No products in the cart.
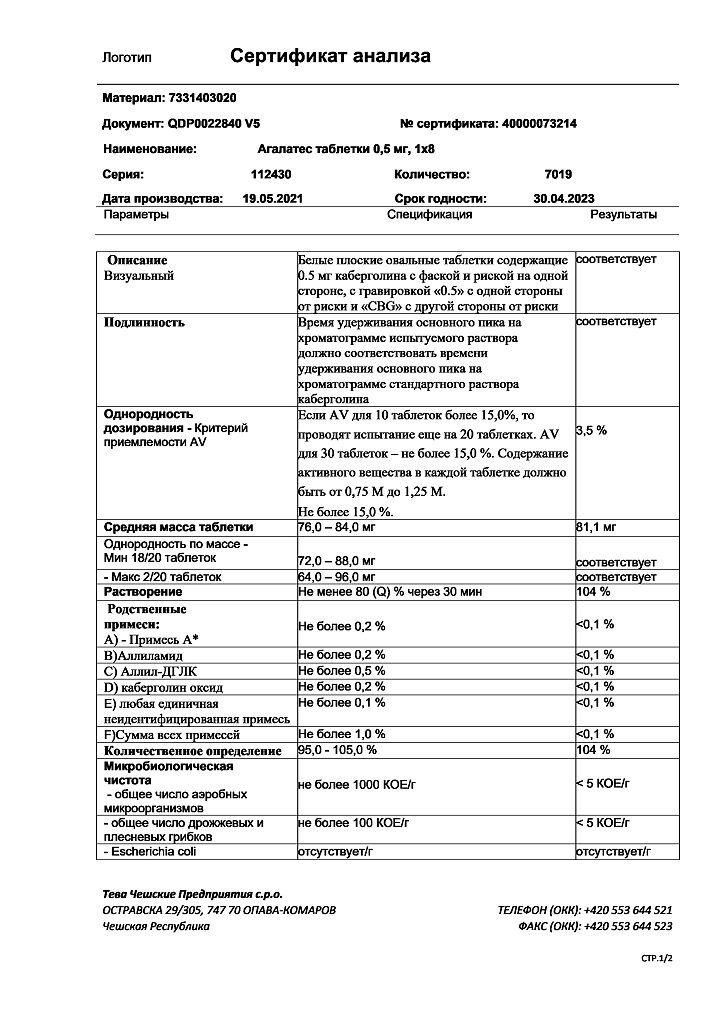
Agalates, tablets 0.5 mg 8 pcs
€53.58 €50.79
Description
Pharmacotherapeutic group: dopamine receptor agonist
ATC code: G02CB03.
PHARMACOLOGICAL PROPERTIES
Pharmacodynamics
Cabergoline is a synthetic ergot alkaloid, ergoline derivative, a long-acting dopamine agonist that inhibits prolactin secretion. The mechanism of action of cabergoline includes stimulation of central hypothalamic dopaminergic receptors. In doses higher than those required for inhibition of prolactin secretion, the drug induces central dopaminergic effect, which is caused by stimulation of dopamine D2-receptors. The action of the drug is dose-dependent. Decrease of prolactin in blood is usually observed after 3 hours and remains during 2-3 weeks, in this connection a single dose of the preparation is usually enough to suppress milk secretion. When hyperprolactinemia is treated, blood prolactin levels normalize after 2-4 weeks of using the drug in an effective dose. Normal prolactin levels may persist for several months after withdrawal of the drug.
Cabergoline is highly selective and has no effect on basal secretion of other pituitary hormones and cortisol. The only pharmacodynamic effect unrelated to the therapeutic action is a decrease in arterial blood pressure (BP). The maximum hypotensive effect usually develops 6 hours after a single drug administration; the degree of BP reduction and the frequency of development of the hypotensive effect are dose-dependent.
