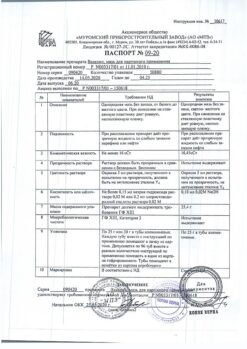
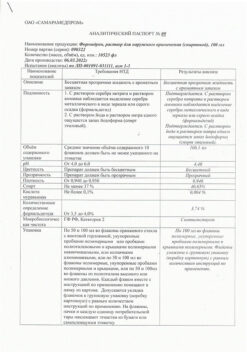
No products in the cart.
Aknecutan, 8 mg capsules 30
€49.92 €41.60
Description
Isotretinoin is the stereoisomer of fully transretinoic acid (tretinoin).
The exact mechanism of action of isotretinoin has not yet been identified, but it has been established that improvement in the clinical picture of severe acne is associated with suppression of sebum activity and a histologically confirmed reduction in its size. Sebum is the main substrate for Propionibacterium acnes growth, so reducing sebum formation suppresses bacterial colonization of the ductus.
Acnecutan suppresses the proliferation of sebocytes and acts on acne by restoring the normal process of cell differentiation and stimulates regeneration processes.
In addition, the anti-inflammatory effect of isotretinoin on the skin has been proven.
Pharmacokinetics
. After oral administration, absorption is variable and the bioavailability of Acnekutan is low and variable – driven by the proportion of dissolved isotretinoin in the drug, and may also increase when the drug is taken with food. In acne patients, the maximum plasma concentrations (Cmax) in equilibrium after isotretinoin 80 mg fasting was 310 ng/mL (range 188-473 ng/mL) and were reached after 2-4 hours. Plasma concentrations of isotretinoin were 1.7 times higher than blood concentrations due to poor isotretinoin penetration into erythrocytes. Binding with plasma proteins (mainly with albumin) is 99.9%.
The equilibrium blood concentrations (Css) of isotretinoin in patients with severe acne who received 40 mg of the drug twice daily ranged from 120 to 200 ng/ml. Concentrations of 4-oxo-isotretinoin (the main metabolite) in these patients were 2.5 times higher than those of isotretinoin.
The concentration of isotretinoin in epidermis is 2 times lower than in serum. It is metabolized with the formation of 3 main biologically active metabolites – 4-oxo-isotretinoin (main), tretinoin (fully transretinoic acid) and 4-oxo-retinoin, as well as less significant metabolites including also glucuronides. Since in vivo isotretinoin and tretinoin are reversibly converted to each other, the metabolism of tretinoin is related to that of isotretinoin. 20-30% of the dose of isotretinoin is metabolized by isomerization. Enterohepatic circulation may play a significant role in the pharmacokinetics of isotretinoin in humans.
In vitro studies have shown that several CYP enzymes are involved in the conversion of isotretinoin to 4-oxo-isotretinoin and tretinoin. None of the isoforms appears to play a dominant role. Isotretinoin and its metabolites have no significant effect on CYP enzyme activity.
The terminal phase elimination half-life for isotretinoin averages 19 hours. The terminal phase elimination half-life for 4-oxo-isotretinoin averages 29 hours.
Isotretinoin is excreted by the kidneys and with the bile in approximately equal amounts. It is referred to natural (physiological) retinoids. Endogenous concentrations of retinoids are restored about 2 weeks after the end of the drug.
Pharmacokinetics in special clinical cases
Because data on the pharmacokinetics of the drug in patients with impaired liver function are limited, isotretinoin is contraindicated in this group of patients. Renal failure of mild to moderate severity does not affect the pharmacokinetics of isotretinoin.
Indications
Indications
Severe forms of acne (nodular-cystic, conglobate, acne with the risk of scarring).
Acne that does not respond to other types of therapy.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Isotretinoin is a stereoisomer of all-trans retinoic acid (tretinoin).
The exact mechanism of action of isotretinoin has not yet been identified, but it has been established that the improvement in the clinical picture of severe forms of acne is associated with suppression of the activity of the sebaceous glands and a histologically confirmed reduction in their size. Sebum is the main substrate for the growth of Propionibacterium acnes, so reducing sebum production inhibits bacterial colonization of the duct.
