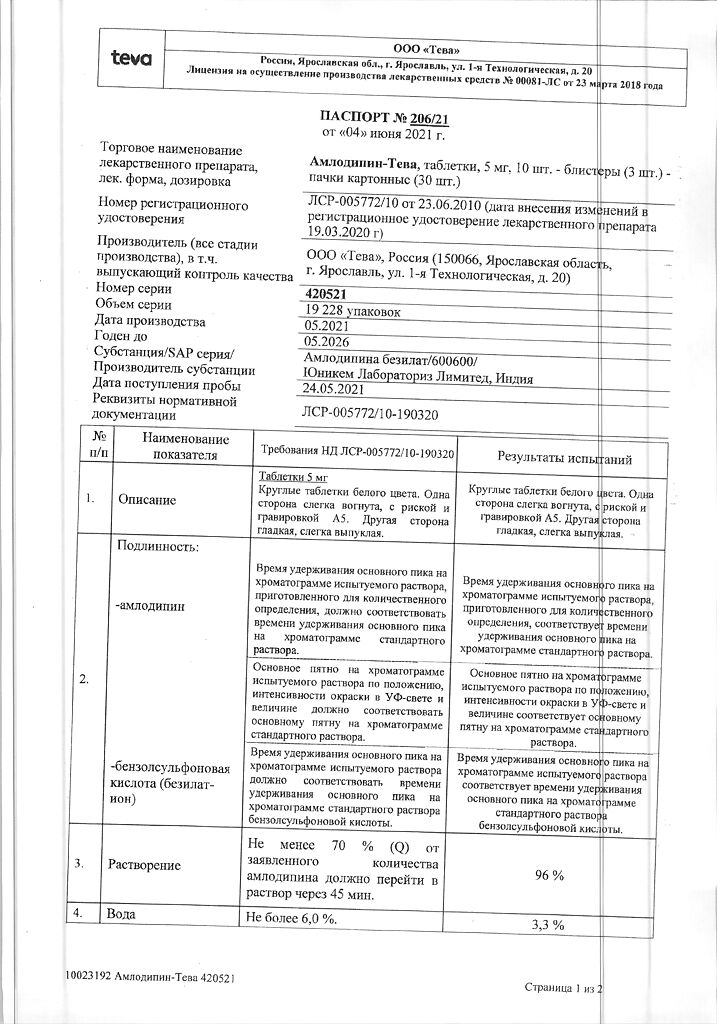
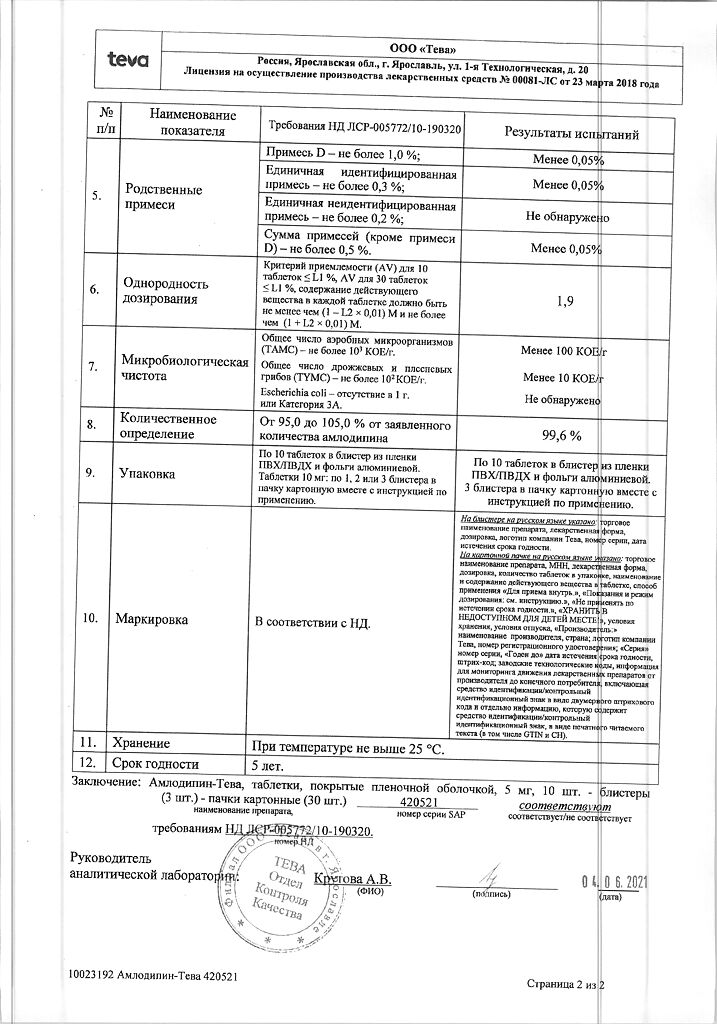
| Shelf life | 5 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | At a temperature not exceeding 25 °C |
| Manufacturer | Teva LLC, Russia |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Teva LLC |
Related products
Buy Amlodipine-Teva, tablets 5 mg 30 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.