Pharmacokinetics
Intake
After oral administration, cabergoline is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract (GIT). Maximal concentration in blood plasma is reached within 0.5-4 h.
Food has no effect on absorption or distribution of cabergoline.
Distribution
Binding of cabergoline (at a concentration of 0.1-10 ng/ml) to plasma proteins is 41-42%.
Metabolism
Metabolites of cabergoline were detected in the urine: 6-allyl-8β-carboxy-ergoline in an amount of 4-6% of the dose taken, as well as three other metabolites with a total of less than 3%. All metabolites inhibit prolactin secretion to a much lesser degree (compared to cabergoline).
Elimination
Cabergoline has long half-life: T1/2 was 63-68 h in healthy volunteers and 79-115 h in patients with hyperprolactinemia.
With this half-life the equilibrium state is reached after 4 weeks. In the urine and feces 18% and 72% of the administered dose were found, respectively. The urinary content of unchanged cabergoline is 2-3%.
Pharmacokinetics are linear up to a dose of 7 mg/day.
Preclinical safety data
As shown in preclinical studies, cabergoline is safe over a significant dose range and has no teratogenic, mutagenic or carcinogenic effects.
Indications
Indications
The drug is used in adults and adolescents over 16 years of age.
Prevention of physiological lactation (secretion of milk by the mammary gland) after childbirth.
Suppression of already established postpartum lactation.
Treatment of disorders associated with hyperprolactinemia (increased levels of prolactin in the blood), including amenorrhea (absence of menstruation for 6 months or more), oligomenorrhea (rare menstruation, but with an interval of at least 60-90 days), anovulation (lack of ovulation in a woman of reproductive age), galactorrhea (spontaneous leakage of milk from the mammary glands unrelated to feeding the baby).
Prolactin-secreting pituitary adenomas (micro- and macroprolactinomas); idiopathic hyperprolactinemia; “empty sella” syndrome in combination with hyperprolactinemia.
If there is no improvement or you feel worse, you should consult a doctor.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacotherapeutic group: dopamine receptor agonist
ATX code: G02CB03.
PHARMACOLOGICAL PROPERTIES
Pharmacodynamics
Cabergoline is a synthetic ergot alkaloid, an ergoline derivative, a long-acting dopamine agonist that inhibits prolactin secretion. The mechanism of action of cabergoline involves stimulation of central dopaminergic receptors in the hypothalamus. At doses higher than those required to suppress prolactin secretion, the drug causes a central dopaminergic effect due to stimulation of dopamine D2 receptors. The effect of the drug is dose-dependent. A decrease in prolactin levels in the blood is usually observed after 3 hours and persists for 2-3 weeks, and therefore one dose of the drug is usually sufficient to suppress milk secretion. When treating hyperprolactinemia, the content of prolactin in the blood is normalized after 2-4 weeks of using the drug in an effective dose. Normal prolactin levels may persist for several months after discontinuation of the drug.
Cabergoline has a highly selective effect and does not affect the basal secretion of other pituitary hormones and cortisol. The only pharmacodynamic effect not related to the therapeutic effect is a decrease in blood pressure (BP). The maximum hypotensive effect usually develops 6 hours after a single dose of the drug; the degree of blood pressure reduction and the frequency of development of the hypotensive effect are dose-dependent.
Pharmacokinetics
Suction
After oral administration, cabergoline is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract (GIT). The maximum concentration in blood plasma is achieved after 0.5-4 hours.
Food does not affect the absorption or distribution of cabergoline.
Distribution
The binding of cabergoline (at a concentration of 0.1-10 ng/ml) to plasma proteins is 41-42%.
Metabolism
Metabolites of cabergoline were found in the urine: 6-allyl-8β-carboxy-ergoline in an amount of 4-6% of the dose taken, as well as three other metabolites with a total content of less than 3%. All metabolites inhibit prolactin secretion to a significantly lesser extent (compared to cabergoline).