Acnecutane suppresses the proliferation of sebocytes and acts on acne, restoring the normal process of cell differentiation and stimulating regeneration processes.
In addition, isotretinoin has been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects on the skin.
Pharmacokinetics
After oral administration, absorption is variable, the bioavailability of Acnecutane is low and variable – due to the proportion of dissolved isotretinoin in the drug, and can also increase when taking the drug with food. In patients with acne, maximum plasma concentrations (Cmax) at steady state after taking 80 mg of isotretinoin on an empty stomach were 310 ng/ml (range 188-473 ng/ml) and were achieved after 2-4 hours. The concentration of isotretinoin in plasma is 1.7 times higher than in the blood, due to poor penetration of isotretinoin into red blood cells. Communication with plasma proteins (mainly albumin) – 99.9%.
Steady-state concentrations of isotretinoin in the blood (Css) in patients with severe forms of acne who took 40 mg of the drug 2 times a day ranged from 120 to 200 ng/ml. The concentrations of 4-oxo-isotretinoin (the main metabolite) in these patients were 2.5 times higher than those of isotretinoin.
The concentration of isotretinoin in the epidermis is 2 times lower than in serum. Metabolized to form 3 main biologically active metabolites – 4-oxo-isotretinoin (main), tretinoin (all-transretinoic acid) and 4-oxo-retinoin, as well as less significant metabolites, which also include glucuronides. Because isotretinoin and tretinoin are reversibly converted into each other in vivo, the metabolism of tretinoin is related to the metabolism of isotretinoin. 20-30% of the isotretinoin dose is metabolized by isomerization. Enterohepatic circulation may play a significant role in the pharmacokinetics of isotretinoin in humans.
In vitro studies have shown that several CYP enzymes are involved in the conversion of isotretinoin to 4-oxo-isotretinoin and tretinoin. However, none of the isoforms appears to play a dominant role. Isotretinoin and its metabolites do not have a significant effect on the activity of CYP enzymes.
The terminal phase half-life for isotretinoin averages 19 hours. The terminal phase half-life for 4-oxo-isotretinoin averages 29 hours.
Isotretinoin is excreted by the kidneys and bile in approximately equal amounts. Refers to natural (physiological) retinoids. Endogenous concentrations of retinoids are restored approximately 2 weeks after stopping the drug.
Pharmacokinetics in special clinical situations
Since data on the pharmacokinetics of the drug in patients with impaired liver function are limited, isotretinoin is contraindicated in this group of patients. Mild to moderate renal impairment does not affect the pharmacokinetics of isotretinoin.
Special instructions
Special instructions
It is recommended to monitor liver function and liver enzymes before treatment, 1 month after treatment, and then every 3 months or as indicated. A transient and reversible increase in liver transaminases was noted, in most cases within normal values. If the level of liver transaminases exceeds the norm, it is necessary to reduce the dose of the drug or discontinue it. Fasting serum lipid levels should also be determined before treatment, 1 month after initiation, and then every 3 months or as indicated. Typically, lipid concentrations normalize after dose reduction or discontinuation of the drug, as well as with diet. It is necessary to monitor a clinically significant increase in triglyceride levels, since their rise above 800 mg/dL or 9 mmol/L can be accompanied by the development of acute pancreatitis, possibly fatal.
In case of persistent hypertriglyceridemia or symptoms of pancreatitis, Acnecutane should be discontinued. In rare cases, depression, psychotic symptoms, and very rarely, suicide attempts have been described in patients treated with Acnecutane. Although their causal relationship with the use of the drug has not been established, special caution should be exercised in patients with a history of depression and all patients should be monitored for the occurrence of depression during treatment with the drug, if necessary, referring them to an appropriate specialist. However, discontinuation of Acnecutane may not lead to the disappearance of symptoms and further observation and treatment by a specialist may be required.
In rare cases, at the beginning of therapy, an exacerbation of acne is observed, which resolves within 7-10 days without adjusting the dose of the drug.