Removal
Cabergoline has a long half-life: T1/2 was 63-68 hours in healthy volunteers and 79-115 hours in patients with hyperprolactinemia.
With this half-life, steady state is achieved after 4 weeks. In urine and feces, 18% and 72% of the dose taken were found, respectively. The content of unchanged cabergoline in urine is 2-3%.
Pharmacokinetics is linear up to a dose of 7 mg/day.
Preclinical safety data
As shown in preclinical studies, cabergoline is safe over a wide range of doses and has no teratogenic, mutagenic or carcinogenic effects.
Special instructions
Special instructions
Driving vehicles and working with machinery
Cabergoline may cause drowsiness and sudden falling asleep. If you experience similar effects while taking the drug, refrain from driving vehicles and machinery and other potentially dangerous activities that require increased concentration and speed of psychomotor reactions.
Agalates contains lactose
If you have an intolerance to certain sugars, talk to your doctor before taking this medicine.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Cabergoline
Composition
Composition
The active ingredient is cabergoline.
Each tablet contains 0.5 mg cabergoline.
Other ingredients (excipients) are: lactose anhydrous, L-leucine, magnesium stearate.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or are planning a pregnancy, consult your doctor before starting to use the drug.
Pregnancy
The drug should be discontinued once pregnancy is confirmed.
Breastfeeding period
The use of the drug by patients during breastfeeding is contraindicated.
Fertility
The use of the drug Agalates restores ovulation and the ability to become pregnant in women with infertility associated with increased production of prolactin. Pregnancy should be excluded before using cabergoline. Since pregnancy can occur before the resumption of menstruation, pregnancy tests are recommended to be carried out at least once every 4 weeks during amenorrhea, and after the restoration of the menstrual cycle – in all cases of their delay by more than 3 days. Women who are not planning a pregnancy are recommended to use effective non-hormonal contraception during treatment with Agalates, as well as after discontinuation of the drug until anovulation recurs. Women who become pregnant should be under medical supervision to promptly identify symptoms of an enlarged pituitary gland, since pre-existing pituitary tumors may increase in size during pregnancy.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Do not take Agalates:
if you are allergic to cabergoline or other ergot alkaloids, or to any of the other ingredients of this medicine listed in section 6 of the leaflet;
if you have a history of fibrotic changes (scar tissue formation) in the lungs, pericardium or retroperitoneum;
if you have anatomical signs of pathology of the valvular apparatus of the heart (such as thickening of the valve leaflet, narrowing of the valve lumen, the presence of mixed valve pathology), confirmed by echocardiographic examination (EchoCG) before starting therapy;
if you have lactose intolerance, lactase deficiency, glucose-galactose malabsorption syndrome (a condition in which intestinal cells cannot absorb sugars – glucose and galactose);
if you are under 16 years old;
if you are pregnant or breastfeeding.
Precautions:
Before taking Agalates, consult your doctor. Agalates, like other ergot derivatives, should be used with caution:
if you have high blood pressure (arterial hypertension) that developed during pregnancy, for example, a severe complication of the second half of pregnancy: increased pressure, swelling and the appearance of convulsive readiness (preeclampsia) or postpartum hypertension (cabergoline is prescribed only in cases where the potential benefit of using the drug significantly outweighs the possible risk);
if you have severe cardiovascular diseases, Raynaud’s syndrome (when exposed to cold, your fingers and toes become blue and cold to the touch, while the pulse cannot be felt, sensitivity is lost, and numbness is noted);
if you have a peptic ulcer, gastrointestinal bleeding;
if you have severe liver failure (lower doses are recommended);
if you have severe psychotic or cognitive impairment (including a history);
if you are taking medications that have a hypotensive effect (due to the risk of developing orthostatic arterial hypotension).
Before starting cabergoline therapy to treat disorders associated with hyperprolactinemia, your doctor will order a complete examination of your pituitary gland.