When prescribing the drug to any patient, the ratio of possible benefits and risks should first be carefully assessed.
Patients receiving Acnecutane are recommended to use moisturizing ointment or body cream, lip balm to reduce dry skin and mucous membranes at the beginning of therapy.
While taking Acnecutane, pain in muscles and joints, an increase in serum creatinine phosphokinase, which may be accompanied by a decrease in tolerance to intense physical activity, are possible.
Deep chemical dermoabrasion and laser treatment should be avoided in patients receiving Acnecutane, as well as for 5-6 months after the end of treatment due to the possibility of increased scarring in atypical places and the occurrence of hyper- and hypopigmentation. During treatment with Acnecutane and for 6 months after it, hair removal using wax applications cannot be performed due to the risk of epidermal detachment, scar development and dermatitis. Since some patients may experience a decrease in night vision acuity, which sometimes persists even after the end of therapy, patients should be informed about the possibility of this condition, advising them to exercise caution when driving at night. Visual acuity must be carefully monitored. Dryness of the conjunctiva of the eyes, corneal opacities, deterioration of night vision and keratitis usually disappear after discontinuation of the drug. If the mucous membrane of the eyes is dry, you can use applications of a moisturizing eye ointment or an artificial tear preparation. Patients with dry conjunctiva should be monitored for possible development of keratitis. Patients with vision complaints should be referred to an ophthalmologist and consider the advisability of discontinuing Acnecutane. If you are intolerant to contact lenses, you should use glasses during therapy. Exposure to solar radiation and UV therapy should be limited. If necessary, use sunscreen with a high protection factor of at least 15 SPF.
Rare cases of the development of benign intracranial hypertension (“pseudotumor cerebri”) have been described, incl. when used in combination with tetracyclines. In such patients, Acnecutane should be immediately discontinued. During therapy with Acnecutane, inflammatory bowel disease may occur. In patients with severe hemorrhagic diarrhea, Acnecutane should be immediately discontinued.
Rare cases of anaphylactic reactions that occurred only after previous external use of retinoids have been described. Severe allergic reactions dictate the need to discontinue the drug and carefully monitor the patient.
Patients at high risk (with diabetes, obesity, chronic alcoholism or lipid metabolism disorders) may require more frequent laboratory monitoring of glucose and lipid levels when treated with Acnecutane. If diabetes is present or suspected, more frequent monitoring of glycemia is recommended.
Patients with diabetes are advised to monitor their blood glucose levels more frequently.
During the treatment period, care must be taken when driving vehicles and engaging in other potentially hazardous activities that require increased concentration and speed of psychomotor reactions (when taking the first dose).
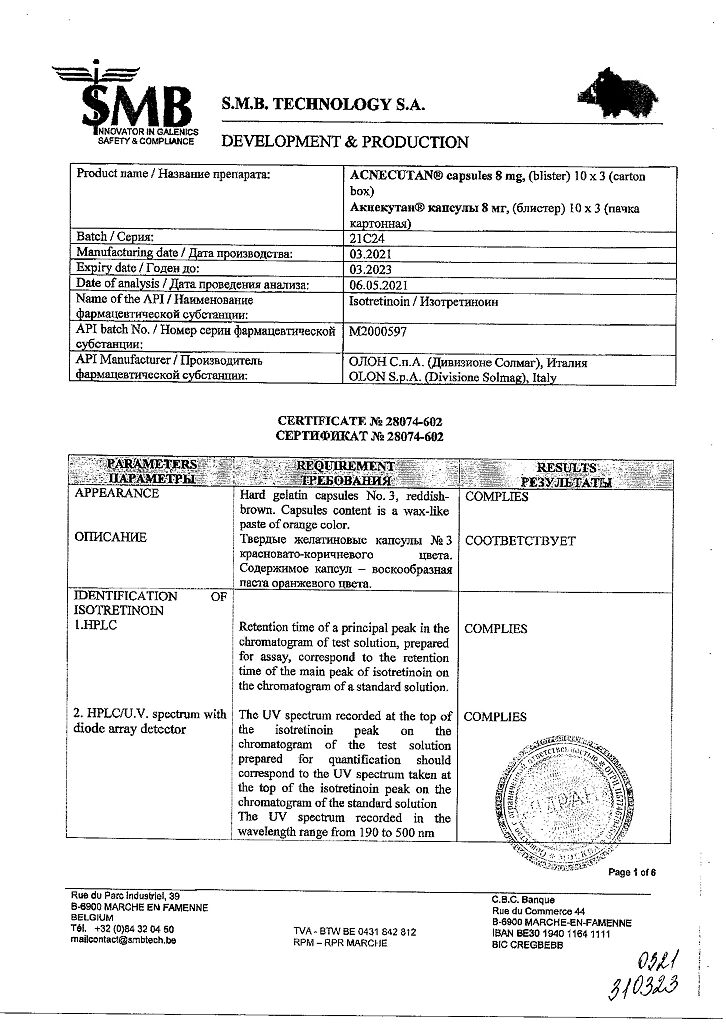
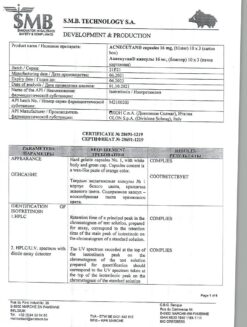