Before starting long-term therapy with Agalates, it is necessary to undergo a cardiovascular examination, including an echocardiogram (to exclude asymptomatic heart defects). In addition, it is advisable to determine CRP or other markers of inflammation, take a chest x-ray, and conduct a study of pulmonary function and kidney function.
Cabergoline should not be used if there are signs of cardiac or respiratory dysfunction associated with fibrotic changes or a history of such conditions.
Cabergoline should not be used if fibrous lesions of the heart valve apparatus are detected (see section “Contraindications”).
Fibrotic disorders can develop asymptomatically. If you experience the following symptoms, contact your doctor immediately:
– pleuropulmonary disorders: such as shortness of breath, difficulty breathing, persistent cough or chest pain;
– renal failure or obstruction of the vessels of the ureters or abdominal organs, which may be accompanied by pain in the side or lumbar region and swelling of the lower extremities, any swelling or tenderness when touched in the abdomen, which may indicate the development of retroperitoneal fibrosis;
– pericardial fibrosis and fibrosis of the heart valve leaflets often characterize heart failure. In this regard, it is necessary to exclude fibrosis of the heart valves (and constrictive pericarditis) when symptoms of heart failure appear.
The heart should be regularly monitored for the development of fibrotic disorders. The first time EchoCG should be performed 3-6 months after the start of therapy. Depending on the assessment of your condition by your attending physician, this examination should then be completed, paying particular attention to the symptoms described above, at least every 6-12 months of therapy.
Your healthcare provider may additionally order other monitoring methods (eg, physical examination including cardiac auscultation, x-rays, computed tomography).
In patients with severe hepatic impairment, low doses of cabergoline should be used for long-term therapy.
The use of cabergoline causes drowsiness. In patients with Parkinson’s disease, the use of dopamine receptor agonists may cause sudden sleep onset. In such cases, your doctor may recommend a lower dose of cabergoline or stop therapy.
The use of cabergoline is not recommended in patients with impaired renal function.
Children and teenagers
The drug Agalates is contraindicated for use in children and adolescents under 16 years of age.
Side Effects
Side Effects
Like all medicines, Agalates can cause side effects, although not everyone gets them.
The most serious adverse reactions reported with cabergoline are:
damage to the heart valves (valvulopathy), including regurgitation (backflow of blood from one chamber of the heart to another), and associated disorders (pericarditis (an inflammatory disease of the tissue lining of the heart) and pericardial effusion). Early signs of heart valve disease may include one or more of the following symptoms: difficulty breathing, shortness of breath, rapid heartbeat, feeling weak, chest pain, back pain, pelvic pain, or swelling of the legs (early signs of a condition called fibrosis, which can affect the lungs, heart/heart valves, or lower back);
skin rash, swelling of the face, lips, tongue or throat, hives (sudden widespread rash of itchy blisters of an allergic nature), difficulty breathing or swallowing (the first signs of an anaphylactic reaction);
the appearance or worsening of regurgitation (backflow of blood from one chamber of the heart to another), narrowing of the lumen of the valves or thickening of the valve leaflets of the heart (detected during an X-ray or echocardiographic examination of the heart).
Stop taking Agalates and tell your doctor immediately if you experience any of the above serious adverse reactions.
The following additional adverse reactions of cabergoline have been reported:
Very common reactions (may affect more than 1 in 10 people):
headache, dizziness (vertigo);
nausea, dyspepsia (indigestion), gastritis (inflammation of the gastric mucosa), abdominal pain;
asthenia (increased fatigue with mood swings, weakness, irritability, sleep disorders);
increased fatigue.
Common reactions (may affect up to 1 in 10 people):
depression;
drowsiness;
with long-term use, cabergoline usually has a hypotensive effect (lowering blood pressure); in some cases, orthostatic arterial hypotension and “hot flashes” may occur;
constipation, vomiting;
mastodynia (discomfort in the mammary glands (swelling, hardening, chest pain, increased sensitivity));
asymptomatic decrease in blood pressure.