During the treatment period and for 30 days after its completion, it is necessary to completely exclude blood sampling from potential donors to completely eliminate the possibility of this blood getting into pregnant patients (high risk of developing teratogenic and embryotoxic effects). Release form Capsules 8 mg and 16 mg. 10 or 14 capsules in a PVC blister covered with aluminum foil.
Blisters-10-N2, N3, N5, N6, N9, N10; blisters-14-N1, N2, N4, N7 in a cardboard box along with instructions for use.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Isotretinoin
Composition
Composition
Composition per 1 capsule:
Active substances:
Isotretinoin 8.0 mg
Excipients:
Gelucir® 50/13 (mixture of stearic acid esters of polyethylene oxide and glycerin),
refined soybean oil,
Span 80® (sorbitan oleate – mixed esters of oleic acid and sorbitol).
Composition of the capsule
body and lid: gelatin, red iron oxide dye (E172), titanium dioxide (E171).
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
Pregnancy is an absolute contraindication for Acnecutane therapy. If pregnancy occurs, despite warnings, during treatment or within a month after the end of therapy, there is a very high risk of giving birth to a child with severe developmental defects.
Isotretinoin is a drug with a strong teratogenic effect. If pregnancy occurs during a period when a woman takes isotretinoin orally (at any dose and even for a short time), there is a very high risk of giving birth to a child with developmental defects.
Acnecutane is contraindicated in women of childbearing age unless the woman’s condition meets all of the following criteria:
she must suffer from severe acne that is resistant to conventional treatments;
she must certainly understand and follow the doctor’s instructions;
she must be informed by the doctor about the danger of pregnancy during treatment with Acnecutane, within one month after it and urgent consultation if pregnancy is suspected;
she should be warned about the possible ineffectiveness of contraceptives;
she must confirm that she understands the precautions;
she must understand the need and continuously use effective methods of contraception for one month before treatment with Acnecutane, during treatment and for a month after its completion (see section “Interaction with other drugs”); it is advisable to use 2 different methods of contraception at the same time, including barrier;
she must have received a negative result from a reliable pregnancy test within 11 days before starting the drug; A pregnancy test is strongly recommended monthly during treatment and 5 weeks after the end of therapy;
she should start treatment with Acnecutane only on the 2-3 day of the next normal menstrual cycle;
she must understand the need for mandatory visits to the doctor every month;
when treated for relapse of the disease, she must constantly use the same effective methods of contraception for one month before starting treatment with Acnecutane, during treatment and for a month after its completion, as well as undergo the same reliable pregnancy test;
she must fully understand the need for precautions and confirm her understanding and desire to use reliable methods of contraception as explained to her by the doctor.
Use of contraception as directed above during treatment with isotretinoin should be recommended even in women who do not routinely use contraception due to infertility (except in patients who have had a hysterectomy), amenorrhea, or who report not being sexually active.
The doctor must be sure that:
the patient suffers from a severe form of acne (nodulocystic, conglobate acne or acne with a risk of scarring); acne that does not respond to other types of therapy;
a negative result from a reliable pregnancy test was obtained before starting the drug, during therapy and 5 weeks after the end of therapy; the dates and results of the pregnancy test must be documented;
the patient uses at least 1, preferably 2 effective methods of contraception, including a barrier method, for one month before starting treatment with Acnecutane, during treatment and for a month after its completion; – the patient is able to understand and fulfill all of the above requirements for pregnancy protection;
the patient meets all of the above conditions.
Pregnancy test
According to current practice, a pregnancy test with a minimum sensitivity of 25 mIU/ml should be performed in the first 3 days of the menstrual cycle:
Before starting therapy:
To rule out possible pregnancy, the result and date of the initial pregnancy test must be recorded by a doctor before starting contraception. In patients with irregular menstruation, the timing of a pregnancy test depends on sexual activity and should be performed 3 weeks after unprotected intercourse. The doctor should inform the patient about contraceptive methods.
A pregnancy test is carried out on the day of Acnekutan’s prescription or 3 days before the patient’s visit to the doctor. The specialist should record the test results. The drug can only be prescribed to patients receiving effective contraception for at least 1 month before starting Acnecutane therapy.
During therapy:
The patient must visit the doctor every 28 days. The need for monthly pregnancy testing is determined in accordance with local practice and taking into account sexual activity and previous menstrual irregularities. If indicated, a pregnancy test is performed on the day of the visit or three days before the visit to the doctor, the test results must be recorded.
End of therapy:
5 weeks after the end of therapy, a test is performed to exclude pregnancy.
A prescription for Acnecutane for a woman capable of childbearing can be issued only for 30 days of treatment; continuation of therapy requires a new prescription of the drug by a doctor. It is recommended that a pregnancy test, writing a prescription and receiving the drug be carried out on the same day.
Acnecutane should be dispensed in a pharmacy only within 7 days from the date of issuing the prescription.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Pregnancy, established and planned (possibly teratogenic and embryotoxic effects), breastfeeding, liver failure, hypervitaminosis A, severe hyperlipidemia, concomitant therapy with tetracyclines.
Hypersensitivity to the drug or its components. Acnecutane is not indicated for the treatment of acne during puberty and is not recommended for use in children under 12 years of age.
With caution
Diabetes mellitus, history of depression, obesity, lipid metabolism disorders, alcoholism.
For male patients:
Existing data indicate that in women, exposure to the drug from the semen and seminal fluid of men taking Acnecutane is not sufficient to cause the teratogenic effects of Acnecutane. Men should exclude the possibility of other persons, especially women, taking the drug.
If, despite the precautions taken, pregnancy occurs during treatment with Acnecutane or within a month after its completion, there is a high risk of very severe fetal malformations. If pregnancy occurs, Acnecutane therapy is discontinued. The advisability of maintaining it should be discussed with a doctor specializing in teratology.
Because isotretinoin is highly lipophilic, it is very likely that it passes into breast milk. Due to possible side effects, Acnecutane should not be prescribed to nursing mothers.
Side Effects
Side Effects
Most side effects are dose dependent. Side effects are usually reversible after dose adjustment or drug discontinuation, but some may persist after treatment is stopped. Symptoms associated with hypervitamnosis A: dry skin, mucous membranes, incl. lips (cheilitis), nasal cavity (bleeding), larynx and pharynx (hoarseness), eyes (conjunctivitis, reversible corneal opacity and contact lens intolerance).
Skin and its appendages: peeling of the skin of the palms and soles, rash, itching, facial erythema/dermatitis, sweating, pyogenic granuloma, paronychia, onychodystrophy, increased proliferation of granulation tissue, persistent hair thinning, reversible hair loss, fulminant forms of acne, hirsutism, hyperpigmentation, photosensitivity, easy skin trauma. At the beginning of treatment, acne may worsen and persist for several weeks.
Musculoskeletal system: muscle pain with or without increased serum CPK levels, joint pain, hyperostosis, arthritis, calcification of ligaments and tendons, tendonitis.