Uncommon reactions (may affect up to 1 in 100 people):
hypersensitivity reactions;
increased libido;
transient hemianopsia (a condition in which half the visual field of both eyes becomes blind), syncope (short-term fainting with loss of consciousness), paresthesia (feeling of numbness, tingling, burning, etc.);
feeling of heartbeat;
vascular spasm of the upper and lower extremities, fainting;
shortness of breath, pleural effusion, pulmonary fibrosis (replacement of lung tissue with fibrous connective tissue), nosebleeds;
rash, alopecia (pathological hair loss);
spasms of the lower extremities;
edema, peripheral edema (edema of the lower extremities);
it is possible that hemoglobin levels may decrease in women with amenorrhea in the first months after the resumption of menstruation.
Rare reactions (may affect up to 1 in 1000 people):
pain in the epigastric region;
deviation from the norm of standard laboratory parameters during long-term therapy with cabergoline.
Very rare reactions (may affect up to 1 in 10,000 people):
pleural fibrosis (thickening of the membrane covering the lungs).
Unknown (based on available data, determine frequency of occurrence)
impossible):
aggressiveness, delusions, hypersexuality, gambling addiction/pathological gambling, psychotic disorders, hallucinations;
attacks of sudden falling asleep, tremors;
visual impairment;
angina pectoris;
breathing problems, respiratory failure, pleurisy (inflammation of the pleura) and chest pain;
liver dysfunction;
increased activity of creatine phosphokinase, deviations from the norm in liver function indicators.
Impulse control disorders such as pathological gambling, increased libido and hypersexuality have been reported in patients receiving dopaminergic agonist therapy, including cabergoline. These effects were usually reversible after dose reduction or drug discontinuation
Interaction
Interaction
Tell your doctor if you are taking, have recently taken, or may start taking any other medications.
Cabergoline should not be used in combination with dopamine receptor antagonists (phenothiazines, butyrophenones, thioxanthenes, metoclopramide, domperidone, alizapride, etc.), because they may weaken the effect of cabergoline aimed at reducing prolactin concentrations.
Long-term use of cabergoline with other ergot alkaloids is not recommended.
Like other ergot derivatives, cabergoline should not be used concomitantly with macrolide antibiotics (for example, erythromycin, josamycin, troleandomycin), because this may lead to an increase in cabergoline levels in the blood.
Agalates with food, drinks and alcohol
Agalates can be taken with or without food.
It is recommended to avoid drinking alcohol and other drugs that cause drowsiness while taking the drug, because this may increase the risk of dizziness.
Overdose
Overdose
There is no information about an overdose of the drug. Based on the results of animal experiments, one can expect the appearance of symptoms due to hyperstimulation of dopamine receptors: nausea, vomiting, decreased blood pressure, disturbances of consciousness/psychosis or hallucinations. If indicated, measures should be taken to restore blood pressure. In addition, with severe central nervous system symptoms (hallucinations), the use of dopamine antagonists may be required.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
Store at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C in a tightly closed original bottle.
Keep the drug out of the reach of children and so that the child cannot see it.
Do not use the drug after the expiration date indicated on the bottle or carton after “Best before:”. The expiration date is the last day of the specified month.
Do not throw the drug into the sewer. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of (destroy) a drug that is no longer needed. These measures will protect the environment.
Shelf life
Shelf life
2 years. Do not use after expiration date.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Teva Czech Enterprises s.r.o., Czech Republic
Additional information
| Shelf life | 2 years. Do not use after the expiration date. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | Store at a temperature not exceeding 25°C in a tightly closed original bottle. Keep out of reach of children! |
| Manufacturer | Teva Czech Enterprises s.r.o., Czech Republic |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Teva Czech Enterprises s.r.o. |
Related products
Buy Agalates, tablets 0.5 mg 8 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.