Central nervous system and mental sphere: excessive fatigue, headache, increased intracranial pressure (“pseudotumor cerebri”: headache, nausea, vomiting, blurred vision, papilledema), seizures, rarely – depression, psychosis, suicidal thoughts. Sense organs: xerophthalmia, isolated cases of impaired visual acuity, photophobia, impaired dark adaptation (reduced twilight visual acuity), rarely – impaired color perception (passing after discontinuation of the drug), lenticular cataract, keratitis, blepharitis, conjunctivitis, eye irritation, optic neuritis, papilledema (as a manifestation of intracranial hypertension); hearing loss at certain sound frequencies, difficulty wearing contact lenses.
Gastrointestinal tract: dryness of the oral mucosa, bleeding from the gums, inflammation of the gums, nausea, diarrhea, inflammatory bowel diseases (colitis, ileitis), bleeding; pancreatitis (especially with concomitant hypertriglyceridemia above 800 mg/dl). Rare cases of pancreatitis with fatal outcome have been described. Transient and reversible increase in the activity of liver transaminases, isolated cases of hepatitis. In many of these cases, the changes did not go beyond the normal range and returned to the initial values during treatment, however, in some situations there was a need to reduce the dose or discontinue Acnecutane.
Respiratory organs: rarely – bronchospasm (more often in patients with a history of bronchial asthma).
Blood system: anemia, decreased hematocrit, leukopenia, neutropenia, increased or decreased platelet count, accelerated ESR.
Laboratory indicators: hypertriglyceridemia, hypercholesterolemia, hyperuricemia, decreased levels of high-density lipoproteins, rarely – hyperglycemia. Cases of newly diagnosed diabetes mellitus have been reported while taking Acnecutane. In some patients, especially those involved in intense physical activity, isolated cases of increased CK activity in the serum have been described.
Immune system: local or systemic infections caused by gram-positive pathogens (Staphylococcus aureus).
Other: lymphadenopathy, hematuria, proteinuria, vasculitis (Wegener’s granulomatosis, allergic vasculitis), systemic hypersensitivity reactions, glomerulonephritis.
Teratogenic and embryotoxic effects: congenital deformities – hydro- and microcephaly, underdevelopment of cranial nerves, microphthalmia, malformations of the cardiovascular system, parathyroid glands, disorders of skeletal formation – underdevelopment of the digital phalanges, skull, cervical vertebrae, femur, ankles, forearm bones, facial skull, cleft palate, low location auricles, underdevelopment of the auricles, underdevelopment or complete absence of the external auditory canal, hernia of the brain and spinal cord, bone fusions, fusion of fingers and toes, developmental disorders of the thymus gland; fetal death during the perinatal period, premature birth, miscarriages), premature closure of epiphyseal growth zones; in animal experiments – pheochromocytoma.
Interaction
Interaction
Tetracycline antibiotics and corticosteroids reduce their effectiveness. Concomitant use with drugs that increase photosensitivity (including sulfonamides, tetracyclines, thiazide diuretics) increases the risk of sunburn.
Concomitant use with other retinoids (including acitretin, tretinoin, retinol, tazarotene, adapalene) increases the risk of hypervitaminosis A.
Isotretinoin may reduce the effectiveness of progesterone preparations, so contraceptives containing low doses of progesterone should not be used.
Combined use with topical keratolytic drugs for the treatment of acne is not recommended due to the possible increase in local irritation. Since tetracyclines increase the risk of increased intracranial pressure, concomitant use with isotretinoin is contraindicated.
Overdose
Overdose
In case of overdose, signs of hypervitaminosis A may appear. In the first few hours after an overdose, gastric lavage may be necessary.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
In a dry place, protected from light, at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C
Shelf life
Shelf life
2 years
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
SMB Technology S.A., Belgium
Additional information
| Shelf life | 2 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | In a dry, light-protected place at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C |
| Manufacturer | SMB Technology S.A., Belgium |
| Medication form | capsules |
| Brand | SMB Technology S.A. |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Aknecutan, 8 mg capsules 30 with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.